Sonic Lessons of the Covid-19 Soundscape

It’s understandable to resist reading or thinking about Covid in late-2021, even as the Delta variant’s new surges are making headlines around the world. Covid has surrounded and overwhelmed us for over a year, and many people’s reluctance to engage meaningfully with it at this time is fueled by feelings of fatigue, mental exhaustion, and frustration. However, I urge in this post that we have a continued responsibility to sustain our sonic engagement and listen to what the Covid-19 soundscape teaches us.
Covid-19, as most of us now know now, is a virus caused by the coronavirus strain SARS-CoV-2. While the symptoms of Covid-19 are many and varied, one symptom seemed most vital and censorious—a nagging and persistent dry cough that became referred to as the “Covid cough” in everyday vernacular. The Covid cough became an intrusive and yet all too familiar presence in the Covid soundscape—an isolated acoustic environment that allows us to study its characteristics. For instance, investigations within the Covid soundscape have studied the noise annoyances of traffic, neighbors, and personal dwellings; have recorded the quieting of the usually bustling streets of New York City; have researched whale stress hormones linked to less noise pollution in our ocean waters; and have analyzed the reception and aural imagery of sirens. I seek to add to this research by bringing the sounds of the Covid body (or a body perceived to have Covid) into the larger soundscape conversation.
It is of vital importance to attend to the Covid soundscape while we are still in it because the Covid soundscape is bound by time and place and is ever-changing. Once Covid is eradicated, our access to the sounds surrounding it disappear as well. So, I dwell in the soundscape where the Covid cough is still an everyday reality. With the Covid cough present in approximately sixty percent of Covid cases according to WebMD, the cough quickly became the virus’s warning bell, identifying who might be infected with the virus. In the early days of the viruses’ rapid spread in the United States, coughing became an acoustic red flag—a sign that danger could be near. So much about the virus and its spread was unknown, and the uncertainty heightened desires for control and reassurance. Because of this, we attended to coughing in ourselves and others, consciously and unconsciously, in ways we probably never had before.

All of this auditory attention focused on coughing is a process of listening. Different from hearing—perceiving sounds—listening requires attentiveness and consideration. Listening to sounds, as Ceraso states, “influences our feelings and behaviors as we move through the world” (176). I, like Eckstein and other sound scholars, insist that sound is an argument and that sounds have persuasive power. Sounds can evoke different responses from different people—perhaps your favorite song elicits painful memories for someone else. Listening then, can be personal. However, sound studies scholars know, and Covid-19 has amplified, that listening is also shaped by social and cultural contexts (Rice, “Listening”). During the pandemic, people listened to bodies in ways that were shaped by the news, the medical community, the culture, and the environment. While listening as a medical practice is used to diagnose and treat, the listening I refer to here is not one of compassionate care, but rather a practice of fear, surveillance, and othering.
For many people—in the United States, particularly white, hetero, cis-gendered, able-bodied, people—their bodily sounds came under social and cultural scrutiny for the first time——bringing up issues of autonomy and self-control. “It’s just allergies,” folks muttered while passing someone in the grocery store, just as a cough that could no longer be suppressed escaped their lips. Suddenly, as suspicious eyes were cast every which way, people felt compelled to disclose their medical histories to complete strangers in order to have their coughs—their bodily sounds—be deemed socially acceptable and their public presence allowable. Shildrick reminds us that bodies are leaky, but Western medicine and practice reinforce European-descended cultural teachings that our bodily boundaries should be secure (i.e. not leaky) and that otherness should be excluded. The “Covid cough” taught many of us for the first time that our bodies are leaky, noisy, and permeable, and they are not always under our command. Listening to our bodies took on an all-new meaning as we attended to our bodily sounds in hyper-vigilant ways.

Attending to the leaky, noisy nature of bodies, however, was certainly not new to everyone. Stoever’s The Sonic Color Line details the hypervigilance and rigid compliance long demanded of Black and brown bodies—often violently—by the white listening ear’s norms regarding “propriety” and personhood. Ehrick’s concept of the “gendered soundscape” thinks through surveillance in regard to female-presenting bodies and vocal gender. Casillas’s notion of “listening loud(ly)” while Chicanx, Martin’s Black feminist soundwalk methodology , and Blake’s discussion of the “gas station voice” many trans people take on to protect themselves from attack reminds us that the stakes for surveillance are higher at the intersection of race, gender, class, sexuality, accent, and citizenship status, but that resistance can also be also quite powerful.
For individuals with health conditions, impairments, or disabilities, too, concerns about control and disclosure are not recent issues, as their bodies have long been listened to in ways non-disabled bodies simply have not. For example, for a time after my mother had emergency surgery for colon cancer, her body required the use of a colostomy bag. One day she and I were shopping in a department store when a sales clerk heard my mother’s body leak (i.e. make sounds that we’ve been taught to believe are only acceptable in private spaces and bathrooms). The sales associate listened to my mother’s body in a way that bordered on disgust and looked at her in a way that beckoned my mom to justify her leaky, fallible body.
This kind of listening—the surveillance of others’ bodies—is used to regulate and control bodies, and is a long-standing tradition in disability history. For instance, St. Pierre highlights the embodied act of stuttered speech that is not only constructed by cultural norms but that challenges our cultural fantasy of the body as an invisible channel for communication and disrupts the disabled/able-bodied binary. Mills’s research on deafness and hearing technologies explores the irony and paradox that hearing aids and cochlear implants were invented to “treat” the invisible disability of deafness, but yet visibly mark their wearers. And while not explicitly writing of disabled bodies, Booth and Spencer contend that non-vocal bodily sounds are rhetorical and therefore create rhetorical challenges and provoke us into attempted management of the sounds our body produces. Individuals with impairments, diseases, and disabilities have long been listened to, scrutinized, and surveilled in these ways. Such listening is culturally bound and rooted in the ableist myth that bodies should be self-contained and controlled at all times.
As the Covid-landscape meant that our ability to visually surveil bodies was diminished due to masks, barriers, and plexiglass partitions, our impulse to sonically surveil became heightened. Thus, many of us listened differently. Our fears of being surveilled were heightened by the fear of the Other—in this case, the fear of being othered as unwell. Our anxiety about the Covid cough was attached to ableism and the horror of being perceived as sick because, as Davis states, the “nightmare of the body is one that is deformed, maimed, mutilated, broken, diseased” (Normalcy: Link 7). The Covid cough reminded all of us that we are not as self-controlled and autonomous as we would like to think, and that we are all capable of being–or of becoming–a dissed (diseased or disabled), othered body, if we are not already.

But what if we could revisit the Covid cough and consciously listen to it in other, less fear-driven ways? If we move from listening to the cough as a surveillance practice and situate our listening as a critical rhetorical practice–a practice that examines the relationship of discourse and power and advocates for social change–then we can begin to think about what the Covid cough can teach us. Novak and Sakakeeny claim that sound only becomes known through its materiality. The Covid cough is indelibly material and embodied; it requires lungs and airways, breath and mucus. The Covid cough, distinguishable from other coughs, was described similarly by medical professionals around the world, reminding us that while listening is a highly cultured act, our sound bodies are comprised of blood, bones, and organs—substance that tethers our listening practices to a material body. We are, as Eidsheim claims in Sensing Sound, interconnected in material terms: “we cannot exist merely as singular individuals” (20). The stuff and guts of our material bodies reminds us of our connectivity, of our shared humanity, of our oneness.
The sound of the Covid cough, then, assures us of our vulnerability—a vulnerability precipitated by our lived, material body. It is important to note that not all individuals have been equally vulnerable. Individuals who are immunocompromised and essential workers, for instance, were much more susceptible to being exposed to the Covid-19 virus, as was anyone unable to work to home and many Black and brown Americans made more vulnerable by years of racist neglect by the nation’s health care system. But, still, no one is invincible. The sounds of the Covid-19 soundscape reify this truth and reinforce that through our material bodies, we are interconnected; we are all sound, and sounding, bodies.

Covid-19 brought, and is still bringing, daily horrors. The sounds of the Covid-19 soundscape are not yet absent from our consciousness or our communities. My hope is that by re-immersing ourselves into its soundscape, we can continue to remember that our fight against Covid-19 is a collective one and that we all have a shared responsibility toward our fellow humans. It is also important for sound studies to think critically and rhetorically about normalized listening practices and how those practices shape cultural understandings of what it means to be sick or disabled. Listening is not only an embodied practice; it also has bodily implications. While the Covid-19 soundscape heightened our awareness of our own vulnerability and, for some, their fears of “the other”—and (hopefully) some reflexivity on how one’s own listening can drive practices of othering—it also reassured many of our connectivity, for better or worse.
We remember those whose lives were lost to Covid-19. We listen to honor them and we listen to learn. . .and hopefully we can listen to one another with renewed empathy to build new collectivities that will forever change the Covid soundscape, along with the many other intersecting inequities that collectively brought us here too.
—
Featured Image: Coronavirus, Playground on Lockdown, Sheffield, UK, Image by Tim Dennell (CC BY-NC 2.0)
—
Sarah Mayberry Scott (Ph.D., University of Memphis) is Assistant Professor of Communication Studies at Arkansas State University in Jonesboro, Arkansas. Her research centers on representations and rhetorics of deafness. Scott is particularly interested in how sound impacts the Deaf community and how multi-modal literacies can be of particular interest and utility. She explores these issues in her works, “Re-Orienting Sound Studies’ Aural Fixation: Christine Sun Kim’s ‘Subjective Loudness,’” (2017), “Disability Gets Dissed: How Listening Rhetorically with Cultural Humility Amplifies the Concerns of Disability Culture,” (2021), and “Toward a More Just Rhetorical Criticism Through Situated Listening” (in press).
—

REWIND! . . .If you liked this post, you may also dig:
my mother’s voice, my father’s eye, and my other body: the sound of deaf photographs— Cara Cardinale
SO! Reads: Steph Ceraso’s Sounding Composition: Multimodal Pedagogies for Embodied Listening--Airek Beauchamp
SO! Podcast #79: Behind the Podcast: deconstructing scenes from AFRI0550, African American Health Activism – Nic John Ramos and Laura Garbes
Queer Timbres, Queered Elegy: Diamanda Galás’s The Plague Mass and the First Wave of the AIDS Crisis– Airek Beauchamp
Listen to yourself!: Spotify, Ancestry DNA, and the Fortunes of Race Science in the Twenty-First Century

If you could listen to your DNA, what would it sound like? A few answers, at random: In 1986, the biologist and amateur musician Susumo Ohno assigned pitches to the nucleotides that make up the DNA sequence of the protein immunoglobulin, and played them in order. The gene, to his surprise, sounded like Chopin.
With the advent of personalized DNA sequencing, a British composition studio will do one better, offering a bespoke three-minute suite based on your DNA’s unique signature, recorded by professional soloists—for a 300GBP basic package; or 399GBP for a full orchestral arrangement.
But the most recent answer to this question comes from the genealogy website Ancestry.com, which in Fall 2018 partnered with Spotify to offer personalized playlists built from your DNA’s regional makeup. For a comparatively meager $99 (and a small bottle’s worth of saliva) you can now not only know your heritage, but, in the words of Ancestry executive Vineet Mehra, “experience” it. Music becomes you, and through music, you can become yourself.
screencap by SO! ed JS
As someone who researches for a living the history of connections between music and genetics I am perhaps not the target audience for this collaboration. My instinct is to look past the ways it might seem innocuous, or even comical—especially when cast against the troubling history of the use of music in the rhetoric of American eugenics, and the darker ways that the specter of debunked race science has recently returned to influence our contemporary politics.
During the launch window of the Spotify collaboration, the purchase of a DNA kit was not required, so in the spirit of due diligence I handed over to Spotify what I know of my background: English, Scottish, a little Swedish, a color chart of whites of various shade. (This trial period has since ended, so I have not been able to replicate these results—however, some sample “regional” playlists can be found on the collaboration homepage).
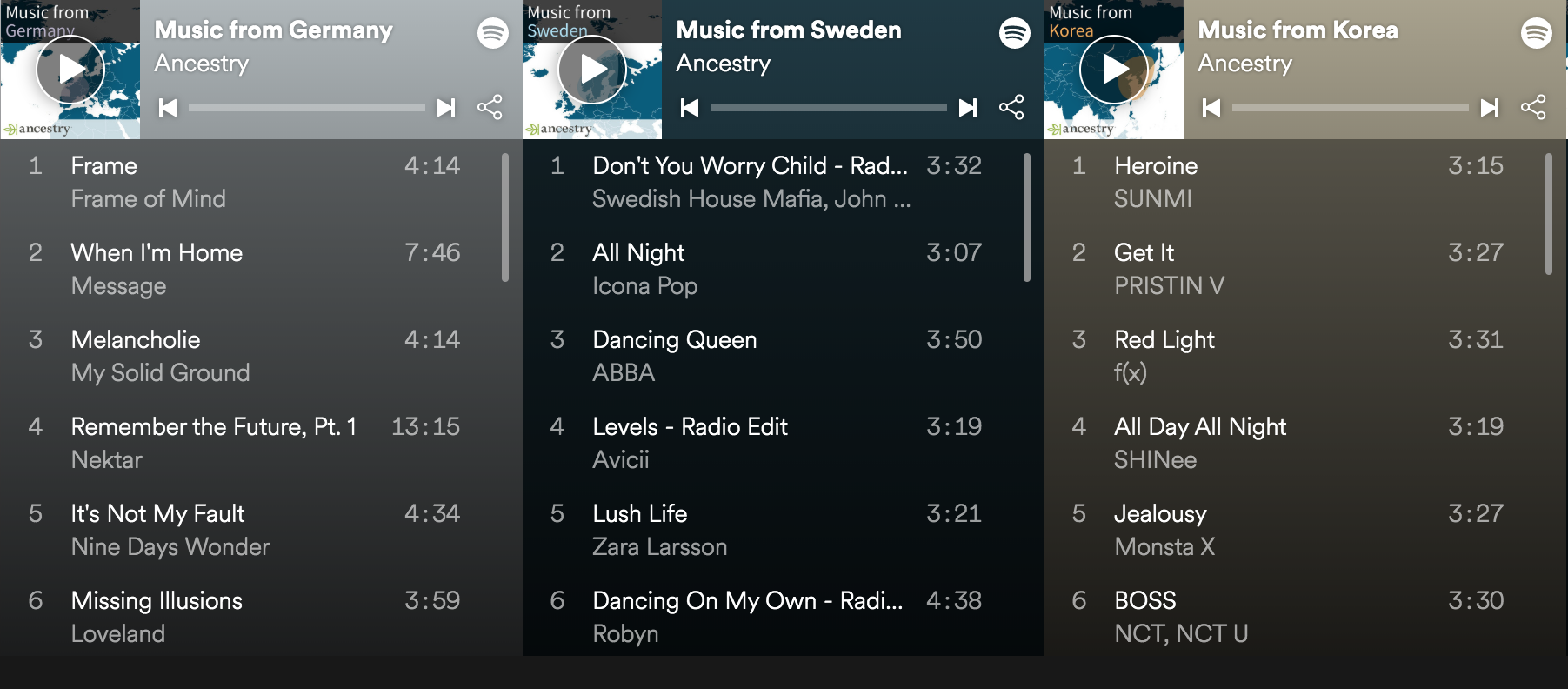
screen capture by SO! editor JLS
While I mentally prepared myself to experience the sounds of my own extreme whiteness, Ancestry and Spotify avoid the trap of overtly racialized categories. In my playlist, Grime artist Wiley is accorded the same Englishness as the Cure. And ‘Scottish-Irish’, still often a lazy shorthand for ‘White’, boasted more artists of color than any other category. Following how the genetic tests themselves work, geography, rather than ethnicity, guides the algorithm’s hand.
As might be expected, the playlists lean toward Spotify’s most popular sounds: “song machine” pop, and hip-hop. But in smaller regions with less music in Spotify’s catalog, the results were more eclectic—one of the few entries of Swedish music in my playlist was an album of Duke Ellington covers from a Stockholm-based big band, hardly a Swedish “national sound.” Instead, the music’s national identity is located outside of the sounding object, in the information surrounding it, namely the location tag associated with the recording. In other words: this is a nationalism of metadata.
One of the common responses to the Ancestry-Spotify partnership was, as, succinctly expressed by Sarah Zhang at The Atlantic: ‘Your DNA is not your culture’. But because of the muting of musical sound in favor of metadata, we might go further: in Spotify’s catalog, your culture is not even your culture. The collaboration works because of two abstractions—the first, from DNA, to a statistical expression of probable geographic origin; and second from musical sound and style characteristics, to metadata tags for a particular artist’s location. In both of these moves, traditional sites of social meaning—sounding music, and regional or familial cultural practice—are vacated.
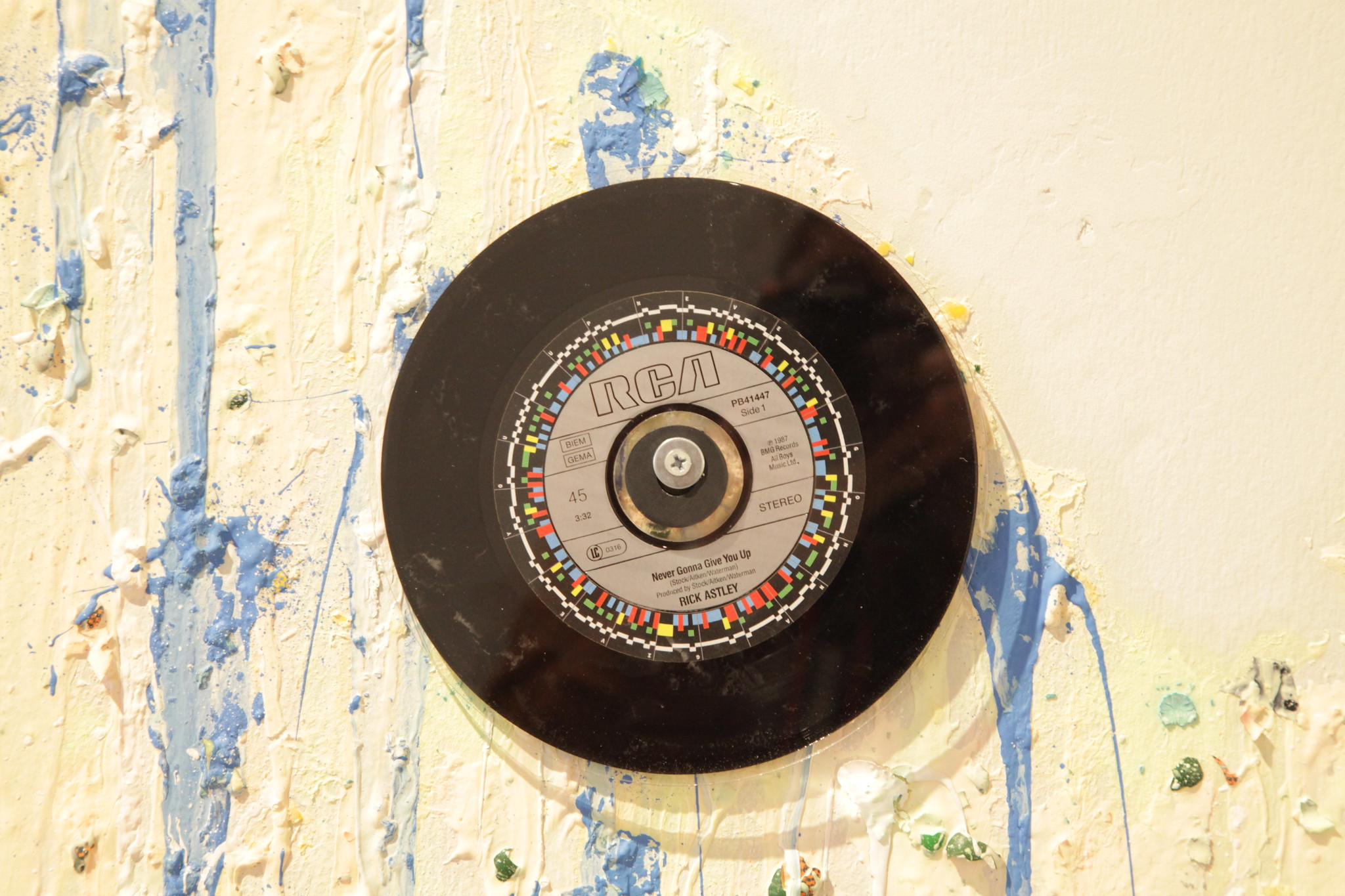

Synthetic Memetic / Matthew Gardiner (AU): Gardiner composed a DNA sequence in such a way that the series of nucleotide bases in it correspond to the letters of the song title “Never Gonna Give You Up” by Rick Astley, and then integrated them symbolically into a pistol. Credit: Sergio Redruello / LABoral Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 2.0 Generic (CC BY-NC-ND 2.0)
There is a way in which this model could come across as subversive (which has not gone unnoticed by Ancestry’s advertising team). Hijacking the presumed whiteness of a Scotland or a Sweden to introduce new music by communities previously barred from the possibility of ‘Scotishness’ or ‘Swedishness’ could be a tremendously powerful way of building empathy. It could rebut the very possibility of an ethno-state. But the history of music and genetics suggests we might have less cause for optimism.
In the 1860s, Francis Galton, coiner of the word ‘eugenics’, turned to music to back up his nascent theory of ‘hereditary genius’—that artistic talent, alongside intelligence, madness, and other qualities were inherited, not acquired. In Galton’s view, musical ability was the surest proof that talents were inherited, not learned, for how else could child prodigies stir the soul in ways that seem beyond their years? The fact of music’s irreducibility, its romantic quality of transcendence, was for Galton what made it the surest form of scientific proof.
Galton’s ideas flourished in America in the first decades of the twentieth century. And while American eugenics is rightly remembered for its violence—from a sequence of forced sterilization laws beginning with Indiana in 1907, to ever-tightening restrictions on immigration, and scientific propaganda against “miscegenation” under Jim Crow—its impact was felt in every area of life, including music. The Eugenics Record Office, the country’s leading eugenic research institution, mounted multiple studies on the inheritance of musical talent, following Galton’s idea that musical ability offered an especially persuasive test-case for the broader theory of heritability. For 10 years the Eastman School of Music experimented on its newly admitted students using a newly-developed kind of “musical IQ test”, psychologist Carl Seashore’s “Measures of Musical Talent”, and Seashore himself presented results from his tests at the Second International Congress of Eugenics in New York in 1923, the largest gathering of the global eugenics movement ever to take place. His conclusion: that musical ability was innate and inherited—and if this was true for music, why not for criminality, or degeneracy, or any other social ill?
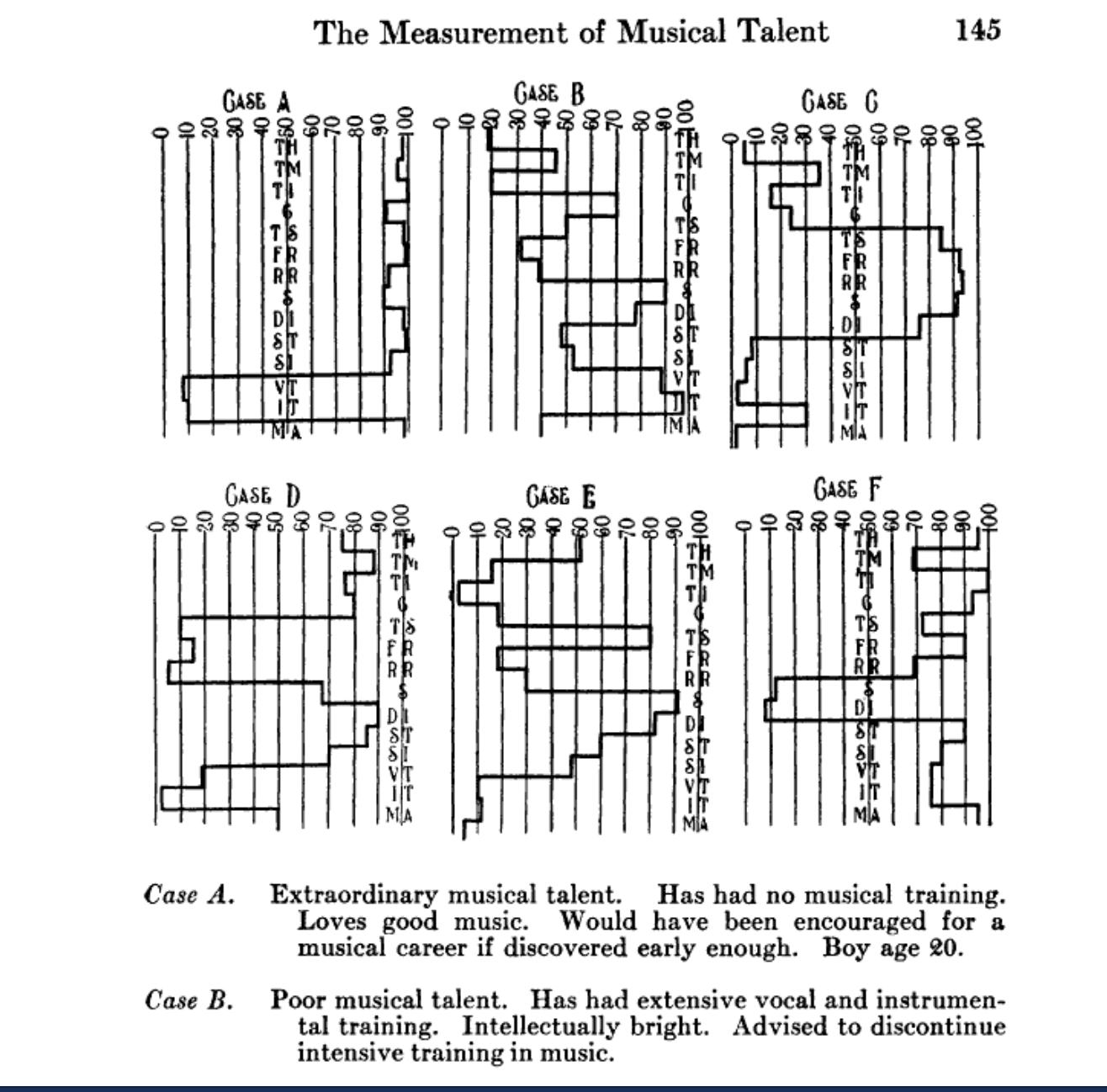
From “The Measurement of Musical Talent,” Carl E. Seashore, The Musical Quarterly Vol. 1, No. 1 (Jan., 1915), p. 125.
Next to the tragedy of the early twentieth century, Spotify and Ancestry teaming up seems more like a farce. But scientific racism is making a comeback. Bell Curve author Charles Murray’s career is enjoying a second wind. Border patrol agents hunt “fraudulent families” based on DNA swabs, and the FBI searches consumer DNA databases without customer’s knowledge. ‘Unite the Right’ rally organizer Jason Kessler ranked races by IQ, live on NPR.. And, while Ancestry sells itself on liberal values, many white supremacists have gone after ‘scientific’ confirmation for their sense of superiority, and consumer DNA testing has given them the answers they sought (though, often, not the answers they wanted.)
As consumer genetics gives new life to the assumptions of an earlier era of race science, the Spotify-Ancestry collaboration is at once a silly marketing trick, and a tie, whether witting or unwitting, to centuries of hereditarian thought. It reminds us that, where musical eugenics afforded a legitimizing glow to the violence of forced sterilization, the Immigration Acts, and Jim Crow, Spotify and Ancestry can be seen as sweeteners to modern-day race science: to DNA tests at the border, to algorithmic policing, and to “race realists” in political office. That the appeal of these abstractions—from music to metadata, from culture to geography, from human beings to genetic material—is also their danger. And finally, that if we really want to hear our heritage, listening, rather than spitting in a bottle, might be the best place to start.
—
Featured Image: “DNA MUSIC” Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 4.0 International
—
Alexander Cowan is a PhD candidate in Historical Musicology at Harvard University. He holds an MMus from King’s College, London, and a BA in Music from the University of Oxford. His dissertation, “Unsound: A Cultural History of Music and Eugenics,” explores how ideas about music and musicality were weaponized in British and US-American eugenics movements in the first half of the twentieth century, and how ideas from this period survive in both modern music science, and the rhetoric of the contemporary far right.
—
 REWIND! . . .If you liked this post, you may also dig:
REWIND! . . .If you liked this post, you may also dig:
Hearing Eugenics–Vibrant Lives
In Search of Politics Itself, or What We Mean When We Say Music (and Music Writing) is “Too Political”–Elizabeth Newton
Poptimism and Popular Feminism–Robin James
Straight Leanin’: Sounding Black Life at the Intersection of Hip-hop and Big Pharma–Kemi Adeyemi


















Recent Comments