“In My Life”: Loving Queerly and Singing Across Generations
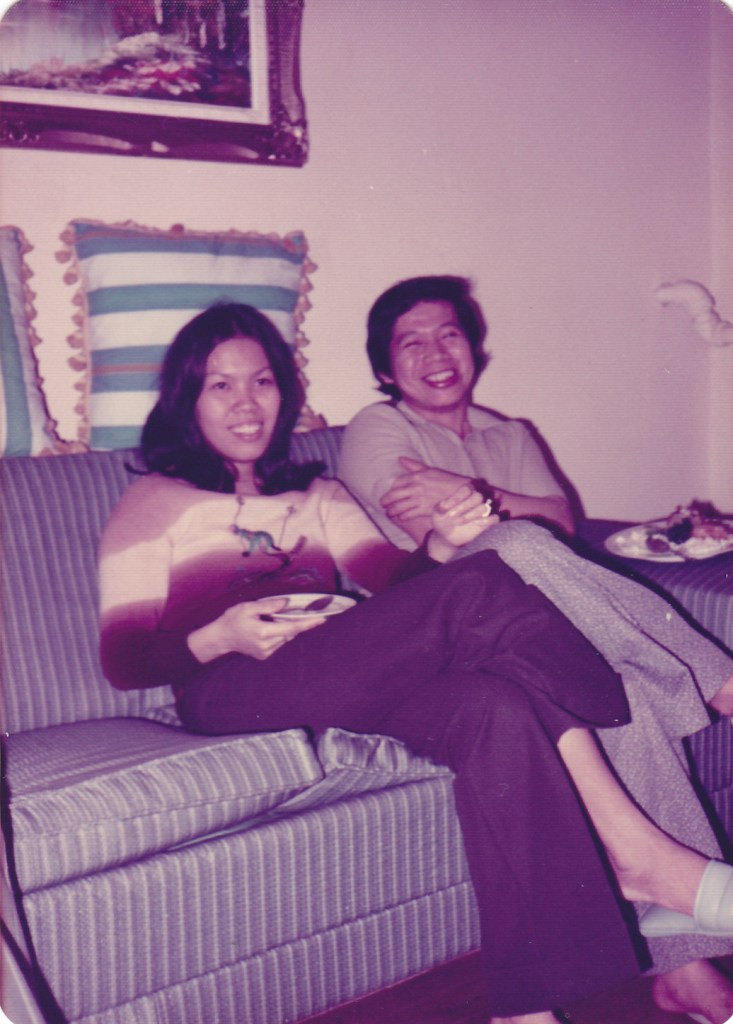

December 1975.
The cold winds staked their claim over Toronto, where my parents had recently arrived from the Philippines. They were underdressed and making their way down Parliament Street. Despite being warned of a shift in temperature, they were not expecting the brutal intensities of Canadian winter. I’m not sure how anyone anticipates the sharp sting of negative temperatures when they are arrivants used to tropical climates. Undeterred, my mother and father headed to a small Filipino grocer, hoping to encounter a semblance of domestic familiarity. Pressed against the biting winds, my mother abruptly stopped, looked at my father and said, “Tumutolo ang sipon” – you have a runny nose. To which my father replied, “Ikaw din” – you do too! They both started laughing and laughed again when they retold me this story 48 years later. When faced with the challenges of migrating to a new and very cold country, they managed to mine humour from a deep well of difficult circumstances. We had been listening to the song “In My Life” by the Beatles (Lennon & McCartney 1965). Something in its expression, melody, and feeling caused my parents to be transported to this small but important moment.
In her conversation with Christine Bacareza Balance, “‘Revolutions in Sound’: Keynote Duet” (2022) Alexandra T. Vazquez writes: “The popular…leaves so much room for engagement with sound artists (musicians without the gallery). None of them need theorists to argue for them, to argue for their mattering because to so many, they already do. How do they instead invite theorists to take part in something alongside them?” (12). I was never a big fan of the Beatles, but regardless of my opinions, they were popular. As a relentlessly oppositional teenager, I was put off by their mass popularity. As Vazquez suggests, despite one’s musical taste, songs are invitations, not scholarly conquests. The memory re-opened by my parents’ connection to “In My Life” was an invitation for me to take stock of the song’s affective and, for them, diasporic trajectories. As Balance (2022) suggests songs request us to “listen long so we hear where another is coming from” (15). For her, “long” describes temporality and commitment. To “listen long” implies that duration and attention are the pretext for empathic relations.
“In My Life” was released in 1965. My mother was fifteen years old when she first heard the song on the radio in a boarding house in Marbel, Philippines. One year later, on July 16, 1966 the Philippine Free Press would announce, “The Beatles Are Coming” (de Manila as cited by Robert Nery in “The Hero Takes a Walk” 2018). At that time, Ferdinand Marcos was the newly elected president of the Philippines, and Imelda Marcos was his First Lady. The Marcoses would later unleash an era of violent dictatorial power and impose Martial Law in 1972, escalating political suppression (Burns 2013). My mother recalls that the band’s first and only appearance in the Philippines was remembered by many less for their two scheduled concerts and more for their “snub” of Imelda. The Beatles were noticeably absent at a lunch reception they were expected to attend with the First Lady at the Presidential Palace. Their absence, attributed to a communication error between the concert promoter and the band’s manager, incited public disapproval and resulted in the sudden disappearance of their security escort and hotel and porter service. Unlike in other cities, the band was refused room service and was forced to carry their own luggage (Nery 2018).
What is striking about this moment is that it breaks from preoccupations with Filipinx desires for assimilation and mimicry of Western imperial projects. In Video Night in Kathmandu and Other Reports from the Not-So-Far East, British travel writer Pico Iyer (1988) famously stated that Filipinx people are the “[m]aster of every American gesture, conversant with every western song…the Filipino plays minstrel to the entire continent (153)” Turning against imperial scripts and the band’s documented disdain of “Mosquito City” and even worse, John Lennon’s comment that a return to the Philippines would require “an H-bomb,” the soured residues of their visit marks a queer rupture in Beatlemania. The public decried that Filipinx people deserved better from the band, capturing what Balance describes in Tropical Renditions: Making Musical Scenes in Filipino America (2016), as “disobedience” in that “disavows a belief in the promises of assimilation” (5). For me, Filipinx non-compliance textures the sonic substance of “In My Life.” While the shadow of the Marcoses cronyism and corruption is an inescapable footnote, it is the defiant voices of hotel employees, dismayed fans, and airport workers that insisted on the “ordinariness” (Wofner & Smeaton, 2003) of the Beatles that holds the song’s queer decibels.
There are places I’ll remember all my life, though some have changed. Some forever, not for better. Some have gone, and some remain.
“In My Life” (Lennon & McCartney 1965).
January 2018.
I am sitting on my couch watching a Toronto Raptors game. The television emits light that flickers through a large window that frames a bright winter moon. I am 41 weeks pregnant at this point (feeling similarly shaped and sized as the moon outside). My stubborn queer resistance to the Beatles somehow dissipated during my pregnancy, and the song “In My Life” made its way to me. I would quietly sing the song to my pregnant belly. Then, that January night, I felt a snap inside my body and a rush of water down my legs. I won’t go into much gratuitous detail other than to say that at 12:49 pm the next day, Asa Cy Dyer-Mecija was born at home.
And these memories lose their meaning when I think of love as something new.
“In My Life” (Lennon & McCartney 1965)
Sometimes, I needed to couch the queerness of pregnancy in words that were not mine. The distance between these words and the ones I had yet to find would help to structure my unfolding love for Asa. Here, queerness presented a modality of encounter with uncensored desires. Queerness is often theorized as a utopian impulse; the queerness of my pregnancy jostled both the hopes and fears brought up by the unknown terrain of parenting amidst heteronormativity. For me, “In My Life” is riven by sentimentality and nostalgia, but it also gave melody to a tender relationship with myself and my new role in the world. This was the sonic throughline to my parents, a queer inheritance of tension made from the hopes for kinder contexts amidst the limitations of harsh realities.
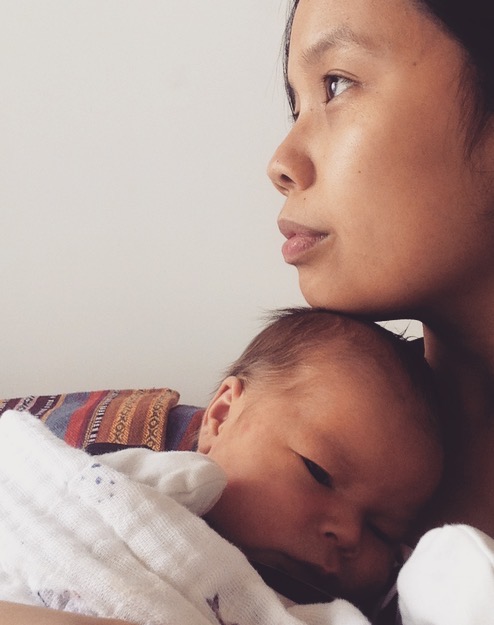

December 2022.
I was invited to perform as part of the Queer Songbook Orchestra’s holiday fundraiser. The Queer Songbook Orchestra is a chamber pop ensemble that hosts an annual concert focused on songs and stories about “chosen family and queer joy” (Queer Songbook n.d.). At that time, Asa was four years old. He is a child of the pandemic. He’s a kid with two moms, a present and kind donor, and is dearly loved by his Lolo and Lola, his grandparents, aunts, titas, uncles, cousins, kuya, ate, and his beautiful chosen family. My partner, Hannah, and I sometimes worry about how his world will be affected by reactions to the makeup of our family, but mostly, we know he’ll be sure he’s loved by many.
To me, the song “In My Life” offers a useful sonic response to homophobia. As a baby, after Asa’s baths, I would often wrap him in a towel, and while rocking him back and forth, I would sing these lyrics from the song: “Though I know I’ll never lose affection for people and things that went before, I know I’ll often stop and think about them. In my life, I love you more” (Lennon & McCartney 1965). To me, this statement is a queer ethos. We know that 2SLGBTQ+ people have necessarily and creatively reworked and reimagined the organization and expression of kinship. When family is so often bounded by what Julianne Pidduck calls “constraints of relationality” in “Queer Kinship and Ambivalence”(2008: 441), the lyrics “In my life, I love you more” are a call to action. More is a word used comparatively to insist that there is something greater, something more exists, something more is possible. I embrace the challenge to love more. My queerness urges me to love more, and parenting Asa does, too. On the evening of the performance, indexed by my parents’ struggles and our shared disdain for the chill of winter, Asa and I performed “In My Life” together. The video of our performance will remain a treasured sonic archive that I will return to often, and as Asa gets older, I hope it reminds him of how beautiful he’s always been.
—
Casey Mecija is an Assistant Professor in the Department of Communication & Media Studies at York University. Her current research examines sound as a mode of affective, psychic, and social representation, specifically in relation to diasporic experience. Drawing on sound studies, queer diaspora studies and Filipinx Studies, her research considers how sensorial encounters are enmeshed and disciplined by social and psychic conditions. In this work, she theorizes sounds made in and beyond Filipinx diaspora to make an argument about a “queer sound” that permeates diasporic sensibilities. She is also a musician and filmmaker whose work has received several accolades and has been presented internationally.
—

REWIND!…If you liked this post, you may also dig:
Blank Space and “Asymmetries of Childhood Innocence” –Casey Mecija
The Sound of What Becomes Possible: Language Politics and Jesse Chun’s 술래 SULLAE (2020) –Casey Mecija
The Cyborg’s Prosody, or Speech AI and the Displacement of Feeling–Dorothy Santos
Tape Hiss, Compression, and the Stubborn Materiality of Sonic Diaspora–Chris Chien
Xicanacimiento, Life-giving Sonics of Critical Consciousness—Esther Díaz Martín and Kristian E. Vasquez
Moonlight’s Orchestral Manoeuvers: A duet by Shakira Holt and Christopher Chien
Enacting Queer Listening, or When Anzaldúa Laughs–Maria Chaves Daza
Echoes in Transit: Loudly Waiting at the Paso del Norte Border Region—José Manuel Flores & Dolores Inés Casillas
The Queerness of Wham’s “Last Christmas”–Justin Burton
Could I Be Chicana Without Carlos Santana?–Wanda Alarcón
Xicanacimiento, Life-giving Sonics of Critical Consciousness


This series listens to the political, gendered, queer(ed), racial engagements and class entanglements involved in proclaiming out loud: La-TIN-x. ChI-ca-NA. La-TI-ne. ChI-ca-n-@. Xi-can-x. Funded by an Andrew W. Mellon Foundation as part of the Crossing Latinidades Humanities Research Initiative, the Latinx Sound Cultures Studies Working Group critically considers the role of sound and listening in our formation as political subjects. Through both a comparative and cross-regional lens, we invite Latinx Sound Scholars to join us as we dialogue about our place within the larger fields of Chicanx/Latinx Studies and Sound Studies. We are delighted to publish our initial musings with Sounding Out!, a forum that has long prioritized sound from a queered, racial, working-class and “always-from-below” epistemological standpoint. —Ed. Dolores Inés Casillas
—
In the past year, we, Esther, a first-generation profesora in Latinx culture and feminist studies in Chicago and Kristian, an L.A-raised Xicano de letras pursuing a doctoral degree in Santa Barbara, engaged in a multi-synchronous dialogue on the life-giving sonics of our critical consciousness. This Xicanacimiento, as theorized in Kristian’s current writing and in conversation with Irene Vasquez and an emerging generation of Chicana/o scholar-educators, refers to the incomplete process and life-giving knowledge forged in the socio-political and pedagogical activities of Chicanx worldmaking.
SO! writers note music listening as a powerful site for critical thinking. Erika Giselda Abad, for instance, teaches the Hamilton Mixtape so her Latinx students may “hear [their stories] from people who look and sound like them.” We reflected on the pedagogical implications of our music listening that informed our coming-into-critical consciousness. In this diálogo, we developed a playlist through experimenting with our sonic memories through the poetics of our rasquache sensibilities. Gloria Anzaldúa suggests something similar with notes from Los Tigres, Silvio Rodriguez, and others in La Frontera. Our auditory imaginary echoes our evolving conocimiento toward spiritual activism.
Here, we offer our musical resonances as shaped by our gendered, place-based, and generational Xicanx experiences as a pathway to hear the auditory dimensions of Xicanacimiento. Our listening is thus counter-hegemonic or a “brown form of listening” as suggested by D. Inés Casillas, “a form of radical self-love, a sonic eff-you, and a means of taking up uninvited (white) space,” when this listening evolves critical anti-imperialist and feminist consciousness that hears 500 years of opresión y resistencia.
Diverging from the mixtape genre, our Xicanacimiento playlist seeks to convey something beyond connection and emotion towards a sustained affective state. Instead of a sonic moment, we hear a sonic stream; a subaltern auditory repertoire that is multi-directional and open to expansion by any and all interpellated Xicanx ears.
Kristian: Tuning-in to Xicanacimiento is a symbiosis of feeling and listening to La Chicanada from Califas to all corners of Aztlán unearthed. I was raised to the sounds of my father’s rancheras played in his truck and the hip-thumping rhythms of bachata and reggaetón played in my mother’s kitchen after a workday.
Yet, my love for UK anarcho-punk and US hardcore punk developed in defiance of public schooling and of a disaffected civil society. As a youth during the Great Recession, a future without higher education meant prison, the military, death by overdose, or the eternal damnation of working the Los Angeles service industry. I thrashed in sound; numbing my ears with noise, bruising in the mosh pit; bearing witness to minors as mota and alcohol addicts; pierced by the cries of police sirens breaking up our communion.
I found refuge in Xicanacimiento as a community college student and as a transfer at UC Los Angeles. I came into Xicanx consciousness by studying Mexican anarchists and Chicanx organizing. As a MEChistA, I came to listen to the ways local elders, youth, organizers, and agents of social transformation in Los Angeles identified their struggle with land, life, and spirit. My primer to social movements gave me language, and it was MEChistAs who offered me a new soundtrack against the escapism of the Los Angeles punk scene. The resonances of marchas, fiestas, and the songs of danza azteca oriented me into a new modality of listening. Xicanacimiento was the sonic web of these social and cultural practices, rooted in my auditory encounters with the verses of Quetzal, the biting guitars of Subsistencia, the rhythms of Quinto Sol, and the lyrical narratives of Aztlán Underground. The life-giving sonics of Xicanacimiento grazed against my wounded sonics of broken glass, nos tanks, drunk noise, and the cacophonous affair of a raided gig as intoxicated Latinx youth disperse into the discordant symphonies of the urban soundscape.
Esther: I listen as a campesina migrante translocada from Jalisco to California, Texas, and Illinois. Some twenty years ago, while attending Cal State en el Valle Central, I heard Xicanacimiento as concientización; an evolving awareness about la lucha obrera, the open veins of Latinoamerica and my place within the interlocked hierarchies of race, class, and gender in US society. With Chicanx and brigadista musics I felt connected to la lucha and acquired the language to name capitalist imperialism rooted in white supremacy as the enemy of humanity and Pachamama.
My early sonic memories include the sequence of my Alien number, the urging tones of radio hablada discussing Prop 187 (insisting we were aliens), Prop 227 (banning our language), and reports of Minuteman harassing la raza. I was immersed in listening; my mother’s sobremesa, my sister’s Temerarios at 5 am, Selena on the school bus, and 90s hits-from Chalino to Morrissey-on Columbia House CDs I traded with my older brother. Among other norteñas, La Jaula de Oro, the theme song of the diaspora of papás mexicanos, played at random-at the marketa, en los files, in passing cars, and so on…- to remind us of my father’s sacrificio en el norte caring for 500 dairy cows, six days a week, in two 5-hour shifts, to provide us el sueño americano.
I studied music in college, playing jazz and orchestral bass until the racist and sexual harassment targeting my young Latina body turned me away. I left the scene but continued my communion with music through library loans, traveling vendors, and trips to Amoeba. In reggae and canción nueva I found otros mundos posibles in the upbeat, cariño in 2 over 3, and the poetics of black and brown history; manos abiertas, muchas manos.
In 2002, “El Rasquache Rudo” a poet from the Rudo Revolutionary Front brought me sounds from Azltán; the UFW unity clap rallying in Modesto, a recitation by José Montoya in Sacramento, and brigadista music synergizing the 1492 quincentennial resistance with the uprising of the Ejército Zapatista de Liberación Nacional (EZLN). As Omar Marquez argues, the Zapatista uprising shifted Chicano ideology to speak from the position of a living indigenous present; still loud in the work of Xicanx activists like Flor Martinez. Into the 21st century, Aztlán Underground, Manu Chao, and Todos Tus Muertos, among others, soundtracked our protests against the invasions of Afghanistan and Iraq.
Julieta Venegas’s distinctly vulnerable voice over the controlled chaos of ska and Martha Gonzalez’s tension over the wall of sound that is Quetzal, was transformative as I heard In Lak’ech; hearing in their voices possibilities for my Chicana existence.
Some of these selections anchor my first-year lectures at the University of Illinois in Chicago, where most of my students are working-class Latinx and Black. I do this with the intention of “opening affective pathways toward Xicanacimiento” as Kristian offered, and to insist on the point that Latina/o/x Studies is to be a critical, anti-hegemonic, subaltern field of study that hears a history from el mundo zurdo.
Outro:
In a gesture to deconstruct the term Xicanacimiento, one might think of the words “renacimiento”and “conocimiento.” What might emerge is a “regenerative force” and “collective knowledges” in consideration to how we listen, what resonances are made, and what sounds we inhabit when Xicanacimiento is invoked or felt as sound. Tuning into this auditory imagination guides the listener to a myriad and select decisions of what constitutes the Xicanx resonance for the local sonic geographies and the soundscapes which emerge from music. This curated sonic experience is one where voice, instrument, memory, and affect intersect.
—
Featured Image by Jennifer Lynn Stoever
—
Esther Díaz Martín is a researcher and educator in the Latin American and Latino Studies and the Gender and Women’s Studies program at the University of Illinois in Chicago. At present, she is working towards finishing her manuscript Latina Radiophonic Feminism(s) which seeks to amplify the acoustic work of popular feminism in contemporary Spanish-language radio and Latina podcasting.
Kristian E. Vasquez is a Xicano writer, poet, and zinester born and raised in Los Angeles, California currently pursuing a doctoral degree in Chicana and Chicano Studies at UC Santa Barbara. His research on the affects, sounds, and semiotics of La Xicanada expands the concept of Xicanacimiento, centering the affective force of expressive culture.
—

REWIND!…If you liked this post, you may also dig:
Ronca Realness: Voices that Sound the Sucia Body—Cloe Gentile Reyes
SO! Podcast #74: Bonus Track for Spanish Rap & Sound Studies Forum—Lucreccia Quintanilla
“Heavy Airplay, All Day with No Chorus”: Classroom Sonic Consciousness in the Playlist Project—Todd Craig
Deep Listening as Philogynoir: Playlists, Black Girl Idiom, and Love–Shakira Holt
Mixtapes v. Playlists: Medium, Message, Materiality–Mike Glennon
SO! Amplifies: Memoir Mixtapes
Could I Be Chicana Without Carlos Santana?–Wanda Alarcón
Tape Hiss, Compression, and the Stubborn Materiality of Sonic Diaspora–Christopher Chien
Sounding Out! Podcast #28: Off the 60: A Mix-Tape Dedication to Los Angeles–J.L. Stoever
“Oh how so East L.A.”: The Sound of 80s Flashbacks in Chicana Literature–Wanda Alarcón


















Recent Comments