Finding Resonance, Finding María Lugones
I am always listening for María: I find her most in the traces of words.
Trained as a literary scholar, I relish in the contours of stories; I savor the nuances found between crevices of language and the shades of implication when those languages are strung together. It is no surprise, then, that since the death of my friend and mentor María Lugones, I have turned to many books, particularly her book, Pilgrimages/Peregrinajes: Theorizing Coalition Against Multiple Oppression, to feel connected to her. I have struggled, though, to write about her, talk about her, even think about her for many years. It wasn’t until I found a passage about spirits and hauntings in Cuban-American writer and artist Ana Menéndez’s novel The Apartment that I found language to describe a way through the grief of the last five years.

Menéndez’s novel follows many characters that all, at some point in time, come to live in apartment 2B in Miami Beach. While each person is seemingly disconnected from the next, they all leaves sonic traces of themselves for the next person’s arrival. Each new tenant leaves behind the creak of a dented floorboard, or the rumbling of the air conditioner, the faint melody of a piano, or the swish of spirits looking for a place to sit down. The climax of the novel revolves around Lenin García, a young Cuban migrant who commits suicide in the Miami apartment shortly after arriving. Anna, a journalist who migrated to the US from the Czech Republic during their communist regime, prepares the apartment for rental after the suicide. When looking through Lenin’s belongings she explains that the “Spirits pressed down on her, and again and again she rejects them. Sends them packing, back to the pre-rational past. Not a haunting, but an echo. The boy’s life a gesture pointing back to her own. A dream of a thousand iterations” (131). These spirits that surround her, that remind her of her own life’s ghosts, provide a particularly sonic connection; the tethers that connect one migration tragedy to another is an echo of commonality that creates a kin experience.
The three years I learned with and from María are overshadowed by the physical distance the pandemic required of me in her final moments. When I try to write about her, my hair stands on end, my eyes water, my nose drips, and I stretch out my hand toward a presence I feel, just out of reach. I know it’s her, I just can’t seem to touch her. I have described María’s death as a haunting—as something that haunts me. I defined this haunting as a physical presence that I could not see, but I could feel, sense. But what if, like Anna, I am feeling, not a haunting, but an echo; or more accurately, the resonances of María that echo around me constantly? What Menéndez’s passage provides is the necessity of reinterpreting my awareness of María from one of general sensing to one of specific aural attunement. If I am listening for her, how, then do I keep her with me?

Lenin, from The Apartment, provides a potential answer: when meeting with a curandera in Cuba, she tells him “The ancestors speak to you from the home of your inner life. When your inner life is spare, there is nowhere for the ghosts to sit. When you furnish your spirit, the ancestors will once again find rest in you” (143). Echoes become an analytic that provide furnishings ‘in the soul’ for sustained company of those who have passed. The reverberation of echoes—reverberations as a prolonged sense of resonance that stretches the meeting of two energies—can, quite literally, allow a reader to connect back to people across space and time. My tether to María is a resonance that simultaneously locates and disperses spatially and temporally. I hear this connection as my harmony to her melody. To further the metaphor, that resonance is the strumming of a guitar, where I am the guitar and she is the musician, and that moment where we both hear for each other, even when we do not know the other exists, is the note.
What happens when I use literary methods of analysis to find people in the interstices of sound? To search for María in what she calls the “enclosures and openings of our praxis” as a reader of her text? Now that I had to search the histories of her echo, I turned to her book, Pilgrimages/Peregrinajes.
When María recommends “to women of color in the United States that we learn to love each other by learning to travel to each other’s ‘worlds’,” (78) I imagine our first few encounters; encounters that were strange, difficult, and lessons in learning to listen to her on her terms. I had been invited to her home in Binghamton, New York for a meeting of a political-intellectual group she hosted, and was nervous to meet the woman I had written my Master’s thesis on, and who was the reason I applied to Binghamton for a PhD program. Her voice rang through the room, slow and clear; her mouth pursed a bit as she thought through her next sentence, her finger pointed as she spoke her next idea. In trying to stay out of her way, I became a barrier when she moved backward; she bumped into me and said simply ‘you must be careful not to trip me’ and moved along. I was mortified.
Our next few encounters were similarly odd, and lead me to think that, maybe, María was not the right choice for my mentoring needs. A few months into this first year in graduate school—where tenured male professors were violent toward me, and I was not sure I should stay in academia—I confessed to a friend in the same political-intellectual group that I was not sure María liked me or that I should work with her. Her response changed everything: this friend, who had worked with María many, many years said: “don’t do that. Don’t make her mother you. It’s not who she is. Travel to her, learn her.” I finally understood that traveling to María’s world meant listening to her from her perspective, not my own. That shift in me “from being one person to being a different person” (89) is how I first found María in the haptic world. I learned to listening to her: I learned the catch in her throat meant she wanted tea; I learned the increase in sighs meant she was in more pain that usual; I learned the shuffling of papers probably meant she was looking for her handkerchief to wipe her forehead as she had a hot flash. Each of these sonic gestures, I could respond to—could show up for her.

But with María’s death, this kind of listening is no longer available to me; I could not listen for hem or hmm or tchps. I had to learn to listen differently. In re-reading Pilgrimages/Peregrinajes I learn that it does not just contain her philosophical interventions for liberatory futures. It is a series of stories; her stories of the echoes that resonate inside of her; stories that she weaves together that happen to name philosophical practices of relationality. It is through the coerced placement of her by her father in an asylum that she finds other woman who teach her to resist; this resistance is sonic: a woman repeating over and over “I am busy, I am busy” as they electroshock her (i). It is through wanting desperately to love her mother that she finds ways her mother taught her to listen differently in order to name the capacity of ‘world’-traveling. What I had felt when I first read her work over a decade ago was a resonance; a sonic reverberation across space and time that connected my to her before our physical meeting, during our time as friends and mentor/mentee, and now after her physical death.
Connecting to María through echoes feels effortless now that I have the language. I hear now María’s warning against the dangers in the primacy of the visual. In “Hablando Cara a Cara/Speaking Face to Face: An Exploration of Ethnocentric Racism,” she explains:
I exercise this playful practice. The appreciation of my playfulness and its meaning may be realized when the possibility of becoming playful in this way has been collectively realized, when it has become realized by us. It is here to be appreciated or missed and both the appreciation and the missing are significant. The more fully this playfulness is appreciated, the less broken I am to you, the more dimensional I am to you. But I want to exercise my multidimensionality even if you do not appreciate it. To do otherwise would be to engage in self-mutilation, to come to be just the person that you see. To play in this way is then an act of resistance as well as an act of self- affirmation (41).
What she taught me here is that being herself meant a practice that was more than being seen. To be what others could only see was an act of mutilation to her multidimensionality. That reminder was crucial to becoming her friend during my time at Binghamton, but even more crucial now that she is gone from this world.

I’ll leave you with the most important story she left behind: she provided a method of learning that was based on the senses and focused primarily on the sonic—what she called “tantear.” This tantear has become instrumental in my own research. It is a fumbling around in the dark, a feeling around tactically that focuses on searching “for meaning, for the limits of possibility; putting our hands to our ears to hear better, to hear the meaning in the enclosures and openings of our praxis” (1). The embodied experience of stumbling, of careful and intense feeling for and with others, requires a capacity of listening deeply. It is listening that undergirds the learning. The language of the sonic provides the understanding of the feelings within the body. Listening becomes a profound practice of relationality; echoes become a mechanism of connection; and resonance becomes the confirmation that I can still be with María.
—
Images courtesy of the author, except where noted.
—
Daimys Ester García is a Latinex writer, artist and educator from Miami. She earned her PhD in Comparative Literature at SUNY Binghamton. She is currently an Assistant Professor in English at the College of Wooster, where her research and teaching is at the intersections of Latinx literatures & studies, Native literatures & studies, women of color feminisms, and decolonial praxis with a focus on coalitional politic. She is working on a book manuscript, tentatively titled Comfort is Colonialism: Coalitional Commitments for Cuban-American Women Writers, which offers a repertoire of practices to re-connect Cuban-Americans with other histories of resistance in the US.
—
Thank you to Wanda Alarcón for care in the form of editorial labor.
—

REWIND!…If you liked this post, you may also dig:
Faithful Listening: Notes Toward a Latinx Listening Methodology–Wanda Alarcón, Inés Casillas, Esther Díaz Martín, Sara Veronica Hinojos, and Cloe Gentile Reyes
Enacting Queer Listening, or When Anzaldúa Laughs–Maria Chaves Daza
“Oh how so East L.A.”: The Sound of 80s Flashbacks in Chicana Literature–Wanda Alarcón
Xicanacimiento, Life-giving Sonics of Critical Consciousness–Esther Díaz Martín and Kristian E. Vasquez
SO! Amplifies: Wu Tsang’s Anthem (2021)


SO! Amplifies. . .a highly-curated, rolling mini-post series by which we editors hip you to cultural makers and organizations doing work we really really dig. You’re welcome! We are excited that today’s post on Wu Tsang’s Anthem, currently on view at the Guggenheim through September 6, 2021, is written by Freddie Cruz Nowell, co-author of the exhibition texts! He is related to the curator of the exhibition and cares deeply about the collaborative, creative endeavors of Wu Tsang & Moved by the Motion.
—
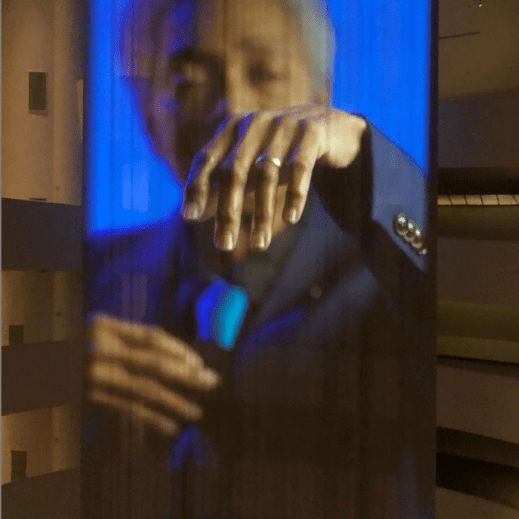
The artist and filmmaker Wu Tsang (b. 1982) creates atmospheric performances, video installations, and films that envelop audiences into spaces where narratives become sensually ambiguous, collective experiences. Tsang’s new site-specific installation, Anthem (2021), was conceived in collaboration with the singer, composer, and transgender activist Beverly Glenn-Copeland (b. 1944, Philadelphia) and harnesses the Guggenheim Museum’s cathedral-like acoustics to construct what the artist calls a “sonic sculptural space.”
Occupying the entire rotunda, Anthem revolves around an immense, eighty-four-foot curtain sculpture that flows down from the building’s glass oculus. Projected onto this luminous textile is a “film-portrait” Tsang created of Glenn-Copeland improvising and singing passages of his music, including a cappella descants and his rendition of the spiritual “Deep River.” Filmed during the COVID-19 pandemic, near Glenn-Copeland’s home in rural Nova Scotia, this non-linear video alternates between scenes of the musician performing with various instruments and stunning landscape shots of the eastern seaboard sky.
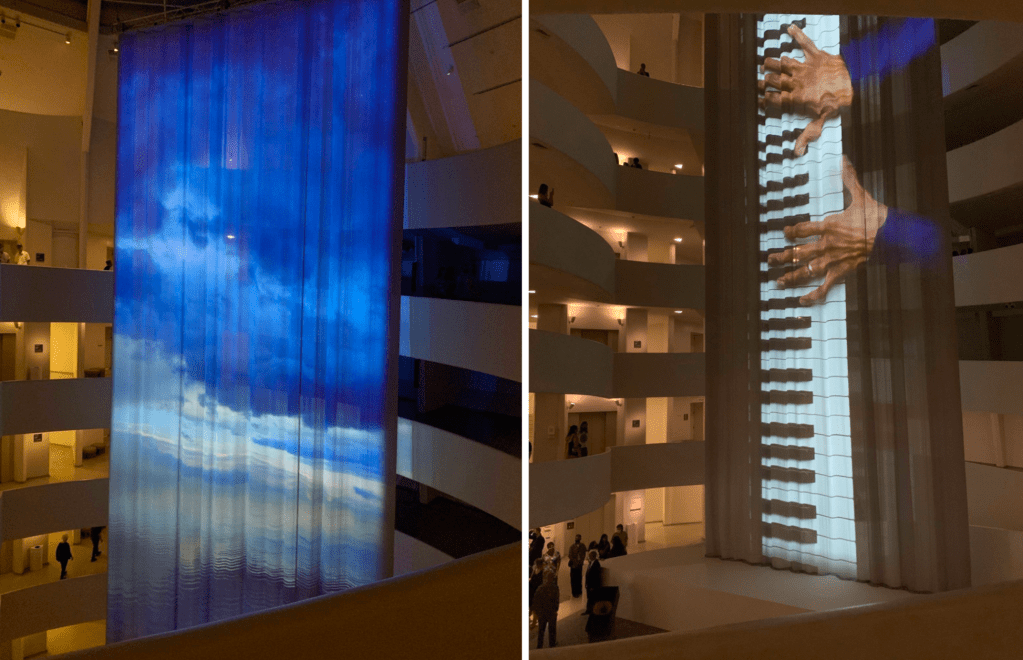

Instrument and Landscape View of Wu Tsang’s Anthem (2021), Images courtesy of The Guggenheim
Harnessing the generous sound-reflecting quality of the Guggenheim’s concrete walls, Anthem weaves Glenn-Copeland’s voice and body percussion into a larger tapestry of other voices and sounds placed along the museum’s circular ramp, building a soundscape that wraps around the space. When I asked the exhibition’s curator X Zhu-Nowell about the striking ethereal, translucent quality of the curtain sculpture, X remarked,
It was a collaboration with the textile company Kvadrat. Wu visited their showroom a few times to select textile from thousands of the samples. This particular textile called power is semi translucent (created almost a hologram feeling), but still able to capture the light from the projectors very well. Wu once said that ‘when there is a curtain in the space, it turns the space into a stage.’ Curtain is very important to Wu’s practice.
The installation’s dimmed light ambiance also veils the fourteen speakers that Tsang positioned along this darkened path, each of which plays a uniquely composed track that accompanies Glenn-Copeland’s music.
Working in collaboration with musician Kelsey Lu and the DJ, producer, and composer duo of Asma Maroof and Daniel Pineda, Tsang conceived this arrangement of sounds as a series of improvisatory responses inspired by the call of Glenn-Copeland’s voice. The musical responses created by this diverse group of musicians include ethereal string tremolos, dreamy whisper sequences, and impromptu drum patterns, among other ambient sounds that help cultivate an alluring and reverberant listening environment.
Harnessing the generous sound-reflecting quality of the Guggenheim’s concrete walls, Anthem weaves Glenn-Copeland’s voice and body percussion into a larger tapestry of other voices and sounds placed along the museum’s circular ramp, building a soundscape that wraps around the space. X Zhu-Nowell described the process for the exhibit’s speaker placement:
We had a few mock-up to test the speaker placement. The two loudspeakers are placed on the rotunda floor because it’s unique capacity to fill the entire rotunda. The 12 additional Bose speakers were placed throughout ramp 3 – 6. We evenly distributed them, 3 speakers for each ramp. Ultimately, the goal is to work with the unique acoustics of the building, and working with the decay, allowing the time and space for the sound to bound on the concrete walls. The piece is 18 mins long, and in a continuous loop. It was not designed to cultivate a single prime viewing location. Instead, the piece was built to be experienced as one move through the space, and 18 mins is around the pace of one walk from the bottom of the rotunda floor to the top of ramp 6.
Visitors are encouraged to traverse upward from the bottom of the museum to the top of the building, and vice versa, and explore how Anthem ascends and descends along the spiral path.
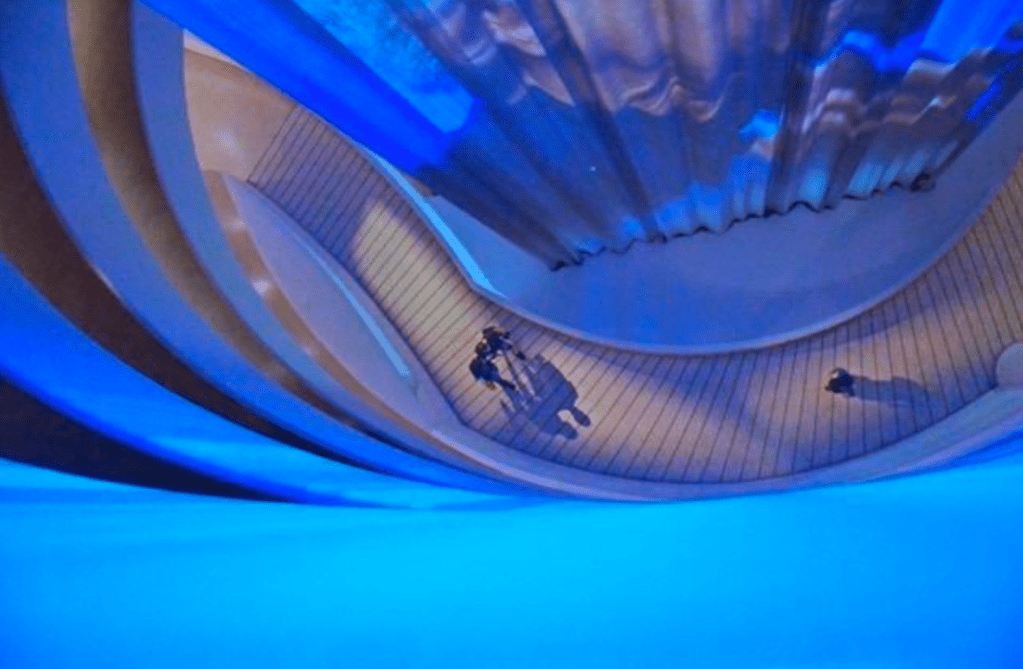

Alternative View of Ramp: Wu Tsang’s Anthem (2021)
The title of this exhibition, Anthem, draws from lesser-known histories of the word meaning antiphon, a style of call-and-response singing associated with music as a spiritual practice. Unlike a conventional anthem, which amplifies the power of a song through loudness and uniform sound, this installation enhances the call of Glenn-Copeland’s voice by combining it with ambiguous vocal timbres, changing tints of ambient sound, and other heterogeneous sonic and visual textures. Within this lush yet complicated auditory environment, Tsang’s Anthem also cultivates moments of quiet, rest, and reflection, reimagining the rotunda as a compassionate atmosphere for collective listening and looking.
In addition to the immersive video installation on view in the rotunda, this exhibition also includes a touching companion film, titled “∞,” which visitors can access behind a luxe pleated curtain that divides the first floor side gallery from the main space. This video is a short interview that Tsang shot during the filming of Anthem of Glenn-Copeland and his partner, Elizabeth Glenn-Copeland, a theater artist, storyteller, and arts educator.

This dialogue captures autobiographical aspects of the couple’s intertwined creative process and artistic development, reflecting on myriad meanings of love in relation to their lives and work. Within the context of the oppressive and exploitive conditions of transgender “visibility” in contemporary culture, Tsang’s seemingly conventional yet uncommon record of this elderly and interracial couple exists in tension with the normative frame of transgender representation. It also extends the conversation within Tsang’s artistic practice around the centrality of collaboration, specifically long-term and intimate collaboration.
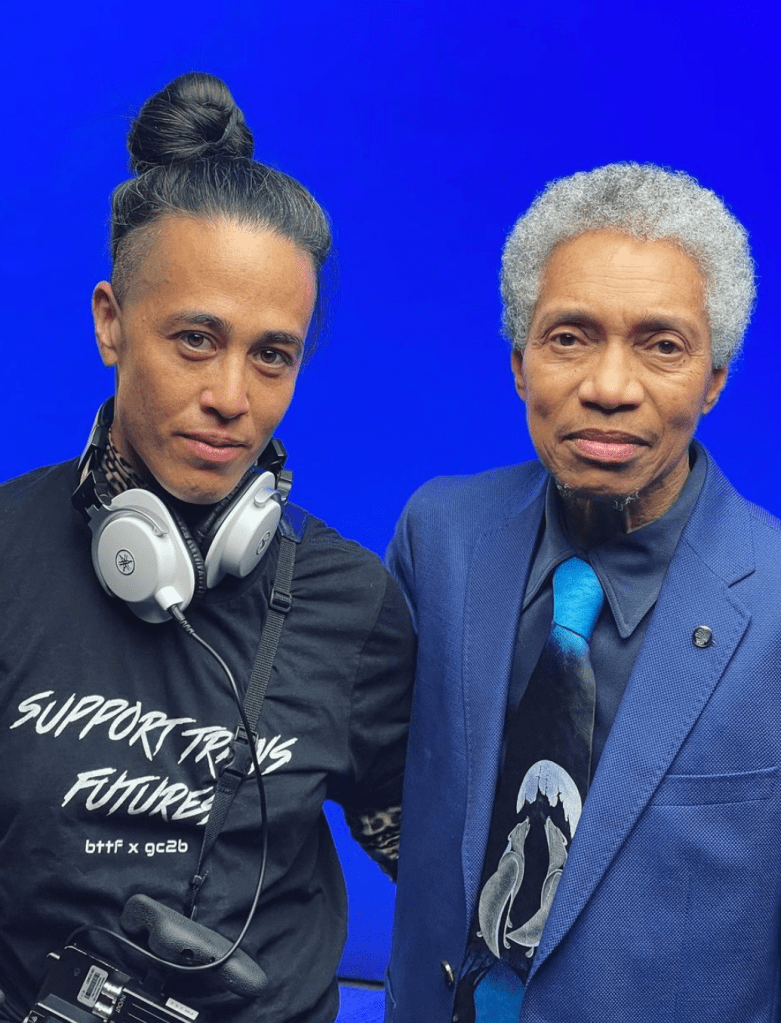

Photo of Wu and Glenn on set in Nova Scotia, from Wu Tsang’s IG feed
Since 2016, Tsang has frequently worked with a “roving band” of interdisciplinary artists called Moved by the Motion, cofounded with the artist Tosh Basco. Core members of this revolving cast include Maroof, Pineda, the dancer Josh Johnson, the cellist Patrick Belaga, and the poet and scholar Fred Moten. Anthem exemplifies how she uses collaboration as an aesthetic strategy for undoing conventional modes of authorship and to make space for marginalized narratives. For Tsang, “making art is an excuse to collaborate.”
On View at the Guggenheim, New York City, July 23-September 6, 2021
—
Featured Image: Still of banner/ installation View of Wu Tsang’s Anthem (2021) at the Guggenheim, courtesy of curator X Zhu-Nowell
—
Frederick Cruz Nowell is a Ph.D. Candidate in Musicology at Cornell University. He is a scholar with a specialty in historical avant-gardes, and cross-disciplinary research into the history of music theory, contemporary art, and popular music. His dissertation research (Supervisor, Prof. Andrew Hicks) lies at the occult intersection of artistic experimentalism, Euro-American counterculture, and the history of music theory in the early twentieth century. It traces how speculative music-theoretical concepts (i.e., cosmic harmony, biological rhythms, color-harmony, and ontologies of sympathetic vibration) fused into the practices of European avant-garde artists via fashionable occult religious movements (i.e., Theosophy and Anthroposophy) and various cults of health and beauty (i.e., harmonic gymnastics, Eurythmics, free body culture (Freikörperkultur)). Intimately intertwined with one another, these social developments were integral to the larger infrastructure of the unwieldy “back to nature” Lebensreform (the reform of life) movement, which laid the foundations for progressive counterculture in the twentieth century.
Before pursuing graduate studies in musicology, Frederick was a University Fellow at Northwestern University in the Department of Art, Theory, & Practice, where he received an MFA. He also holds a BFA from SAIC (the School of the Art Institute of Chicago). Since 2018, he has co-curated exhibitions with X Zhu-Nowell under the moniker Passing Fancy.
—

REWIND!…If you liked this post, you may also dig this:
Instrumental: Power, Voice, and Labor at the Airport--Asa Mendelsohn
SO! Amplifies: Anne Le Troter’s “Bulleted List”
“Finding My Voice While Listening to John Cage“–Art Blake
SO! Amplifies: Shizu Saldamando’s OUROBOROS
SO! Amplifies: Mendi+Keith Obadike and Sounding Race in America
Sound and Curation; or, Cruisin’ through the galleries, posing as an audiophiliac–reina alejandra prado


















Recent Comments