The Top Ten Sounding Out! Posts of 2019!

For your end-of-the year reading pleasure, here are the Top Ten Posts of 2019 (according to views as of 12/4/19). Visit this brilliance today–and often! Listen out for us in 2020!
—

10). Charles Mingus, Rotary Perception, and the “Fables of Faubus”
Earl Brooks
Jazz composer and bassist Charles Mingus’s infamous protest song “Fables of Faubus,” (1959) channeled the anger and frustration of the Black community in response to the staunch racism of Orval Faubus, Governor of Arkansas, who refused to acknowledge the U.S. Supreme Court’s decision to support school integration in the 1954 case Brown v. Board of Education. Faubus infamously used the Arkansas National Guard to prevent Black students from attending Little Rock Central High School. The visual imagery of “The Little Rock Nine” walking to school, bombarded by riotous mobs and surrounded by cameras and military escorts, remains permanently seared into the American collective memory of the Civil Rights Movement.
What makes the imagery of “The Little Rock Nine” so sonically distinctive is the contrast between the silent procession of the students and the loud and intimidating screams from the white racist protestors. When images contain explicit visual references to particular sounds, there is an inescapable cognitive referent that allows one to experience that sound through the vehicle of one’s “sonic imagination”–or the mechanism that allows us to “hear” a song in our heads even when there is only silence. Listening involves an active–not passive–engagement with sounds real and imagined. In the same vein as comic books, which rely on visual sound-cues to enhance the experience of the text, the optical power of “The Little Rock Nine” invites viewers to process both the visual and aural data presented by the image. In other words, the image is empowered by its multimodality. When combined with related source material, such as “Fables,” we stand to gain a greater sense of its meanings and an awareness of why sound, especially music, is critical to the recording, or archiving of the kinds of lived experiences that exceed easy translation. [Click here to read the full piece!]
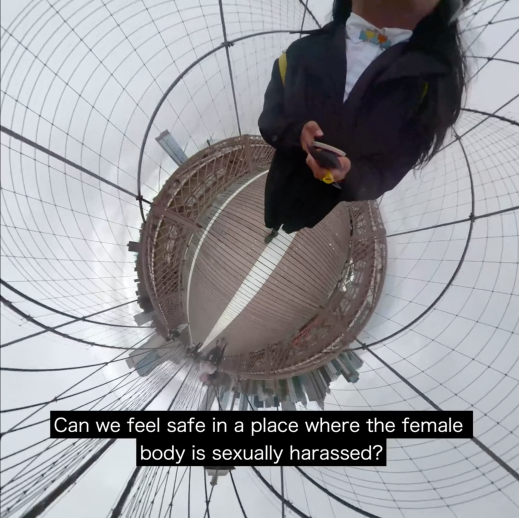

Amanda Gutiérrez
Flâneuse>La caminanta is a video soundwalk project, edited as a virtual reality (VR) interactive environment that I created using a 360-degree camera to document participants’ journeys. Its title emphasizes a missing word in the French and Spanish languages for women as wanderers, a gap that also represents the lack of inclusive public spaces that allow female-identifying and non-conforming bodies safe passage and co-existence. The VR environment exposes the perspective of four women of color who navigate urban landscapes in Mexico City, Abu Dhabi, Manhattan and Brooklyn. The participants selected their own locations, building from places that have a personal meaning or memory in their everyday journeys.
This post discusses Flâneuse>La caminanta, its influences, previous iterations, and use of the methodology of the soundwalk as an intervention exposing the dangers inherent in public space for women of color. To begin, Flâneuse>La caminanta is the virtual reality iteration of my previous film essay and photo series, Walking in Lightness. Walking in Lightness departs from my experience walking in the neighborhood of Sunset Park, Brooklyn. The soundscapes I recorded during soundwalks became a pivotal medium for offering subtle observations of a woman’s cultural identity, recording my interactions and tracing a psychogeographic path as the camera navigates urban spaces. [Click here to read the full piece!]

Alexis Deighton MacIntyre
What is a voice, and what does it mean to voice?
Definitions of the voice may be pragmatic: working titles that depend in part on their institutional basis within ethnomusicology, literature, or psychoacoustics, for example.
“
Or, to take another strategy, voice is given by an impartial biological framework, a respiratory-laryngeal-oral assembly line. Its product, an acoustic signal, is transmitted via material vibration to an ear, and then a brain. The mind of a listener is this system’s endpoint. Although this functional description may smack of scientific reductionism, the otolaryngeal voice often stands in for embodiment in humanist discourse. [Click here to read the full piece!]

7). Everyone’s Going to the Rumba: Trap Latino and the Cuban Internet
Mike Levine
Trap Latino has grown popular in Cuba over the past few years. Listen to the speakers blaring from a young passerby’s cellphone on Calle G, or scan through the latest digital edition of el paquete semanal (the weekly package), and you are bound to hear the genre’s trademark 808 bass boom in full effect. The style however, is almost entirely absent from state radio, television, and concert venues. To the Cuban state (and many Cubans), the supposed musical and lyrical values expressed in the music are unacceptable for public consumption. Like reggaetón a decade before, the reputation of Trap Latino (and especially the homegrown version, Trap Cubano) intersects with contemporary debates regarding the future of Cuba’s national project. For many of its fans however, the style’s ability to challenge the narratives of the Cuban state is precisely what makes Trap Latino so appealing.
In an article published last year by Granma (Cuba’s official, state-run media source), Havana-based journalist Guillermo Carmona positions Trap Latino artists like Bad Bunny and Bryant Myers as a negative influence on Cuba’s youth, claiming the music sneaks its way into the ears of unsuspecting Cuban youth via the illicit channels of Cuba’s underground internet. With lyrics that celebrate the drug trade and treat women as “slot machines,” coupled with a preponderance of sound effects instead of “music notes,” Carmona considers Trap Latino aggressive, dangerous, and perhaps most perniciously of all, irredeemably foreign. [Click here to read the full piece!]
6. Cardi B: Bringing the Cold and Sexy to Hip Hop
Ashley Luthers
“Ran down on that bitch twice” was all I heard in this tight, dark basement filled with black and brown bodies, sweat dripping everywhere from everyone. Girls danced all over, yelling and shouting lyrics as they clapped and pointed along to the fast, upbeat rhythm of the song, feeling their own sensations and pleasure from the vibe, and rapping with the catchiness of the repeated phrase, “Ran down on that bitch twice!” As everyone was jumping, the space around me shook because there was so much body movement and flow; it was lit. This wasn’t the first time I heard Cardi B, but dancing along to her song “Foreva” was definitely the first I remember hearing her. Since that dark basement party, I realized that the attitude and energy Cardi B invokes through her raps and lyrics is addicting.
Listening repeatedly to “Foreva,” and the rest of her debut mixtape Gangsta Bitch Music Vol.1, has attuned me to Cardi B as a stone cold, gangster bitch: someone who is fearless, tough on the outside and inside. She doesn’t hesitate; she doesn’t bluff. She gets straight to the point and lets you know that she will fuck you up if and when necessary. A ‘G’ she is, as some would say when describing a person who shows no fear and is always hustling—except that someone is imagined as a black male from the so-called ‘hood who affiliates with drugs, gangs, etc. The music itself reflects this gangster feel, through the hard trap sounds and beats in every track. Trap music as a style and subset of Hip-Hop, and arguably a genre on its own, originated in Atlanta, and has over time become mainstream all across the U.S. specifically within the Northeast region. Within Cardi’s performed, stone cold bitch lyrical persona, she embodies an aggressive femme sexuality, a racialized femme hunger for sex with black men, and an emotional depth that makes her endearing to listeners. Her embodiment of this multiplicity—stone cold attitude, femme sexual thirst, and emotional complexity—can be heard in her music, through the explosion of beats, rhythms, and lyrics that keep listeners hooked to the sound of her self-image. In other words, Cardi B’s sonic and lyrical movements work in tandem with her audio-visual construction of black, Caribbean, Bronx femme desire. [Read the full piece here!]

5). On the Poetics of Balloon Music: Sounding Air, Body, and Latex (Part One)
Carlo Patrão
I see them in the streets and in the subway, at dollar stores, hospital rooms, and parties. I see them silently dangling from electrical cables and tethered to branches of trees. Balloons are ghost-like entities floating through the cracks of places and memories. They are part of our rituals of loss, celebration and apology. Yet, they are also part of larger systems, weather sciences, warfare and surveillance technologies, colonialist forces and the casual UFO conspiracy theory. For a child, the ephemeral life of the balloon contrasts with the joy of its bright colors and squeaky sounds. Psychologists encourage the use of the balloon as an analogy for death, while astronomers use it as a representation for the cosmological inflation of the universe. In between metaphors of beginning and end, the balloon enables dialogues about air, breath, levity, and vibration.
The philosopher Luce Irigaray argues that Western thought has forgotten air despite being founded on it. “Air does not show itself. As such, it escapes appearing as (a) being. It allows itself to be forgotten,” writes Irigaray. Air is confused with absence because it “never takes place in the mode of an ‘entry into presence.’” Gaston Bachelard, in Air and Dreams, calls for a philosophy of poetic imagination that grows out of air’s movement and fluidity. For Bachelard, an aerial imagination brings forth a sense of the sonorous, of transparency and mobility. In this article, I propose exploring the balloon as a sonic device that turns our attention to the element of air and opens space for musical practices outside classical traditions. Here, the balloon is defined broadly as an envelope for air, breath, and lighter-than-air gases, including toy balloons, weather balloons, hydrogen and hot-air balloons. [Read the full piece here!]

4). Hearing Change in the Chocolate City: Soundwalking as Black Feminist Method
Allie Martin
In July 2018 I visited Oxford, Mississippi for the first time, to attend a workshop on conducting oral histories. Upon walking with a friend back to our accommodations on the University of Mississippi campus, we heard a voice calling to us from far away, up a hill somewhere. It was a catcalling voice—that much I definitely recognized—but I also felt sure that I heard the word “nigger.” My friend, who is also a black woman, heard the taunting sounds of the voice but not that word specifically. Herein lies one of the difficulties of black womanhood: I was unable to distinguish which of my two most prominent identity markers (blackness and womanhood) the speaker was using to harm me in that moment. I found it ironic that I came to Mississippi to learn best practices for listening to people’s stories, but could not hear my own story, could not say for sure what had happened to me.
In the time since that visit, I have come to embrace the speculative sonic ephemerality of black womanhood and utilize it on my soundwalks. Soundwalks are a popular method for understanding the everyday sonic life of a place. Reminiscent of Michel de Certeau’s “Walking in the City,” soundwalks offer the kind of embodied experience missing from other more static soundscape recordings. I argue here that soundwalks can operate as black feminist method, precisely because they allow me to center the complex, incomplete sonorities of black womanhood, and they are enough in their incompleteness. One of our foremost thinkers on black feminism, Patricia Hill Collins, has argued that black women’s knowledge is subjugated (1990). I understand this to mean that my knowledge is tainted somehow, too specialized or not specialized enough, and not considered fit for application by a broader audience. Soundwalks as method, though, rely on my own subjugated knowledge. What did I hear? Black feminism centers and humanizes black women, and I utilize soundwalks to humanize myself in a soundscape that would otherwise disregard my sonic perceptions in favor of white hearing as the default standard of sound. [Read the full piece here!]

3). Can’t Nobody Tell Me Nothin: Respectability and The Produced Voice in Lil Nas X’s “Old Town Road”
Justin Burton
t’s been ten weeks now that we’ve all been kicking back in our Wranglers. allowing Lil Nas X’s infectious twang in “Old Town Road” to shower us in yeehaw goodness from its perch atop the Billboard Hot 100. Entrenched as it is on the pop chart, though, “Old Town Road”’s relationship to Billboard got off to a shaky start, first landing on the Hot Country Songs list only to be removed when the publication determined the hit “does not embrace enough elements of today’s country music to chart in its current version.” There’s a lot to unpack in a statement like that, and folks have been unpacking it quite consistently, especially in relation to notions of genre and race (in addition to Matthew Morrison’s recommended reads, I’d add Karl Hagstrom-Miller’s Segregating Sound, which traces the roots of segregated music markets). Using the context of that ongoing discussion about genre and race, I’m listening here to a specific moment in “Old Town Road”— the line “can’t nobody tell me nothin”—and the way it changes from the original version to the Billy Ray Cyrus remix. Lil Nas X uses the sound of his voice in this moment to savvily leverage his collaboration with a country music icon, and by doing so subtly drawing out the respectability politics underlying Billboard’s racialized genre categorization of his song. [Read the full piece here!]

2). TiK ToK: Post-Crash Party Pop, Compulsory Presentism and the 2008 Financial Collapse
Dan DiPiero
As pundits increasingly speculate about the likelihood and character of another recession, I’m thinking about the one from which we’re still recovering. Specifically, I’m thinking about a certain strain of American pop music—or a certain sentiment within pop music—that it seems to me accelerated and concentrated just after the 2008 financial collapse. This strain, which obviously co-existed with many other developments in popular music at the time, takes party songs and adds to them two interconnected narrative elements: on the one hand, partying is cranked up, escalated in one or multiple ways, moving the music beyond a party anthem and into something new. On the other hand, the rationale for such a move consistently derives from an attitude of compulsory presentism, in which the future is characterized as unknown, irrelevant, or is otherwise disavowed.
In the American context, the popular (and, I argue, misguided) take on the music of the great recession is that we didn’t have any—in other words, because no one was directly singing about the crisis, there was no music that responded to it. But this is an extremely limited way of understanding how music and socio-political life interact. In this post, I consider specifically American notions of mainstream party culture to argue that the strain of party music described above and below is the music of the crash, not because it literally speaks about it but because it reflects a certain attitude expressed and experienced by those at the front of both popular music listening at the time and the collapse itself: the graduating classes of 2008-2012. [Click Here to read Full Piece!]

1). The Sound of Feminist Snap, or Why I Interrupted the 2018 SEM Business Meeting
Alex W. Rodriguez
I begin this essay with an apology, addressed to the Society for Ethnomusicology President Gregory Barz:
I am sorry that I interrupted your opening remarks at least year’s SEM Business meeting. In the moment that I chose to make my intervention, I underestimated the pain that it has clearly caused you. Furthermore, I have come to realize that it was unskillful of me to locate my frustration and anger with you as an individual. The affective release of my voice in that moment could have been better directed towards positive change in a time of great need for many of us. I fully intend to work towards doing better in the months to come, urging anyone who occupies the office of President of this organization to use the power and standing inherent in this position office to take direct steps to address the harms many of its members are experiencing.
Because my intervention arose so quickly and unpredictably—for readers outside of the Society for Ethnomusicology who may not know, I stood up and yelled “You’re a hypocrite!” then left the meeting—it seems worthwhile to explore my actions in a more thoughtful space of written discourse. I want to clarify that my sonic interruption was not premeditated; as I explain below, it arose out of a deep anger and longing for justice. As SEM 2019 convenes in November in Bloomington, Indiana on November 7th, I hope that my disruptive event can be better understood as a call to collective inquiry into the structural factors that constrain our Society from functioning in a healthy way. [Read the Full piece here!]
Featured Image: “Write on!” by J. Stoever
—
 REWIND! . . .If you liked this post, you may also dig:
REWIND! . . .If you liked this post, you may also dig:
The Top Ten Sounding Out! Posts of 2018!
The Top Ten Sounding Out! Posts of 2017!


















Trackbacks / Pingbacks