Music Video as Process: “Revitalize” by T-Rhyme

What is a music video, anyway? Historically dismissed by film theorists as cinematically flawed or by the public as mere promotional snippets, music videos didn’t used to get the credit they deserve as a serious artistic medium. In the 1990s, Carol Vernallis challenged both notions, suggesting that they are actually a unique genre where music and visuals aren’t just paired—they communicate deeply with each other. Since then, scholars have taken diverse approaches to try to make sense of how film theory is applicable to these delicious nuggets of musical storytelling. For example, Phoebe Macrossan argues that Beyoncé’s Lemonade is a signal example of “film worlding,” indicating how the artist uses video to create her own intimate and all-encompassing environment. Additionally, Olu Jenzen and colleagues have found that political remix videos use recombinations of existing sounds and images to make rhetorical points that can challenge mainstream media reporting in real time. According to Stan Hawkins and Tore Størvold, from the perspectives of musicology or music theory, perhaps it is the video that amplifies the song’s harmonic structure or musical form, as suggested by their analysis of Justin Timberlake’s “Man of the Woods.”
Through skillful harmonic analysis or rhetorical analysis or cataloging of film techniques, scholars and critics now take music videos seriously. Yet, across interdisciplinary research approaches to music videos, what is largely taken for granted is that the music video is an object, a work to which various theories can be applied. What if we extend these approaches further and consider the music video not just as an object of analysis to be dissected, but as a representation of a creative process that entwines sound and vision in innovative ways to connect people and forge relationships? Such an analysis is especially possible when listening to independent creators who take an active role in conceptualizing, shooting, and editing their videos. By shifting our perspective to view the music video as documenting an ongoing creative and relational journey rather than solely as an object for analysis, we open up new possibilities for understanding the deeper significance of these works. Music videos can serve not just as vehicles for artistic expression, but as catalysts for strengthening bonds, preserving cultural knowledge, and fostering a sense of pride and resilience within communities.
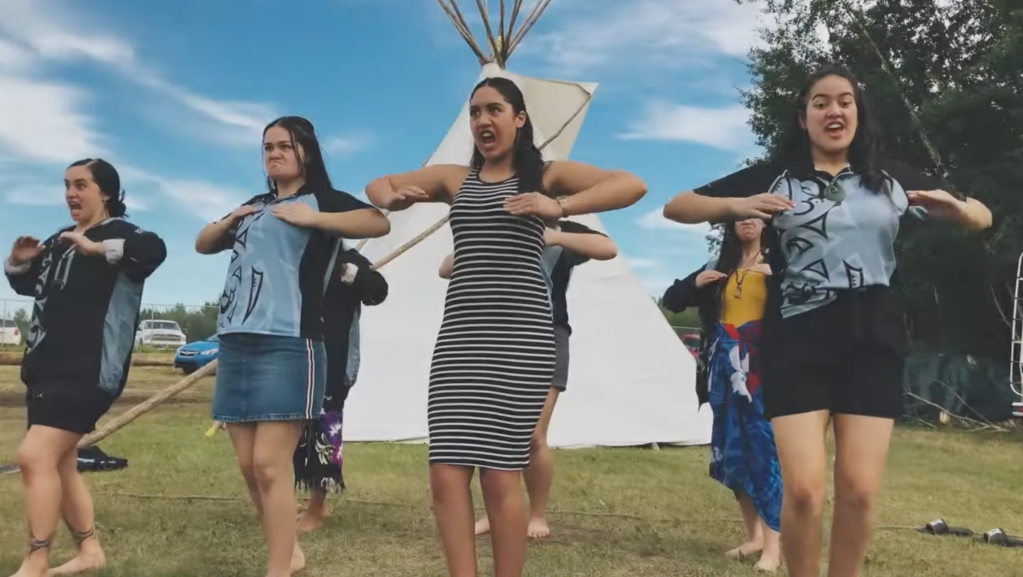
Music Video as Process
In 2023, I co-organized a series of performances for Native Jam Night at UC Riverside, an annual music showcase featuring Indigenous artists from California and across Turtle Island. One way my colleagues and I honed in on guest artists was by asking students to listen to several playlists and recommend the music that spoke to them. The song “Revitalize” by T-Rhyme came up as a favorite. T-Rhyme has released music that tells personal stories and responds to contemporary social realities. At times, this music responds to her lived experience as a woman with Nehiyaw and Denesuline roots.
The music video for “Revitalize” is not only a popular extension of the song’s appeal, but an audiovisual series of connections and interactions. Paying attention to it in this way shows what can emerge from one kind of nontraditional listening posture, this one inspired by my conversations with T-Rhyme and also grounded in the way I have been opening my ears to her music. I first got to know T-Rhyme in-person when I invited her and MC Eekwol to perform as part of the Show & Prove hip hop event in 2018. We stayed in touch over the next several years.

As part of T-Rhyme’s return visit to California in 2023, we got to drive around and talk music business, have dinner with Native directors and actors as part of an Indigenous Storytelling event, go shopping, and get tacos at one of my favorite hole-in-the-wall spots. When it came time to make plans around the release for my book Sonic Sovereignty: Hip Hop, Indigeneity, and Shifting Popular Music Mainstreams, I knew it made sense to keep building on dialogues with musicians. Instead of just talking about myself, or even ideas that were already published, I wanted to keep the conversation going, continue listening, and find ways to share what I was hearing with more audiences. When I talked with T-Rhyme in the winter and spring of this year, then, it was to hear more about her creative process beyond any single project, to talk about what I was hearing and how I was listening, and to make space for that meaning making that almost approaches a musical flow that can bubble up out of a good dialogue.
Revitalization
A years-long process led up to “Revitalize,” T-Rhyme told me, and there are goals for the song that stretch beyond the moment of recording. To make the video, T-Rhyme went out to ceremonial grounds with her family and her photographer cousin Tennille Campbell’s family, spending time out with buffalo so Campbell could record. Looking back, she went through over a year and a half of her recordings of family and friends to select moments of daily life to interweave with special moments of celebration.
To convey the importance of land with viewers, the rapper worked with her brother, who shared his drone landscape footage that he recorded where he lives in northern Saskatchewan. She filmed other pieces at a powwow in Treaty Six territory in Alberta, finding inspiration from old friends she reconnected with for the occasion, as well as other Indigenous musicians and dancers she met while looking to connect there. T-Rhyme delivers the chorus and rapped verses over a beat by Doc Blaze, while collaborators in the music video mouth key words, notably “revitalize,” to her audio. Each aspect of the video was made with family or friends, and together they encompass years of work and hopes for the future.

From her past work, T-Rhyme recalled that shooting a music video can be stressful and involve intense time pressure. Instead, she told me, “I wanted none of those vibes to be involved with this project. I wanted the whole entire thing to be good vibes. And positive because part of our healing is through laughter and joking and being together as family.”
So, what is “revitalization” in the context of making music with family and friends? For T-Rhyme, “These are people I trust, I grew with, I evolved with, I changed with. All these people make me feel good and that I’m proud of, that I want to show off.” Paying attention to how musicians choose to tell their stories and further relationships with others is part of recognizing their sovereignty through sound. Sonic sovereignty is an active process.
The notion of “sonic sovereignty” builds from Jolene Rickard’s determination in “Diversifying Sovereignty and the Reception of Indigenous Art,” that “the idea of our art serving Indigenous communities reinforced my understanding that sovereignty is more than a legal concept”(82), and Tewa and Dine scholar-filmmaker Beverly Singer’s working through what she refers to as “cultural sovereignty,” in Wiping the War Paint off the Lens: Native American Film and Video, “which involves trusting in the older ways and adapting them to our lives in the present”(2). It’s meaningful to move into celebration together, as T-Rhyme explains: “Part of revitalization, especially when it comes to our healing as Native people, is we need to remember love. We don’t need to be in survival mode all the time.”
Intergenerational Teaching
Generations of T-Rhyme’s family stretch throughout the video for “Revitalize”. In the first verse, the musician’s mother stands in a bright red ribbon skirt at the edge of the river, near a photo frame.Then this photo of the rapper’s grandparents smiles out from the rocky shores of a river. A kid in sneakers runs nimbly over these same rocks, generations converging at the water. When T-Rhyme raps in the chorus, “raise your fists high in the air right now,” viewers see her mother raising her fist, the river greenery behind her, then proudly holding the picture of her own parents.

Music videos are often associated with youth culture, especially in a North American context. Yet in process and in content, this music video showcases intergenerational teaching and learning, with the involvement of elders, parents, children, and friends, connecting embodied knowledge across generations. Men and boys teaching intergenerationally feature onscreen, notably a father and son in regalia and an entrepreneur who runs Cree Coffee Company. Community leaders and scholars across Turtle Island share stories of diverse Indigenous masculinities, highlighting the kinds of teaching, leadership, and care that men, boys, and masculine people share from the present into the future. T-Rhyme reflected, “we have men out here who are trying to be warriors still, in their own way, whether they’re dancing powwow, whether they’re running their own business, and just being present fathers.”

T-Rhyme described that over the years, her relationship with her mother has changed. And yet, they have an ongoing push and pull between being serious and being playful together. With her mom, she says, “laughter and joking is our medicine.” She laughed as she recalled that for filming, “we’d be trying to have a serious moment and I’d say ‘okay mom, stand in the water’ and she’d say, ‘okay, like this.’ ‘Yeah, that looks good. Rest your face. You look real Kookum right now.’ Just cracking jokes at her.” T-Rhyme uses a word for grandmother to kid with her mom.
The process of writing the lyrics, too, involved reflecting on the relationship she has had with her mom across the past, present, and future. T-Rhyme raps, “My mother is sacred, she’s a survivor for real, though it’s taken her and I so many decades to heal.” This comes from what the rapper describes as a way to highlight how her mom is a “survivor and somebody that I respect and ultimately, enabled and motivated me to do my own healing too.”
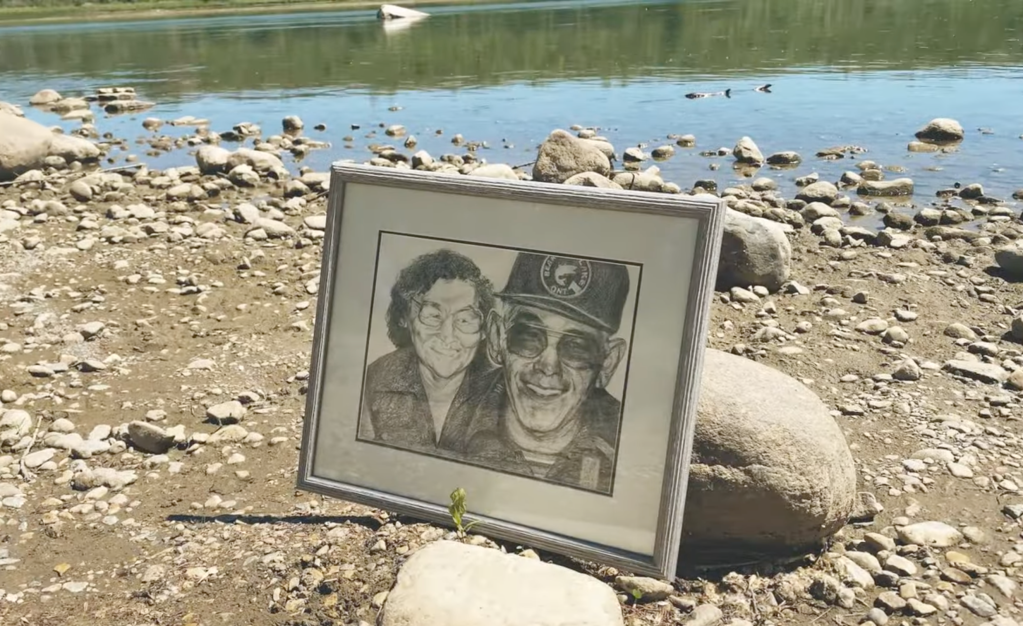

In the context of intergenerational healing, T-Rhyme’s music video, which involves multiple generations of her family, embodies Indigenous survivance –the active transition from mere survival to resilience—in the face of historical and ongoing colonial violence. T-Rhyme brought her grandparents into the filming through their photograph, and their living memory. She explained, “Without them, I wouldn’t be here, my kids wouldn’t be here and my mom wouldn’t be here. Speaking of revitalization, they were the ones that were the front lines of maintaining our culture through a literal, cultural genocide in our communities.” Since “they really had to do their part in maintaining our culture enough to survive through residential school,” she recalls, “It was important to me to acknowledge them as survivors.”
T-Rhyme included her daughter in ‘Revitalize,” as well as in other music videos, notably the title track on “For Women By Women.” She explains, “I always want to feature her because she’s such a powerhouse.” T-Rhyme’s visual narrative brings in a photo of her daughter dancing at one of her shows, and the rapper has made music videos with her son as well.
When they were all getting stir-crazy from COVID shutdowns, T-Rhyme and her kids made the video “Trap’d,” for which the rapper helped then-12-year-old Joaquem act as videographer. Teaching her son and daughter and giving them space to make their own art, she calls her kids her “heroes,” explaining, “I just love including them where I can.”
The Story Beyond the Video
Watching and listening to the work of independent artists, such as T-Rhyme, complements existing writing on music video that comments on mainstream names like Madonna and Beyoncé. Furthermore, approaching music videos as processes through which relationships are built and furthered rather than solely as objects for analysis invites other forms of listening, especially modes that acknowledge the network of people whose interactions create the sounds that vibrate audience members’ eardrums.

The people who click play on the finished music video make up what is traditionally understood as its audience. By witnessing relationships behind musical choices, we can recognize that there is another group, too, that the video is for: media professionals, family members, and community participants who work together to create it. Making a piece as complicated as a music video can become an occasion for all of these actors to further and strengthen relationships: filming may offer the excuse everyone needed to visit an important location together, or storyboarding brings people in the room together who hadn’t been able to find the time, or the song provides a vehicle for talking about a topic that would otherwise be repeatedly put on the shelf for another day. Listening for process in this way can encourage audience members who view the video, too, to use this communally crafted artistic labor as an invitation for connection.
“Revitalize” particularly serves as an example of how making a music video can involve collaboration with family and friends over an extended period, encompassing years of documentation and strengthening relationships. In addition to sharing a past and inspiring interaction for the making of the video, the song carries hopes for a future. As T-Rhyme says, “I want “Revitalize” to be a catalyst for healing and pride.” Paying attention to how musicians tell their stories and build relationships through music videos is part of recognizing their sovereignty and cultural continuity through sound and visuals.
—
Featured Image: Still from music video for “Revitalize” by T-Rhyme (2021)
—
Dr. Liz Przybylski (pronunciation) is an ethnomusicologist and pop music scholar working in hip hop and electronic music in the US and Canada. Dr. Przybylski is an Associate Professor of Ethnomusicology at the University of California, Riverside. A graduate of Bard College (BA) and Northwestern University (MA, PhD), Liz’s research appears in Ethnomusicology, Journal of Borderlands Studies, and IASPM Journal, among others. Dr. Przybylski has presented research nationally and internationally, including at the Society for Ethnomusicology, Native American and Indigenous Studies Association, Feminist Theory and Music, International Association for the Study of Popular Music, and International Council for Traditional Music World Conferences. Recent and forthcoming publications analyze how the sampling of heritage music in Indigenous hip hop contributes to dialogues about cultural change in urban areas. Dr. Przybylski has also published on popular music pedagogy. Liz was awarded a National Endowment for the Humanities Faculty Fellowship and a Fulbright Fellowship. Liz’s most recent book Sonic Sovereignty: Hip Hop, Indigeneity, and Shifting Popular Music Mainstreams was published in July 2023 (NYU Press). This follows Liz’s first book, Hybrid Ethnography: Online, Offline, and In Between (SAGE Publications, 2020) which develops an innovative model of hybrid on- and off-line ethnography for the analysis of expressive culture. In addition to university teaching, Liz has taught adult and pre-college learners at the American Indian Center in Chicago and the Concordia Language Villages program of Concordia College in Bemidji. On the radio, Liz hosted the world music show “Continental Drift” on WNUR in Chicago and has conducted interviews with musicians for programs including “At The Edge of Canada: Indigenous Research” on CJUM in Winnipeg. Dr. Przybylski served as the Media Reviews Editor for the journal American Music, the President of the Society for Ethnomusicology, Southern California and Hawaii Chapter, and on the Society for Ethnomusicology Council.
—

—
REWIND! . . .If you liked this post, you may also dig:
Sounding Out! Podcast #40: Linguicide, Indigenous Community and the Search for Lost Sounds–Marcella Ernest
The “Tribal Drum” of Radio: Gathering Together the Archive of American Indian Radio–Josh Garrett Davis
Sonic Connections: Listening for Indigenous Landscapes in Kent Mackenzie’s The Exiles–Laura Sachiko Fugikawa
Unsettling the World Soundscape Project: Soundscapes of Canada and the Politics of Self-Recognition–Mitchell Akiyama
Becoming Sound: Tubitsinakukuru from Mt. Scott to Standing Rock–Dustin Tahmahkera
EPISODE 60: Standing Rock, Protest, Sound and Power–Marcella Ernest
A Tribe Called Red Remixes Sonic Stereotypes–Christina Giancona
I’m on my New York s**t”: Jean Grae’s Sonic Claims on the City––Liana Silva
How not to listen to Lemonade: music criticism and epistemic violence–Robin James
Listening to Digitized “Ratatas” or “No Sabo Kids”

This series listens to the political, gendered, queer(ed), racial engagements and class entanglements involved in proclaiming out loud: La-TIN-x. ChI-ca-NA. La-TI-ne. ChI-ca-n-@. Xi-can-x. Funded by an Andrew W. Mellon Foundation as part of the Crossing Latinidades Humanities Research Initiative, the Latinx Sound Cultures Studies Working Group critically considers the role of sound and listening in our formation as political subjects. Through both a comparative and cross-regional lens, we invite Latinx Sound Scholars to join us as we dialogue about our place within the larger fields of Chicanx/Latinx Studies and Sound Studies. We are delighted to publish our initial musings with Sounding Out!, a forum that has long prioritized sound from a queered, racial, working-class and “always-from-below” epistemological standpoint. —Ed. Dolores Inés Casillas
—
This post is co-authored by Sara Veronica Hinojos and Eliana Buenrostro
Cardi B eloquently reminds us that our español, as US Latinxs, might seem “muy ratata;” an apt phrase, heard lyrically within her music, used here to characterize inventive, communicative Spanglish word play. Yet, the proliferation of hashtags used to shame and silence second and later generations of Latinx kids runs counter to Cardi B’s ratata blessings.
The hashtags #nosabokid #nosabokids #nosabokidsbelike #nosabokidsorry #iamanosabokid represents a collective acknowledgment of Gloria Anzaldúa’s “linguistic terrorism.” Featured on NBC News, Locatora Radio, the Los Angeles Times and, surely, referenced within familial discussions, #nosabo has brought, once again, to the fore the coupling and, we fiercely argue, the need to decouple language (“proficiency”) from that of Latinx identities. The phrase “no sabo” – a non-standard Spanish conjugation of the phrase “no sé” for “I don’t know” – has become a stand-in as both a linguistic (bad) sign of Americanization and/or a (good) marker of ethnic, bicultural pride.
Anzaldúa has long warned us that, “[e]ven our own people, other Spanish speakers nos quieren poner candados en la boca [want to put locks on our mouths]” (1999, 76). In many ways, the “no sabo” label silences or “locks” one’s mouth. The institutional attempts to Americanize Spanish-speaking individuals constitute a form of violence that has led to the erosion of Spanish spoken among Mexican and Latino families in the United States. Today, children of immigrants are ridiculed for speaking “broken” Spanish, yet, for decades Mexicans raised in the United States experienced harsh consequences and blatant discrimination for speaking Spanish in public; this racism continues today.
As scholars of Latinx listening, these social media posts can be incredibly frustrating. They remind us of the sad reality that many Latinx people do not know their own history or better yet futures. Anzaldúa would describe the intraethnic linguistic policing as, “peleando con nuestra propia sombra” (fighting with our own shadow) (1999, 76); it’s both unproductive and self-inflicting. Poet Michele Serros describes her experiences being policed in her 1993 poem “Mi Problema”:
Eyebrows raise
My sincerity isn’t good enough
when I request:
“Hable mas despacio por favor.”
My skin is brown
just like theirs,
but now I’m unworthy of the color
‘cause I don’t speak Spanish
the way I should.
Then they laugh and talk about
mi problema
in the language I stumble over [. . .]
–Opening stanza of “Mi Problema” from Chicana Falsa
Applied to speakers (mostly kids) whose Spanish is identified as grammatically wrong or heard with an Anglicized accent, “no sabo” hashtags can encourage people to police each other’s tongues. Social media videos even show parents testing their children’s Spanish. When a child cannot remember or (mis)pronounces a Spanish word, or worse, uses a Spanglish iteration, they are disparagingly called “no sabo kids” (Stransky et al. 2023). Other posts reveal Latinx users’ fear of having and raising a “no sabo kid” or not wanting to date a “no sabo kid.”
Lastly, other posts proudly admit to being a “no sabo kid.” The latest series of “no sabo kids” hashtags are also unapologetic declarations that their language does not define the totality of their being or experiences.
Indeed, speaking Anglicized Spanish as Latinx can surface feelings of embarrassment, disappointment, and mockery from presumed “perfect” Spanish speakers or self-appointed “real” Spanish-English bilinguals. Televised instances of Latin Americans chastising the Spanish spoke of Latinx speakers or the public praise thrown at Ben Affleck for his spoken Spanish in comparison to the public side eyes given to wife, Bronx-raised, Jennifer Lopez are both hyper-mediated instances of #nosabokids.
White people might be praised for learning Spanish – no matter how Anglicized their accent – yet Latinx people whose Spanish is detected as Anglicized, are (racially whitewashed) “no sabo kids” (Urciuoli 2013). And yes, the use of the word “kids” alone infantilizes the speaker as some social media posts point to both children and adults as “no sabo.”
Irrespective of the proficiency in English or Spanish, Latinx individuals share experiences of being corrected in educational settings, at home, or online. The misuse of verb conjugation, such as using “sabo” instead of “sé,” is a developmental challenge encountered even by Spanish-speaking children who are learning solely Spanish. In other words, it is not an exclusive practice among Spanish-English bilingual speakers, despite what social media posts insist. The public discourse that some Latinx social media users are battling is what Jonathan Rosa calls “looking like a language” and, in this case, not “sounding like a race” (Rosa 2019).
Speaking, listening, and living “muy ratata” with inventive modes of Spanish and English in the U.S. is clearly heard as threatening. For instance, knowledge of another language has always challenged monolingual conservative speakers. Bilingual speakers and listeners routinely teach us how to resignify language practices and ultimately, the meaning of being a “no sabo kid.” (Or how Nancy Morales argues about Los Jornaleros del Norte and Radio Ambulante in the ways they offer new forms of belonging by understanding themselves and respecting each other.)
Entrepreneurs with Chicana and Latina feminist identities are modeling refashioned ways of belonging. For example, Los Angeles-based brand Hija de tu Madre created t-shirts and crewneck sweatshirts with the words “no sabo” to counter the ridicule heard and circulated within social media and to loudly claim a racial, linguistic identity that has nothing to do with shame. Similarly, the card game “Yo Sabo,” founded by a first generation college student of Mexican descent, Carlos Torres, looks for ways to improve his Spanish and simultaneously creates another way to connect with immigrant family members. Labels like “no sabo ” that are intended to categorize people in harmful ways are being repurposed to build community.
The podcast Locatora Radio: A Radiophonic Novela released an episode on April 12, 2023, Capítulo 160: No Sabo Kids, detailing historical reasons why Latinx ethnicities have structurally been banned from learning and speaking Spanish. Perhaps most importantly, Locatora Radio shares with listeners lengthy listener-recorded testimonios.
They provide diverse personal reasons for identifying as a “no sabo kid.” One listener, Paula, is a transracial adoptee whose first language was Spanish. However, because of forced family separation and the foster care system in Virginia, she “lost” her Spanish. Paula was enrolled in Spanish language classes throughout her formal schooling and accepts that her reclaiming of culture and language is a lifelong process. The use of verbal testimonios, a format that makes it possible for podcast listeners to listen to fellow listeners, moves away from posts above that wag their digital finger at “no sabo kids” and instead gives them a space to speak for themselves.
The intense personal and communal fear of losing aspects of culture or language makes it difficult to understand how shifts in language practices and accents are important new forms of belonging as Latinx in the U.S. If we cannot accept our own linguistic diversity, how do we expect others to listen to us?
—
Featured Image: A selection of TikTok #nosabo memes from @marlene.ramir, @yospanishofficial, and @saianana
—
Sara Veronica Hinojos is an Assistant Professor of Media Studies at Queens College, CUNY. Her research focuses on representation of Chicanx and Latinx within popular film and television with an emphasis on gender, race, language politics, and humor studies. She is currently working on a book manuscript that investigates the racial function of linguistic “accents” within media, called: GWAT?!: Chicanx Mediated Race, Gender, and “Accents” in the US.
Eliana Buenrostro is a Ph.D. student at the University of California, Riverside in the Department of Ethnic Studies. She received her master’s in Latin American and Latino Studies from the University of Illinois at Chicago. Her research examines the criminalization, immigration, and deportation of Chicanes and Latines through the lens of music and other forms of cultural production. She is a recipient of the Crossing Latinidades Mellon Fellowship.
—
—

REWIND!…If you liked this post, you may also dig:
Ronca Realness: Voices that Sound the Sucia Body—Cloe Gentile Reyes
From Spanish to English to Spanish: How Shakira’s VMA Performance Showcases the New Moment in Latin Music “Crossover”—Petra Rivera-Rideau and Vanessa Díaz
Echoes in Transit: Loudly Waiting at the Paso del Norte Border Region—José Manuel Flores & Dolores Inés Casillas
Xicanacimiento, Life-giving Sonics of Critical Consciousness—Esther Díaz Martín and Kristian E. Vasquez
“Don’t Be Self-Conchas”: Listening to Mexican Styled Phonetics in Popular Culture*–Sara Hinijos and Inés Casillas


















Recent Comments