“In My Life”: Loving Queerly and Singing Across Generations
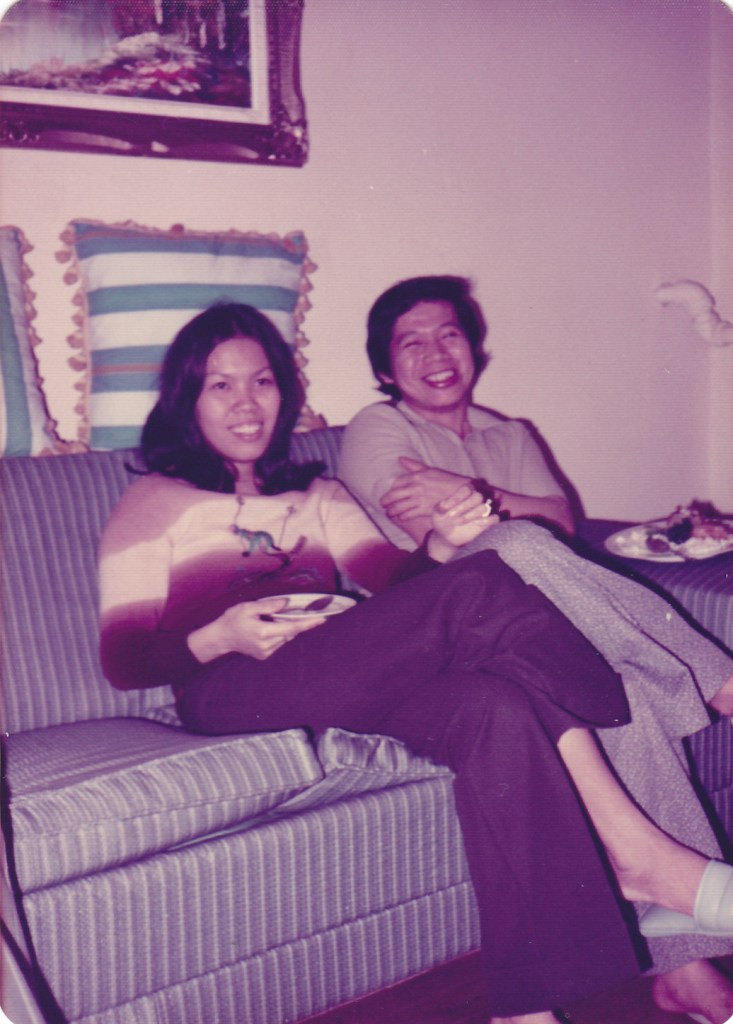

December 1975.
The cold winds staked their claim over Toronto, where my parents had recently arrived from the Philippines. They were underdressed and making their way down Parliament Street. Despite being warned of a shift in temperature, they were not expecting the brutal intensities of Canadian winter. I’m not sure how anyone anticipates the sharp sting of negative temperatures when they are arrivants used to tropical climates. Undeterred, my mother and father headed to a small Filipino grocer, hoping to encounter a semblance of domestic familiarity. Pressed against the biting winds, my mother abruptly stopped, looked at my father and said, “Tumutolo ang sipon” – you have a runny nose. To which my father replied, “Ikaw din” – you do too! They both started laughing and laughed again when they retold me this story 48 years later. When faced with the challenges of migrating to a new and very cold country, they managed to mine humour from a deep well of difficult circumstances. We had been listening to the song “In My Life” by the Beatles (Lennon & McCartney 1965). Something in its expression, melody, and feeling caused my parents to be transported to this small but important moment.
In her conversation with Christine Bacareza Balance, “‘Revolutions in Sound’: Keynote Duet” (2022) Alexandra T. Vazquez writes: “The popular…leaves so much room for engagement with sound artists (musicians without the gallery). None of them need theorists to argue for them, to argue for their mattering because to so many, they already do. How do they instead invite theorists to take part in something alongside them?” (12). I was never a big fan of the Beatles, but regardless of my opinions, they were popular. As a relentlessly oppositional teenager, I was put off by their mass popularity. As Vazquez suggests, despite one’s musical taste, songs are invitations, not scholarly conquests. The memory re-opened by my parents’ connection to “In My Life” was an invitation for me to take stock of the song’s affective and, for them, diasporic trajectories. As Balance (2022) suggests songs request us to “listen long so we hear where another is coming from” (15). For her, “long” describes temporality and commitment. To “listen long” implies that duration and attention are the pretext for empathic relations.
“In My Life” was released in 1965. My mother was fifteen years old when she first heard the song on the radio in a boarding house in Marbel, Philippines. One year later, on July 16, 1966 the Philippine Free Press would announce, “The Beatles Are Coming” (de Manila as cited by Robert Nery in “The Hero Takes a Walk” 2018). At that time, Ferdinand Marcos was the newly elected president of the Philippines, and Imelda Marcos was his First Lady. The Marcoses would later unleash an era of violent dictatorial power and impose Martial Law in 1972, escalating political suppression (Burns 2013). My mother recalls that the band’s first and only appearance in the Philippines was remembered by many less for their two scheduled concerts and more for their “snub” of Imelda. The Beatles were noticeably absent at a lunch reception they were expected to attend with the First Lady at the Presidential Palace. Their absence, attributed to a communication error between the concert promoter and the band’s manager, incited public disapproval and resulted in the sudden disappearance of their security escort and hotel and porter service. Unlike in other cities, the band was refused room service and was forced to carry their own luggage (Nery 2018).
What is striking about this moment is that it breaks from preoccupations with Filipinx desires for assimilation and mimicry of Western imperial projects. In Video Night in Kathmandu and Other Reports from the Not-So-Far East, British travel writer Pico Iyer (1988) famously stated that Filipinx people are the “[m]aster of every American gesture, conversant with every western song…the Filipino plays minstrel to the entire continent (153)” Turning against imperial scripts and the band’s documented disdain of “Mosquito City” and even worse, John Lennon’s comment that a return to the Philippines would require “an H-bomb,” the soured residues of their visit marks a queer rupture in Beatlemania. The public decried that Filipinx people deserved better from the band, capturing what Balance describes in Tropical Renditions: Making Musical Scenes in Filipino America (2016), as “disobedience” in that “disavows a belief in the promises of assimilation” (5). For me, Filipinx non-compliance textures the sonic substance of “In My Life.” While the shadow of the Marcoses cronyism and corruption is an inescapable footnote, it is the defiant voices of hotel employees, dismayed fans, and airport workers that insisted on the “ordinariness” (Wofner & Smeaton, 2003) of the Beatles that holds the song’s queer decibels.
There are places I’ll remember all my life, though some have changed. Some forever, not for better. Some have gone, and some remain.
“In My Life” (Lennon & McCartney 1965).
January 2018.
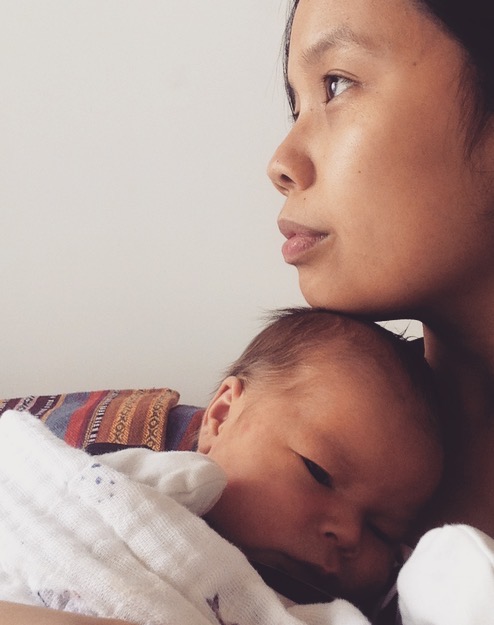
I am sitting on my couch watching a Toronto Raptors game. The television emits light that flickers through a large window that frames a bright winter moon. I am 41 weeks pregnant at this point (feeling similarly shaped and sized as the moon outside). My stubborn queer resistance to the Beatles somehow dissipated during my pregnancy, and the song “In My Life” made its way to me. I would quietly sing the song to my pregnant belly. Then, that January night, I felt a snap inside my body and a rush of water down my legs. I won’t go into much gratuitous detail other than to say that at 12:49 pm the next day, Asa Cy Dyer-Mecija was born at home.
And these memories lose their meaning when I think of love as something new.
“In My Life” (Lennon & McCartney 1965)
Sometimes, I needed to couch the queerness of pregnancy in words that were not mine. The distance between these words and the ones I had yet to find would help to structure my unfolding love for Asa. Here, queerness presented a modality of encounter with uncensored desires. Queerness is often theorized as a utopian impulse; the queerness of my pregnancy jostled both the hopes and fears brought up by the unknown terrain of parenting amidst heteronormativity. For me, “In My Life” is riven by sentimentality and nostalgia, but it also gave melody to a tender relationship with myself and my new role in the world. This was the sonic throughline to my parents, a queer inheritance of tension made from the hopes for kinder contexts amidst the limitations of harsh realities.

December 2022.
I was invited to perform as part of the Queer Songbook Orchestra’s holiday fundraiser. The Queer Songbook Orchestra is a chamber pop ensemble that hosts an annual concert focused on songs and stories about “chosen family and queer joy” (Queer Songbook n.d.). At that time, Asa was four years old. He is a child of the pandemic. He’s a kid with two moms, a present and kind donor, and is dearly loved by his Lolo and Lola, his grandparents, aunts, titas, uncles, cousins, kuya, ate, and his beautiful chosen family. My partner, Hannah, and I sometimes worry about how his world will be affected by reactions to the makeup of our family, but mostly, we know he’ll be sure he’s loved by many.
To me, the song “In My Life” offers a useful sonic response to homophobia. As a baby, after Asa’s baths, I would often wrap him in a towel, and while rocking him back and forth, I would sing these lyrics from the song: “Though I know I’ll never lose affection for people and things that went before, I know I’ll often stop and think about them. In my life, I love you more” (Lennon & McCartney 1965). To me, this statement is a queer ethos. We know that 2SLGBTQ+ people have necessarily and creatively reworked and reimagined the organization and expression of kinship. When family is so often bounded by what Julianne Pidduck calls “constraints of relationality” in “Queer Kinship and Ambivalence”(2008: 441), the lyrics “In my life, I love you more” are a call to action. More is a word used comparatively to insist that there is something greater, something more exists, something more is possible. I embrace the challenge to love more. My queerness urges me to love more, and parenting Asa does, too. On the evening of the performance, indexed by my parents’ struggles and our shared disdain for the chill of winter, Asa and I performed “In My Life” together. The video of our performance will remain a treasured sonic archive that I will return to often, and as Asa gets older, I hope it reminds him of how beautiful he’s always been.
—
Casey Mecija is an Assistant Professor in the Department of Communication & Media Studies at York University. Her current research examines sound as a mode of affective, psychic, and social representation, specifically in relation to diasporic experience. Drawing on sound studies, queer diaspora studies and Filipinx Studies, her research considers how sensorial encounters are enmeshed and disciplined by social and psychic conditions. In this work, she theorizes sounds made in and beyond Filipinx diaspora to make an argument about a “queer sound” that permeates diasporic sensibilities. She is also a musician and filmmaker whose work has received several accolades and has been presented internationally.
—

REWIND!…If you liked this post, you may also dig:
Blank Space and “Asymmetries of Childhood Innocence” –Casey Mecija
The Sound of What Becomes Possible: Language Politics and Jesse Chun’s 술래 SULLAE (2020) –Casey Mecija
The Cyborg’s Prosody, or Speech AI and the Displacement of Feeling–Dorothy Santos
Tape Hiss, Compression, and the Stubborn Materiality of Sonic Diaspora–Chris Chien
Xicanacimiento, Life-giving Sonics of Critical Consciousness—Esther Díaz Martín and Kristian E. Vasquez
Moonlight’s Orchestral Manoeuvers: A duet by Shakira Holt and Christopher Chien
Enacting Queer Listening, or When Anzaldúa Laughs–Maria Chaves Daza
Echoes in Transit: Loudly Waiting at the Paso del Norte Border Region—José Manuel Flores & Dolores Inés Casillas
The Queerness of Wham’s “Last Christmas”–Justin Burton
Could I Be Chicana Without Carlos Santana?–Wanda Alarcón
The Sound of What Becomes Possible: Language Politics and Jesse Chun’s 술래 SULLAE (2020)

“To this day I think about all the strange words I missed out on, all the losses I’m still carrying from faraway…I still think of the time when I spoke one language, and that language was whole.”
Chun 2020
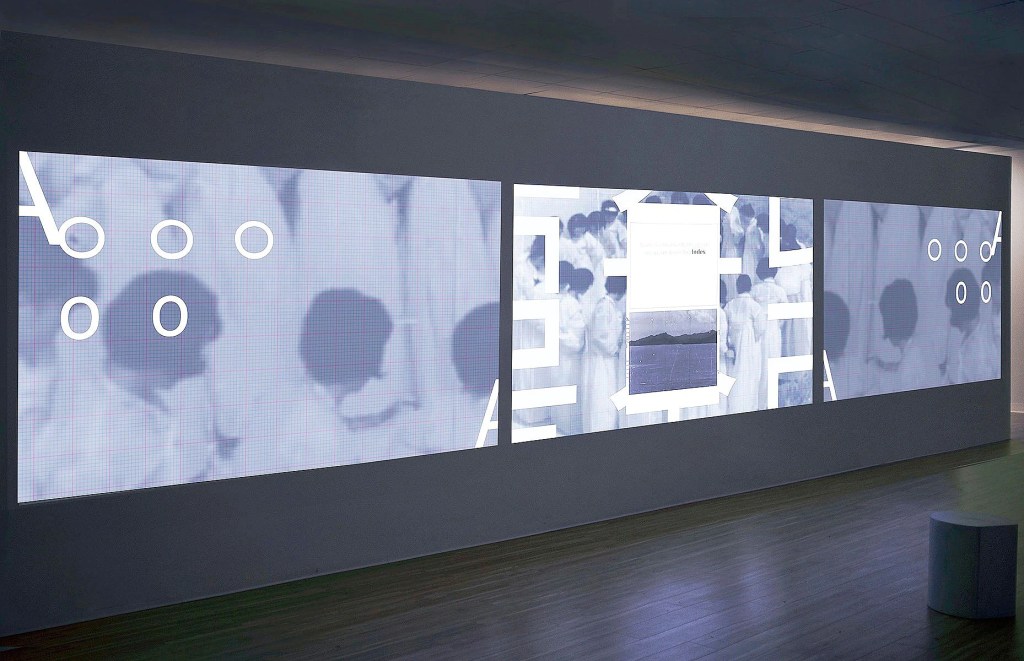
Language can be a site of loss, a wholeness with which one, due to migration, has never really known. In the above passage, artist, Jesse Chun, reflects on how her grandmother spoke words in a language she did not understand, but yearned to hear and feel those sounds after her passing. There is a sonic residue that sticks to diasporic experiences. There are sounds that can stir up a blend of affect and ideation that is comforting when whiteness is unsettling. It is this disjuncture between words, meaning, and their sounds, that drew me to Chun’s work, 술래 SULLAE (2020). This piece reminded me of how sound, in its most ambiguous and queer forms, can hold the contingencies of history, language, memory, family, and the genealogies of loss that mark these sites of colonial dispossession.
술래 SULLAE (2020) is a single channeled video that draws from ganggang sullae, a Korean seasonal harvest and fertility ritual that integrates song and dance and is typically performed by women under the glow of moonlight. The participants hold hands forming a circle that through their movement, expands, disassembles, and changes its form. The songs can be both impromptu or pre-determined and encourages the participants to express their feelings in chorus with one another.
Diana Seo Hyung Lee (2020) suggests that historically ganggang sullae was meant to provide a forum for its participants to express emotions connected to living within patriarchal systems of power and oppression. She writes: “the women participating would not have been able to, in their everyday lives, sing, speak loudly, nor leave the house at night, in the patriarchal society of ancient Korea. This dance was a license for their one release.” In 술래 SULLAE, the dance proves to be a defiant presence. The women flash on screen as an unbreakable chain reinscribing a gendered history with new sounds and images that gesture to emancipatory possibilities.
술래 SULLAE combines archival clips of ganggang sullae, index pages from intonation books, images of Hangul and English consonants and audio splices from YouTube tutorials on how to pronounce English correctly. In the video, language becomes unhinged from expectation but at the same time, given form through history. The sound of the English language is disembodied and spliced into phonemic pulses. In 술래 SULLAE, Chun has created an encounter with the grammars of polyphony; a simultaneity of sounds that are both restrained by and resistant to the imposition of English on the Korean diaspora. Through what Chun has described as a form of “unlanguaging” following Rey Chow, her audience is witness to new meanings produced through the abstraction, manipulation, and redaction of sounds and symbols from the English language.

Chun’s editing and manipulation of English sounds is intentional. In an interview with Art Forum, Chun shares: “Taking the sound apart but still keeping it within the conceptual framework of English made me think about what else is embedded in making a language. English is tied up with legacies of imperialism; there’s so much unseen violence that is part of how this language is institutionalized.” What remains after the edits is an inventory of sounds that disrupts the primacy of the vowel as central to English word construction and thus, central to colonial imagination.
Like Chun, I realize that my conceptualizing of language is within an English framework, but my hope is that when we turn to the affective and when we begin to pull language a part, something different, something resistant, is produced. I am neither an expert in English nor Korean linguistics, it was the sounds in this work that pulled me into it. In thinking with 술래 SULLAE, I’m interested in what becomes possible in the absence of the vowel. I turn to the interruptive potential of consonant sounds to affect and incite methods of communication outside of those steeped in colonial dominance. What does it mean to de-emphasize the function of vowel sounds in language and reorient our listening to the consonant? What do consonant sounds teach us about the sonics of race that underwrite hierarchies of language? What methods of communication become possible when we do away with words and are left with only their sonic substance?
Through her assemblage of consonant sounds in 술래 SULLAE, Chun is making a deliberate choice to describe and animate a politics of language through refusing its colonial enclosures and turning to the aesthetic in order hold the excesses of description. She refuses the vowel in this piece, not by denying its presence, but instead relegating it to the soundless and the unfamiliar, a space of, in her words, “untranslatability.” In this undoing, consonants become the emotive force where new meanings and orientations to the sounds that mark our words are forged.
술래 SULLAE opens with the sound ssshhh; a pairing of consonant sounds that is often associated with insisting on silence, a sound meant to reprimand. Chun extracts and emplaces this sound in a new aesthetic landscape that is independent and unregulated by colonial schemas of enunciation and translation. The prominent soundscapes of the video are consonant sounds and when removed from their phonetic relations to vowels these sounds undo the presumptive structuring or potential reprimand of English. In 술래 SULLAE, we are meant to experience the fullness of the consonants’ timbre…ssshhh, ppp, ddd, tttt, kkkk…these edited clips of sound originally meant to instruct and assimilate speech into English pronunciations now serve a different function. For me, they secure Chun’s political orientation: one that is about the crafting of a world that involves the careful consideration of the logistics, function, and embedded emotions of the sounds that inhabit it.

graphite, watermarks, paper, aluminum frame, 13 x 16 inches
All languages contain their own unique set of vowels and consonants, but, Anne Carson reminds us that: “The importance of vowels to human speech has remained. There are words in English without consonants, but so central are vowels to word construction that there isn’t a word in English that doesn’t include a vowel.” In speech, consonants sounds are meant to break up the intended agenda of vowels. The ssshhh, ppp, ddd, tttt, kkkk, are antithetical to the circle or the rounded mouth needed to voice a vowel sound. Unlike the openness of a vowel, producing consonant sounds involves a narrowing of the vocal tract. This narrowing is referred to as constriction or the obstruction of breath whereby sound is produced by a form of corporeal tension. Consonant sounds also demand all the mechanics of the mouth: the lips, the teeth, the tongue, and the palette. Shhhh, requires the corners of the lips to lower and rather than rounding, the lips become pursed, and teeth become exposed. Parts of the mouth are drawn in. The soft palate is raised, and the tongue reaches upwards towards the roof of the mouth without touching it and then the tip of the tongue lowers behind the teeth.
Consonants emerge out of collectivity. Where a vowel is sounded without vocal constraint, consonants require more effort. Their sounds are produced through intricate bodily choreographies in the mouth that involve both constriction and collaboration. Ganggangsullae likewise relies on effort and interdependence. Participants collectively determine the speed and/or shape of their dance. They may even become serpentine or separate into smaller circles depending on what the group decides. The dance also provides an aesthetic space for its participants to voice frustration, anger, and tension through song with the hopes of producing reprieve from gendered hardships. Chun has decided to withhold these songs from her audience; we never hear the women singing. Through this erasure, Chun embeds the consonant sound with affective force whereby a politics of language and gendered presence is enunciated through and beyond a form of silencing. The dance redirects trajectories of dominance whereby the shushing takes on a new voice imbued with agency and hope. Because of how Chun isolates and amplifies its sound, ssshhhh is free to take on different meanings and associations. For me, I was reminded of rushing water or gusts of wind, or the sound used to lull my child to sleep. I was brought into another index of knowing and relating.

The sounds of language hold erasures and layered histories often obfuscated by our mundane encounters with them. Largely understood as the most sonorous part of the syllable, vowels produce the loudest speech sounds and their capacity for holding larger amplitudes or louder volumes have been linked to the sonic expression of emotion. Consonant sounds are more pragmatic than vowels. They are known for their functionality, for the ways in which they assemble the semantic structure of words and for their capacities to hold vowels in place or as Anne Carson describes as “delineating meaning amid the flow of open vowel sounds.” Consonant and vowel sounds map out different functional trajectories by virtue of the shape of mouth and orientation of breath that these sounds demand. Like Chun, I’m interested in what political orientations become possible when we source emotion elsewhere, beyond the confines of spoken words imposed upon us.
The word consonant is a noun, a word used to identify or classify, a semantic enclosure that establishes a subject or object. But unlike the word vowel, consonant is also an adjective. A consonant possesses the capacity to describe, to name, to tell us more. Adjectives parcel out description on states of being, in this way, they are inherently phenomenological. In 술래 SULLAE, Chun empties vowels of their sonic substance leaving behind traces of fragmented characters and differently shaped circles in their wake. They are stripped of breath and their symbolic value forming a new method of communication that reroutes expectations of what language, as we know it, can do and sound like. Like, ganggang sullae, the vowel is premised on the shape of a circle, but in 술래 SULLAE, Chun provokes us to think about what becomes possible beyond the circular structuring device, what becomes possible beyond the purview of the violent embeddedness of English and its colonial exigencies.

untitled (ㄷ), 2020, a functional concrete stool, courtesy of artist
Chun has noted that the moon that hovers above the ganggangsullae is yet another site of imperial conquest. In Art Forum, Chun states: “when I look up at it to feel comforted or to find solace, I’m reminded of colonial violence and an agenda that’s projected onto it. In that way, the moon also reflected how I see language.” Chun’s turn to consonants signals a reshaping of the colonial frame that does not disavow or idealize the legacies of imperialism on systems of communication, but instead highlights the tensions and obstructions produced in its shadows.
—
Featured image: 술래 SULLAE, 2020, single-channel version, courtesy of artist
—
Casey Mecija is an Assistant Professor in the Department of Communication & Media Studies at York University. Her current research examines sound as a mode of affective, psychic and social representation, specifically in relation to diasporic experience. Drawing on sound studies, queer diaspora studies and Filipinx Studies, her research considers how sensorial encounters are enmeshed and disciplined by social and psychic conditions. She is also a musician and filmmaker, whose work has received a number of accolades and has been presented internationally.
—

REWIND! . . .If you liked this post, you may also dig:
Blank Space and “Asymmetries of Childhood Innocence” –Casey Mecija
Re-orienting Sound Studies’ Aural Fixation: Christine Sun Kim’s “Subjective Loudness”–Sarah Mayberry Scott
Tape Hiss, Compression, and the Stubborn Materiality of Sonic Diaspora–Chris Chien


















Recent Comments