- by justindburton
- in American Studies, Article, Black Studies, Class, Cultural Studies, Dance/Movement, Diasporic Sound, Film/Movies/Cinema, History, Live Music, Music, Performance, Place and Space, Popular Music Studies, Race, Religion and Religious Studies, Ritual, Sound Studies, Soundscapes, Time
- 2 Comments
“Just for a Few Hours, We Was Free”: The Blues and Mapping Freedom in Sinners (2025)

In the 2025 blockbuster Sinners, Ryan Coogler has a vampire story to tell. But before he can begin, he needs to tell another story—a blues one. Sinners opens with a voiceover thesis statement performed by Wunmi Mosaku (who plays Annie in the film—more on her below) about the work the blues can do, then rambles the narrative through and around 1932 Clarksdale, eventually settling into a juke joint outside of town. Here, the blues story builds to a frenzied climax, ultimately conjuring the vampires propelling the film’s second half. It’s those vampires that most immediately register as cinematic spectacle, but Coogler’s impetus to film in IMAX and leverage all of his professional relationships for the movie wasn’t the monsters—it was to showcase the blues at a scale the music deserves. In Sinners, the blues takes center stage as a generative sonic practice, sound that creates space to be and to know in the crevices of the material world, providing passage between oppression and freedom, life and death, past and future, and good and evil.
I’m not exaggerating in calling the opening voiceover a thesis. In a movie where Coogler trusts his audience with a great deal of interpretation, he puts an incredibly fine point on the role that blues performs here. We’re told that some musicians—be they Irish, West African, Native American, or southern US Black—are so skilled that they can pierce the veil separating the living from the dead, and while this piercing can help heal a community, it can also attract a certain evil that wants to exploit this rupture. The narrator doesn’t say “It’s the blues!” but the next visual information we get is that it’s Clarksdale, MS, in 1932, and an injured, blood-soaked Sammie (Miles Caton) is stumbling into his father’s church, clutching what’s left of the neck of a guitar. No one in Sinners says the word “crossroads,” but here we are, at the place where the blues meets the devil—where the end meets the beginning–and our young hero has a choice about which way he’s going to go.
If Coogler doesn’t fully trust his audience to know what to do with the blues without being told, it’s likely due to decades of commercialized attempts to defang the genre that have filtered out 21st century listeners’ ability to hear most of what makes the blues potent. Drawing on what Clyde Woods in Development Arrested (1998) has termed the “blues epistemology,” a blues way of knowing, B Brian Foster speaks with contemporary Black Clarksdalians in I Don’t Like the Blues (2020) to chart much of the current state of the blues. Pulling on one particular thread of Foster’s ethnography can help clarify what’s happening in Sinners, as he unpacks the many reasons why the blues don’t resonate quite like they used to.
In Woods’s framework, the blues is more than a musical genre; it’s a way of understanding and, crucially, reshaping one’s world. The blues, a genre arising in the late 19th century and reverberating through the 20th, functioned as epistemology in order to explore a way out from under plantation power after Reconstruction and through Jim Crow. Woods chronicles centuries of “plantation power” in the Delta and how that power reconfigures itself over and again through different eras of US history, always with the goal of extracting labor and life from Black Mississippians. The blues pushed against the edge of what was considered possible and sought to imagine and create a world that was free—not just from plantation power but from all the logics that support it or would circumscribe Black self-determination and autonomy. In I Don’t Like the Blues, Foster encapsulates the heart of blues epistemology with a flourish: “While many people hear the blues as performance and play, Black residents of Clarksdale knew it to be flesh and bone, a spirit in the dirt. Their blues was a conduit. A map. A method” (15-16). Throughout his book, Foster demonstrates that what the blues was is no longer what the blues is. One of those reasons is that resistance to plantation power (whether in the Delta or beyond) simply sounds different now, having worked its way through jazz and funk and soul and hip hop and trap.

In Sinners, Coogler starts by telling us what the blues could do, then he shows us that power in a climactic scene midway through the film, reminding his audience that a blues epistemology might not always sound the same, but it can still do the work of mapping out freedom. After the camera cuts away from Sammie at the crossroads in his church, we loop a bit back in time to meet Sammie’s cousins, the SmokeStack brothers (twins played by Michael B Jordan), who purchase the juke joint’s eventual location. The first half of the movie follows the brothers as they split up and get the band—and hospitality crew—together to open the venue that night. Sammie is new to this life, but a deeply gifted bluesman, and he receives counsel along the way about what the music is and how it works. Once the juke is packed, the booze is flowing, and the dancefloor is sweating, Delta Slim (Delroy Lindo) invites Sammie to take the stage and tell the people who he is and where he’s from. What follows is an ambitious narrative and technical feat that pays off the opening voiceover.
Sammie, also known as Preacher Boy, launches into a song called “I Lied to You,” addressed to his minister father (played by Saul Williams). It’s a confession that he’ll take the blues over the church any day. His singing pierces the veil, and we witness a litany of musicians joining the space from the past, present, and future: an Afrofuturist rock guitarist, hip hop DJs, breakers, twerkers, a ballerina, a Zaouli dancer, and Beijing opera performers, among others. Weaving in and out of Sammie’s blues, the sounds of each of these musicians layer and feed back into the mix to create a densely ecstatic sequence. This is the community healing piece of the voiceover thesis. The performers joining from far-flung places and times connect to an ancestral lineage of creative self-determination that runs through the patrons of the juke joint (Bo and Grace—played by Yao and Li Jun Li, respectively—are Chinese shop owners helping out at the juke joint and the presumed source of the Beijing opera performers).
Sinners’s musical conjuring isn’t an academic article, but it does have some musicological points to make. Audiences encounter musical styles uprooted from specific times and places, all mingling around this blues moment in 1932 Clarksdale. Coogler structures the scene by stacking out-of-time sound and movement, emphasizing the potency of a blues epistemology while also acknowledging that the blues’s power is situational. In its time—post-Reconstruction and Jim Crow—the blues could call in and draw on the fullness of diasporic music-making and world-mapping. But at other times, and in other places—say, a 2025 music venue—the blues is less likely to ignite such a moment as it is to show up as a participant, arriving as one of many in the musical ancestry to support the veil-piercers of the day. This phenomenon is the “changing same” of Black music, as Amiri Baraka put it in Blues People: “consistent attitudes with changed contexts” that explain why the sound changes over time (153). In Sinners, the immediate context is a community of Mississippi sharecroppers who seek healing, and the blues widens the frame so that the juke joint revelers can connect to and draw strength from a broader, deeper community beyond the edges of their material world.
As “I Lied to You” mingles with sounds past and future, the camera moves through the juke in a counterclockwise motion, grounding the scene further in diasporic ancestral practices. In Slave Culture (1987), Sterling Stuckey traces elements of Bakongo burial ceremonies throughout the New World, focusing especially on the ring shout, a sacred ceremony practiced by enslaved people in the United States involving a shuffling circular dance accompanied by song. Consistent across these traditions is counterclockwise movement:
Wherever in Africa the counterclockwise dance ceremony was performed—it is called the ring shout in North America—the dancing and singing were directed to the ancestors and gods, the tempo of the circle quickening during the course of movement. The ring in which the Africans danced and sang is the key to understanding the means by which they achieved oneness in America (12).
The counterclockwise circulation rehearses the life cycle, with the sun rising in the east (birth) and setting in the west (death), only to rise again (gesturing toward the connected nature of all life).
Stuckey draws on Robert Farris Thompson to note that special emphasis on counterclockwise motion would happen in Bakongo rituals that superimposed a cross on the circular movement, where the horizontal line represented the division between the living (above) and the dead (below). Here is the dividing line of Sinners, then: an ancestral ceremony with a crossroads superimposed on it, a blues invocation where the audience is propelled counterclockwise through the circle of juke joint dancers, where the dead and not yet alive join in the festivities.
The theme of lineage and ancestry courses through Coogler’s work. On the personal level, this may play out as a boxer sparring with his late father’s legacy. On a larger scale, Coogler often traverses the land of the Great Migration and the sea of the Middle Passage, tying back together the threads left dangling by the terrorisms of the transatlantic slave trade and Jim Crow. For a people whose lineage was savagely untethered by their ancestors’ enslavers, the power of a blues epistemology comes from its ability to tap into traditions and rituals that couldn’t be fully severed, restoring the “oneness” of those engaged in the dance and fueling their ability to imagine and create a path to freedom.
There is the other part of the voiceover’s thesis statement, though. When you pierce the veil, evil seeks to charge through. As the “I Lied to You” sequence hits peak intensity, Coogler treats movie audiences to another visual effect that the blues performers cannot see but feel; the juke joint appears to spontaneously combust and its roof is on fire (the roof, the roof. . .). Coogler metaphorically lets the motherfucker burn, down to the concrete foundation supporting the people as they continue to dance. At the edge of the dusty parking lot, the movie’s villain—an Irish vampire named Remmick—watches lustily while flanked by his latest converts. He wants Sammie; particularly what Sammie knows how to do.
Because Remmick hive-minds with whomever he turns into a vampire, taking on their memories and abilities, if he can get at Sammie, he’ll be able to pierce the veil, too, and commune once again with his long lost ancestors. We could read Remmick’s drive as an allegory about cultural appropriation, a white man who wants to steal the blues, and certainly there’s an element of that at play. But the “Killmonger was right” corollary of Coogler films suggests that villains are often more complex than they may at first seem. In Sinners, there’s a mob of Klansmen that function as the more straightforward baddies, but Coogler isn’t interested in giving them much screen time. Yet he lingers with Remmick just as he did with Killmonger and Namor in his two Black Panther installments. In each of these cases, Coogler explores different experiences of what it’s like when the boot of Empire is on your neck. Remmick, coming from Britain’s first colony, speaks of his home being taken and of religion being forced on him. He seems to hold genuine disdain for the Klan and notes that he’s happy to turn them all to prey, not because he wants what they have but because they deserve a gruesome death. He plays and dances to the music of his ancestors with care and devotion. And he argues that what he has to offer—community with his coven, the power to overtake the plantation class, eternal life—is better than what Smoke, Stack, Sammie, and the rest of the juke joint patrons currently have.
No one living trusts Remmick—in fact, Annie (Mosaku), the heart, brain, and wisdom of the movie, specifically distrusts him even before he reveals his true vampiric nature. And Coogler doesn’t position Remmick to be perceived as “good” in any sense of the word, except at playing that banjo. But, like Killmonger and Namor, Remmick gets to be right about some things. It appears in flickers of concession on characters’ faces when Remmick tells them they live in a place where they’ll always have to fight to even try to be truly free. It appears again when the juke joint protectors melt a bit during Remmick & Co’s performance of “Pick Poor Robin Clean,” a glimmer of a thought of “wait, should we let them come inside and play this absolute bop??” (for detailed historical context for this song see Daphne Brooks’s “See My Face on the Other Side” [2017]). Coogler’s villains ultimately suffer defeat, but before they do, he makes sure audiences glimpse how they’ve suffered under Empire, offering an understanding of their destructive actions as born of unhealed generational trauma.
Piercing the veil is tricky work. Dangerous work. In The Long Emancipation (2021), Rinaldo Walcott notes that “much of what we have come to call Black culture is a mode of living life within, against, and beyond plantation logics” (20), not only a rejection of logics of oppression but also a practice of creating and nurturing something else. To set about finding knowledge and being, as Sylvia Wynter puts it, “completely outside our present conception of what it is to be human” is to set off into the not-fully-known, where one may encounter a variety of ideas and beings who won’t ultimately lead you to freedom but who may offer you something a little better than what you’ve got (Wynter, 2000 interview with David Scott, 136). Walcott calls this the difference between emancipation and actual freedom. While emancipation is often mistaken for freedom, Walcott argues that “postemancipation acts of Black life have been consistently interdicted, thereby preempting and often violently preventing Black life from authorizing its own desires for bodily autonomy” (105), preventing Black life from being free.
In Sinners, Coogler shows us the way the blues could clear space for finding freedom, but none of the characters in the movie make it all the way there. It’s a movie situated in the long emancipation, where an imposed religion calls the blues the devil’s music, where plantation sharecropping and the Klan violently forestall Black freedom (but sometimes get what’s coming to them), and where various vampires carrying their own intergenerational trauma try to seduce Black people into accepting a different flavor of emancipation in place of the freedom the blues leads them toward. The map to freedom may not sound like the blues anymore, but Sinners reminds us the work isn’t done.
—
Featured images: Screen Capture by SO!: Sammie’s right hand clutching broken guitar neck, black cross in the background against white wall [2:10]
—
Justin Burton is a Professor of Music at Rider University, teaching primarily in the Music Production degree as well as in the Gender & Sexuality Studies program, and author of Posthuman Rap (Oxford, 2017) and co-editor of the Oxford Handbook of Hip Hop Music (Oxford, 2018).
—

REWIND! . . .If you liked this post, you may also dig:
They Can Hear Us: Surveillance and Race in “A Quiet Place”–Justin Burton
Can’t Nobody Tell Me Nothin: Respectability and The Produced Voice in Lil Nas X’s “Old Town Road”–Justin Burton
SO! Amplifies: The Blues and Jazz Dance Book Club–Chelsea Adams
“Music More Ancient than Words”: W.E.B. Du Bois’s Theories on Africana Aurality — Aaron Carter-Ényì
Music Meant to Make You Move: Considering the Aural Kinesthetic–Imani Kai Johnson
Black Mourning, Black Movement(s): Savion Glover’s Dance for Amiri Baraka

I don’t worry about the look of it so much. Choreography comes later, when I’m putting together a piece. I’m into the sound; for me, when I’m hittin’, layin’ it down, it’s all about the sound. –Savion Glover, My Life in Tap
It has been a little over a year since Amiri Baraka passed, and still I hear the echoes of his presence. I am especially attentive to the ways his work has been carried on by those involved in recent black uprisings in Ferguson, New York City, and Baltimore. Powerful political poetics that have emerged from these events include work by Danez Smith, Claudia Rankine and the many contributors to blackpoetsspeakouttumblr.com.
And yet, part of what I’ve witnessed in the streets, actual physical spaces of public protest against police violence and systemic racial oppression, is an example of what Thomas DeFrantz has termed “corporeal orature,” or the ability of bodies to resonate throughout public space and shift political discourse. In these moments, the body talk of protesters is not simply the sound of clattering feet through city streets, but a commitment to the ways in which physical gestures can speak truth to power. I am especially interested in connecting Baraka’s legacy to the larger conversation about the aural kinesthetic that Imani Kai Johnson has proposed, and in teasing out the various dimensions and potentials embedded in that category.
Dance at Ferguson Protests, 2014, Image by Shawn Semmler
For me, Savion Glover exemplified the lingering sound of Baraka’s spirit in his tap dance at his memorial service. Whenever I listen to the recording—which still brings tears to my eyes—I am reminded of the abundant sense of joy, sadness, and love that characterized Baraka’s service. Listening to Glover’s dance is an aural kinesthetic experience, like watching a comet pass across the night’s sky. I am reminded, too, of the way I clamored to record that moment, to keep a piece of the poet alive on my iPhone even after his public passing. And indeed, that performative sound of feet tapping, that measured excess of the body produced through movement, has kept Baraka alive for me; like his groundbreaking work, it is powerfully resistant to the proper rubrics of any one discipline except, perhaps for the study of sound itself.
So, this post then, is about tap dance and its ability to sound out Baraka’s name and life. But in a larger context, the intricate vibrations of Glover’s performance facilitate a deeper understanding of the relationship between sound and mourning, and a kind of mourning that is particularly African American, that is to say, American. It is a mourning that exists beyond the word, written text, or image and a sound practice that enables the bereaved to make a joyful noise and a mournful one at the very same time. So I ask, how do you write a eulogy with the body? How do you perform an embodied love? What does Black love and a reverence for Black life sound like? Sometimes, the answer is tap.
Audio Clip of Savion Glover’s Dance at Amiri Baraka’s Funeral, 18 Jan 2014
The dance explodes on stage like a burst of light. It begins with something approximating a drum roll – and then hard slow taps, hammering away like someone at a typewriter, I imagine, or a train gaining steam.
It is coming.
Slow, insistent and strong, with a little riff now and then, a little picking up of speed here and there. It is coming on louder now, that explosive thing, the tension you are noticing. He is doing the thing. And then there is that skillful, smooth, strong tap. Glover is at work, y’all.
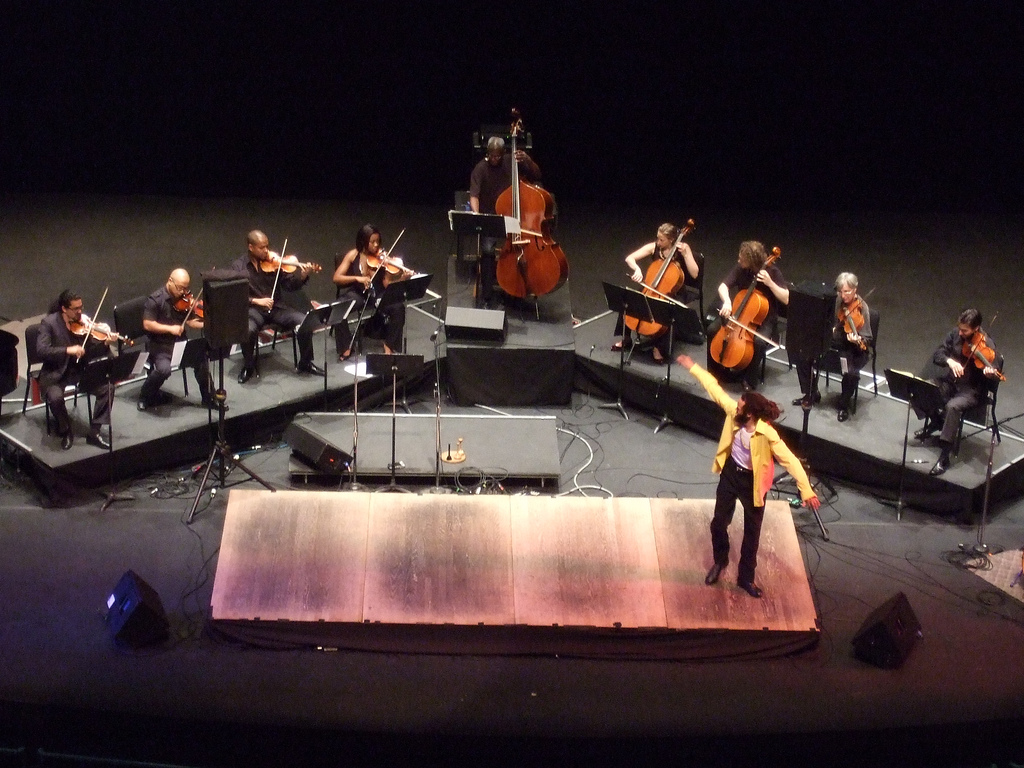

Savion Glover at Work, Image by Flickr Users Raquel and Soren
As a tribute to Baraka, Glover’s dance bears numerous stylistic implications. Among them, I understand the rhythm of Glover’s tap as the rhythm of writing, an aesthetic that complicates the way his dance can be understood as a manifestation of the black vernacular. Sketching out the early connections between her son’s artistry and the percussive taps of the keyboard, Yvette Glover says. “‘I was working for a judge, as an assistant, when I was pregnant with Savion…And when I would type, and the carriage would automatically return, he’d walk, he’d follow it, in my stomach. You could see him move” (39). He does it still. In the audio clip, Glover’s footwork evokes the dexterity of Baraka’s language, all the while telling a story of its own.

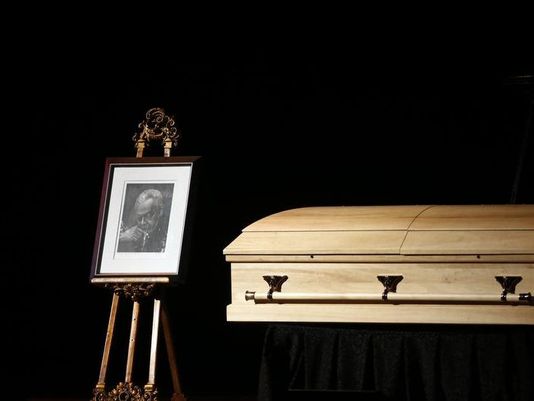
Savion Glover’s Shoes, Sadler’s Wells, 2007, Image by Tristram Kenton
But what about the intensity of the dance, its crescendo toward the end of the service, a flurry of percussive steps beside Baraka’s coffin? Baraka himself reminds us this particular musicality is so necessary here. In his discussion of “Afro-Christian Music and Religion” in Blues People, Baraka notes that in Black diasporic religious services, “the spirit will not descend without a song” (41). Glover’s dance takes place at a moment in the service when emotion exceeds the power of language, but not sound. He uses his body as an instrument of sound in its fullest sense. His performance is a choreography of embodied sound: full-on and at-once body poetry, mourning and tribute.
Elucidating the use of his body as an instrument of sound, Glover declares:
It’s like my feet are the drums and my shoes are the sticks[…]My left heel is stronger, for some reason, than my right; it’s my bass drum. My right heel is like the floor tom-tom. I can get a snare out of my right toe, a whip sound, not putting it down on the floor hard, but kind of whipping the floor with it. It get the sounds of a top tom-tom from the balls of my feet. The hi-hat is a sneaky one. I do it with a slight toe lift, either foot, so like a drummer, I can slip it in there anytime. And if I want cymbals, crash crash, that’s landing flat, both feet, full strength on the floor, full weight on both feet. That’s the cymbals. So I’ve got a whole drum set down there (19).
Combining his body’s drumbeat with the tic of Baraka’s keystrokes, Glover embeds the pattern of Baraka’s life in this tap dance, communicating it with the kind of deep and reverential love you are taught to have for your elders when you are young, appropriate and deep.
 But as powerful as his body-poetry is, Glover’s silences are also key. In those inaudible spaces, Glover spreads out his arms, offering up the dance in a gesture of expansive love; the immensity of the silent gestures mirroring the immensity of Baraka’s life. He holds it out as a gift towards the audience, bows his head, too.
But as powerful as his body-poetry is, Glover’s silences are also key. In those inaudible spaces, Glover spreads out his arms, offering up the dance in a gesture of expansive love; the immensity of the silent gestures mirroring the immensity of Baraka’s life. He holds it out as a gift towards the audience, bows his head, too.
In moments of sound and silence, the audience calls out to Glover the way they would a preacher. At these moments, the dance becomes a call and response akin to the way Baraka’s life’s work was a call and response. A call to respond. A call to take what was given to you and make it mean. Listeners to the dance are called up out of themselves. We are changed by the dance and by the listening.
Tap tap tap.
Glover’s performance shows us how his specific blend of African and European dance traditions exists in a spiritual and artistic dimension. There is a religious explanation for this, too. In African Dance, Kariamu Welsh-Asante explains the function of the African funeral dance in definite terms:
All African dances can be used for transcendence and transformational purposes. Transcendence is the term usually associated with possession and trance. Dance is the conduit for transcendent activities. Dance enables an initiate or practitioner to progress or travel through several altered states, thereby achieving communication with an ancestor to deity and receiving valuable information that he/she can relate back to the community. Repetition is key to this process as it guides the initiates, or dancers, through the process of the ceremony. The more a movement is repeated, the greater the level of intensity and the closer a dancer gets to the designated deity or ancestor. Transformation means to change from one state, or phase, to another (16).
Glover certainly brought us close to Baraka. And yet, I would go a step further to suggest that this is, above all, blues dance. As such, it reveals continuing relevance of social dance and movement to Baraka’s political legacy. Baraka and Glover work directs us towards the propulsive nature of black social/percussive dance forms. These sonic gestures clarify the ways black life matters, impacts the public sphere and policy. The politicized nature of Black Arts Movement performances and the performative elements of contemporary Black protest are still linked through sound. Politicized Black aesthetics continue to offer us multiple opportunities to witness the convergence of sound and movement. Ras Baraka, affirms this in his own eulogy for his father:
Have you seen black fire it burns deep it never goes out you can try and extinguish it but it never goes out it never goes out it never goes out only up or out as in broad as in multiply as in blues black base of the fire dancing flickering at times but never all the way gone dancing flickering at times but never all the way gone…
The power of the dance, of the Black Movement to move is still with us.
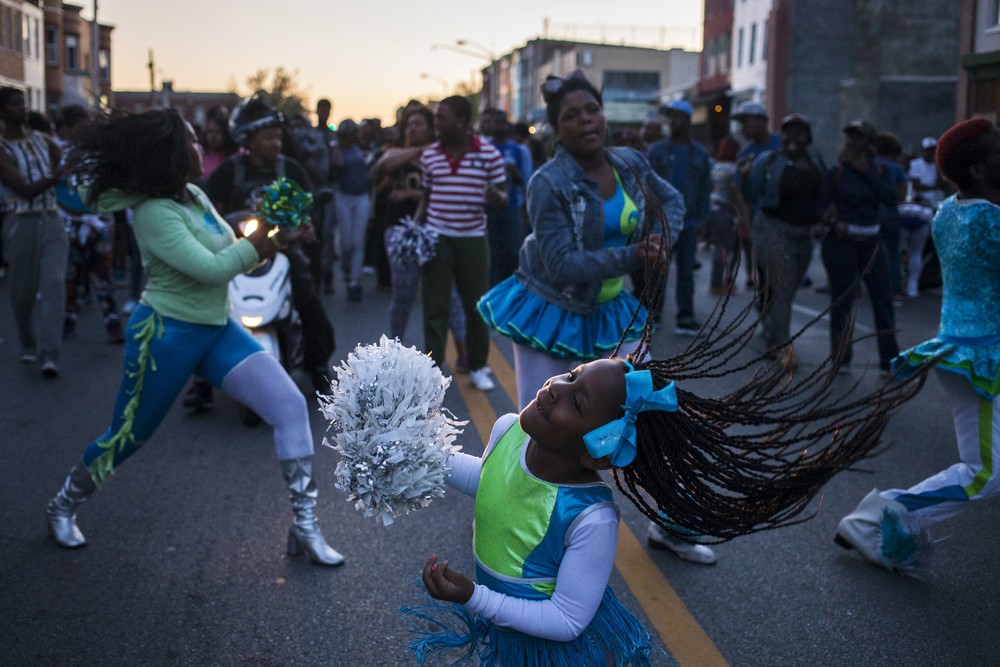
Protestors dance to a community band, Baltimore, MD, 28 April 2015, Photo by Adrees Latif/Reuters
—
Featured Image, Screen Capture of Savion Glover dancing by JS
—
Kristin Moriah is the editor of Black Writers and the Left (Cambridge Scholars Press, 2013) and the co-editor of Adrienne Rich: Teaching at CUNY, 1968-1974 (Lost & Found: The CUNY Poetics Document Initiative, 2014). Her critical work can be found in Callaloo, Theater Journal, TDR and Understanding Blackness Through Performance (Palgrave Macmillan, 2013). Moriah is completing a dissertation on African American literature and performance in transnational contexts at the CUNY Graduate Center. Her research has been funded through grants from the Social Science and Humanities Council of Canada, the Freie Universität Berlin and the Graduate Center’s Advanced Research Collaborative. She is a 2014-15 @IRADAC_GC Archival Dissertation Fellow and spring 2015 Scholar-in-Residence at the NYPL Schomburg Center for Research in Black Culture. Sometimes she tweets via @moriahgirl.
—
 REWIND! . . .If you liked this post, you may also dig:
REWIND! . . .If you liked this post, you may also dig:
“HOW YOU SOUND??”: The Poet’s Voice, Aura, and the Challenge of Listening to Poetry-John Hyland
Pretty, Fast, and Loud: The Audible Ali–Tara Betts
The Sounds of Anti-Anti-Essentialism: Listening to Black Consciousness in the Classroom-Carter Mathes
ISSN 2333-0309
Translate
Recent Posts
- The Absurdity and Authoritarianism of Now: My Chemical Romance’s The Black Parade Resonates Queerly, Anew
- SO! Reads: Alexis McGee’s From Blues To Beyoncé: A Century of Black Women’s Generational Sonic Rhetorics
- SO! Reads: Justin Eckstein’s Sound Tactics: Auditory Power in Political Protests
- Impaulsive: Bro-casting Trump, Part I
- Top Ten Sounding Out! Posts of 2025!
Archives
Categories
Search for topics. . .
Looking for a Specific Post or Author?
Click here for the SOUNDING OUT INDEX. . .all posts and podcasts since 2009, scrollable by author, date, and title. Updated every 5 minutes.


















Recent Comments