Sonic Homes: The Sonic/Racial Intimacy of Black and Brown Banda Music in Southern California


This series listens to the political, gendered, queer(ed), racial engagements and class entanglements involved in proclaiming out loud: La-TIN-x. ChI-ca-NA. La-TI-ne. ChI-ca-n-@. Xi-can-x. Funded by an Andrew W. Mellon Foundation as part of the Crossing Latinidades Humanities Research Initiative, the Latinx Sound Cultures Studies Working Group critically considers the role of sound and listening in our formation as political subjects. Through both a comparative and cross-regional lens, we invite Latinx Sound Scholars to join us as we dialogue about our place within the larger fields of Chicanx/Latinx Studies and Sound Studies. We are delighted to publish our initial musings with Sounding Out!, a forum that has long prioritized sound from a queered, racial, working-class and “always-from-below” epistemological standpoint. —Ed. Dolores Inés Casillas
—
No tengo nada de sangre de Mexico. Soy afro americano.
(I have no Mexican blood. I am African American.)
El Compa Negro (Ryhan Lowery)
The grain is the body in the singing voice, in the writing hand, in the performing limb.
Roland Barthes (The Grain of the Voice,1971)
***This post is co-authored by Sara Veronica Hinojos and Alex Mireles
Sarah La Morena (Sarah the Black woman), or Sarah Palafox, was adopted and raised by a Mexican family in Mexico. At the age of five, she moved to Riverside, California, a predominantly Mexican city an hour east of Compton. Palafox started singing as a way to express the racism she faced as a child in Southern California, feeling caught between her Black appearance and her Mexican sound. She found her voice in church, a nurturing environment where she could be herself, surrounded by her family’s love. She gained attention with a viral video of her rendition of Jenni Rivera’s “Que Me Vas a Dar.” Palafox delivers each note with profound emotion and precision, leaving even the accompanying mariachi violinist in awe.
Similarly, El Compa Negro (The Black Friend/Homie) or Rhyan Lowery heard the sounds of banda coming from his neighbor’s backyard in Compton; a historically Black-populated city with a current Mexican majority. Lowery couldn’t shake the song out of his head and learned the song’s Spanish-language lyrics. Like Palafox, videos of him singing in Spanish during high school made him a viral sensation. “They called me ‘el compa negro’ (…) All I heard was ‘blah blah blah negro or negro’ and I wasn’t having it until they explained to me what it meant. And I was like ‘ok, cool’.”
The sonic stylings of El Compa Negro and Sarah La Morena within the banda genre enable transcultural connections beyond the pan-Chicano-Mexican-Central American popularity of tecnobanda and la quebradita. The 1990s banda craze, writes George Lipsitz “challenged traditional categories of citizenship and culture on both sides of the US-Mexico border.” Banda music might sound like it was established south of the border, but multicultural listeners and dancers continue to influence its vibrations. Pop stars like Snoop Dogg, Shakira, Bad Bunny, and Karol G have released (tokenized) songs with Mexican-tinged, banda-recognizable beats. Yet, both El Compa and Sarah demonstrate a form of musical Black/Brown, working-class intimacy. Their respective musics are much less about a pop star (duet) kind of solidarity and much more about a deep knowing, a sensibility among working-class cultures and othered people that resonates through the aesthetics of sound. As Karen Tongson writes in Relocations: Queer Suburban Imaginaries, about her experience of “queer, brown, immigrant musical discovery” in Riverside, the hometown she shares with Sarah La Morena: “It is the music that inspires us to ask questions” (26).
Certainly, US Mexican immigrant culture does not have the same (mainstream) cultural caché as African American culture, unless somehow softened or filtered. Jalapeños get “de-spicifed“; pre-made Día de Los Muertos altares are now at Wal-Mart, and huipiles are available as fast-fashioned “peasant blouse;” filtering out their Mexican-indigenous origins. Thus, classics like “La Yaquesita” and originals like “Yo Soy Compton” heard through the grain of Black voices affirm the possibilities of U.S. Mexican belonging or what D. Travers Scott characterizes as a form of “intimate intersubjectivities;” rooted in long-established Black/Brown co-existences across the borderlands and city barrios. Turning the volume up on these artists serves an important counterpoint to Latino anti-Black racism.
Their voices, blending with brass and tambora, embody a Black-Brown sonic and symbolic solidarity, or spatial entitlement. As theorized by Gaye Theresa Johnson in Spaces of Conflict, Sounds of Solidarity, innovative applications of technology, creativity, and space foster new collectives which, even when “unheard” by historians, assert social citizenship and pave the way for new working-class political futures. In the contested neighborhoods of greater Los Angeles, Black and Brown communities are often pitted against one another through processes of containment and confinement leading to competitions for jobs, housing, status, and political power. Yet, they share the experiences of labor exploitation, housing segregation, and cultural vilification. Filmed in the intimate settings of backyards, the viral videos underscore Black/Brown hood/barrio soundscapes as multi-generational, familial, and culturally hybrid. Home is where shared class, racial, and gender politics are negotiated and resolved.
Asserting Black identity and the choice to perform in Spanish creates a unique visual and auditory experience within the Mexican-dominant world of banda. In fact, in 2024, Lowery made history as the first Spanish-language artist signed by Death Row Records, a label known primarily for hip hop. The lively rhythms of banda – oompah-oompah-oompah – offers both banda and hip hop listeners a new orientation to discern the racial-cultural politics of broader Los Angeles.
Like the mid-century Haitian-Mexican bolero singer Antonia del Carmen Peregrino Álvarez, alias “Toña La Negra,” the added tags “Negro” and “la Morena” signals Black singers’ recognition of the meaning(s) of their racial difference within the transnational Mexican music scene. The auditory discomfort that their vocal grain might cause is named and thus recognized as the persistent colorism of listeners at large. Lowery describes his initial unease with the given “Compa Negro” nickname. “My Mexican friends always tell me ‘Hey, compa negro, you’re Mexican, man. God just left you in the oven a little too long.’” The harassment came from both Black peers and Mexicans alike, for liking banda, dating Latinas, or dressing “like a Mexican.” “They would say, ‘You hate being Black. Self-hate. Self-hate. I’m like man it ain’t that I self-hate, it’s just that I embrace something. I took the time to have an open mind and study something, you know?” His way of being made sense in the context of a Compton teenage experience. “Becoming Mexican” by way of musical/cultural engagement surpassed skin tone-deep and nationalist differences.
Or, as Mexican ranchera singer Chavela Vargas–born in Costa Rica–famously asserted, “Mexicans are born wherever the hell they want!” Try listening to Juan Gabriel’s “Amor Eterno” to find out. Black creatives like Evander, Vaquera Canela, and Terry Turner are just a few more examples of Black mexicanidad. Yessica Garcia Hernandez reminds us that Black and Brown sonic solidarities have been the driving pulse of US popular music. She argues, “Home and sound is acknowledging that both corridos, hip-hop, and G-funk relationally, has formed paisas.”
El Compa Negro’s “Verde es Vida,” a tribute to California’s weed culture, lowriders, and corridos, booms loudly. The song begins with an accordion playing reggae rhythms, soon interrupted by percussion, guitars, and El Compa’s fast-paced verses. About a minute in, the accordion slows the tempo with a few reggae notes before the vocals return, reintroducing the corrido rhythm: “Hoy andamos en LA bien tranquilitos. En el lowrider escuchando corridos.” The reggae-corrido fusion ends with the familiar “pom pom pom pom!” of the drums, typical of banda and corrido finales, as the accordion plays its last note. Through Lowery’s reggae corrido, we hear his “sonic home” rooted in Black and Brown Los Angeles.
—
Featured Image: still from Sarah La Morena’s “La Llorona” (2020)
—
Sara Veronica Hinojos is an Assistant Professor of Media Studies and on the advisory board for Latin American and Latino Studies at Queens College, CUNY. Her research focuses on representations of Chicanx and Latinx within popular film and television with an emphasis on gender, race, language politics, and humor studies. She is currently working on a book manuscript that investigates the racial function of linguistic “accents” within media, called: GWAT?!: Chicanx Mediated Race, Gender, and “Accents” in the US.
Alex Mireles is a PhD student in the Department of Feminist Studies at UC Santa Barbara. She writes on Latinx identity and queerness, labor, and global capitalism through aesthetic movements in fashion, beauty, media, and visual cultures. Her dissertation explores the queer potential and world-making capabilities of Chicanx popular culture through Mexican regional music, social media, queer nightlife, and film.
—

REWIND!…If you liked this post, you may also dig:
Boom! Boom! Boom!: Banda, Dissident Vibrations, and Sonic Gentrification in Mazatlán—Kristie Valdez-Guillen
Listening to MAGA Politics within US/Mexico’s Lucha Libre –Esther Díaz Martín and Rebeca Rivas
Ronca Realness: Voices that Sound the Sucia Body—Cloe Gentile Reyes
Echoes in Transit: Loudly Waiting at the Paso del Norte Border Region—José Manuel Flores & Dolores Inés Casillas
Sounding Out! Podcast #28: Off the 60: A Mix-Tape Dedication to Los Angeles–Jennifer Stoever
Femmes Fucking the Camera: Listening to the Sonics of Boudoir Photography

Pictured above areRaven Von Scrumptious (right) an Sepia Jewel (left), two burlesque dancers from San Diego, California. Raven and Sepia started “eye fucking” in burlesque classes with Coco L’Amour and later they transferred these gestures to the photo studio and the stage, gestures that as Juana Maria Rodriguez notes, “dance, flirt and fuck” (2014). “Eye fucking” is transmitting tease, a play with your audience that is coquettish. Eye fucking entails going beyond the gaze of the audience into a realm where you meet your inner erotic, your inner gaze. Eye fucking creates arousal, homosociality, agency, femme desire, confidence, and a queer space with a lot of glitter. As Smiley LaRose—the name I chose to take on as my student burlesque name—I have learned to “fuck the camera lens” from these two women and the burlesque community in San Diego, who encourage me to embrace what Celine Parreñas Shimizu calls “productive perversity.”
In this post, I reflect on the sonic intimacies between burlesque and boudoir photography. I am sharing part of a larger film project titled #GlitterBabes, where I tell a story of how burlesque as a recreational practice empowers women to engage their sensual selves. The film came about when I signed up for a Soloist Workshop and my burlesque stage persona Smiley LaRose was born. I tell this story through Glitter Tribe Studio, the first studio dedicated to the art of burlesque in San Diego.
In fact, both the dance and photography studios I write about here have an intimate relationship. The film starts with Smiley’s curiosity about how her classmates and teachers engaged the art of tease and navigated all the different aspects of it. As a fat performer, I was particularly interested in the way that my burlesque sisters and myself would navigate topics of body confidence, sensuality and stripping. As it turned out, these practices require a practice of listening to the details of our bodies and its engagement with musicality, the rhythm of our tease(s), and our awareness for how the camera can capture our corporeal erotic wavelengths both on and off stage.
In other words, I engage in ‘dirty listening’ to describe the sonics of boudoir photography and the erotic sounds that go into capturing sensuality in its most intimate ways. In their qualitative study of erotic photographers, Wentland and Muise found that in order to have a successful shoot it was crucial to create “relaxing and comfortable” spaces for femmes. A common practice among the photographers was to have “constant dialogue with their clients, both at the beginning and during the photo shoot, in order to help their clients relax.” They allowed femmes to have control over the shoot and explained every step along the way. In fact, as photo shoots progressed, several clients “requested shots that were more revealing than what they had initially discussed” (106). The findings by Wentland and Muise share many commonalities with the way photographers in San Diego also engage the practice of Boudoir, particularly the understanding that agency is experienced along a continuum and photographers support their clients by accommodating different techniques that can silence their negative self-talk.
At Bad Kitty Photography, where both Raven and Sepia had their shoots, a layer enabling femmes to get into an affective state of sensual comfort is music. To prepare for shoots, Bad Kitty asks their clients to think about their favorite music to set the mood. On their website, they list creating a music playlist as a recommendation to prepare for the shoot. This recommendation intrigued me and aroused an intellectual sonic orgasm. As a scholar of music, sound, and sexuality, their suggestion reminded me of a post by Robin James, where she argues that “we can understand the physical pleasures of listening to music, music making, and music performance as kinds of sexual pleasure.” In Modernity’s Ear: Listening to Race and Gender in World Music, Roshanak Khesti has described the erotic aspects of aurality, and has described the ear, as an ‘invaginated organ’ that penetrates the body with pleasure-in-listening. Here, music is consumed in a femme-centered space to get the model and its photographer to a state of intoxicating perversity.
Beyond the music recommendation, the photographer who worked with me also used sonic techniques to help me get relaxed and comfortable. Ashley Rae, aka “My Bomb Ass photographer,” no longer works at Bad Kitty, but her impact there particularly with other women of color clients is remembered. While we were choosing my outfits, I shared with Ashley, how nervous I was about not being able to make sexy faces. She looked at me and said, “It’s easy! All you have to do is pronounce ‘juice.’” She later asked me to look at the mirror while I practiced. The trick in the exercise was how slow I said “juice” the slowness and softness or my pronunciation created a shape in my lips that unconsciously also influenced the way my eyes moved. After juice she told me to pronounce “prune.” Ppppp-rrrr-uuuuuuu-nnnnnn—ee.
I look at my photos and I see the effect it created. “vocal utterances function as another kind of embodied gesture – opening the mouth and projecting sounds, words, and breath imprinted by the unique physical qualities of our inhabited bodily instruments,” as she points out in Sexual Futures, Queer Gestures, and other Latina Longings (124).

“Give me more bootyhole,” Ashley said.
Rodriguez asks, “what happens when I talk dirty to you? How does the address of speech transform the performative gesture of its utterance?” (125). Dirty talk– how my photographer engaged me in dialogue – contributed to my afloje (looseness) as the shoot progressed. The address of her speech, along with her gestures, made me get lost in her camera. Witnessing the way she touched herself–and the way she wanted me to touch my body–formed a collective vision of sensuality, one where all femmes of color could feel like goddesses. It was her dirty talk, the tone of her voice, and the power of her Black Femme gaze that helped me get there. Following Audre Lorde’s vision for the power of the erotics, we imaged a different world with her camera, a world where femmes eye fuck each other, and for each other, constantly displacing the male gaze. Her foreplay allowed me to listen to how my Eyes Talked, My Eyes Teased, My Eyes Fucked.
Beyond the shoot, the boudoir photos that she took of me would capture forever the fat perversity that she inspired in me. The energy we created inside that studio lingers in my skin. I remember her dirty talk and when we pose, my friends who have also gone through her spell also say, “give me more bootyhole” Like that, my remix yells “si, metete con mi Cucu!”

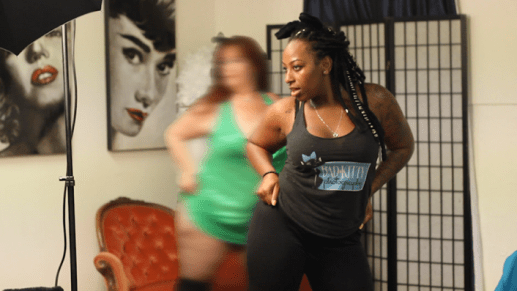

As a fat student of burlesque, my dirty talk, my dirty listening, is inspired by other women of color, fat performers, and porn stars. I gaze upon them for inspiration, guidance on eye fucking, and poses. On March 9, 2018, I participated in the second annual Plus Size Art Show at Meseeka Art studio in San Diego, California. I submitted 20 pieces of boudoir photography to the show that celebrated the bodies of five women of color plus-size burlesque performers from San Diego. They included Buttah Love, Raven VonScrumptious, Lucy May, Sepia Jewel and Smiley LaRose. The other art pieces in the show also centered fat perversity by presenting women in shibari, bikinis, nude, and boudoir.

Photographed by Ahnyung Nadine
The all-women DJ collective Chulita Vinyl Club de San Diego played at the show while people danced, drank, and viewed the live fat artwork in formation. Listening to the charlas in the room, you could hear fat women share the power they felt from seeing other fat women feeling sexy. One of the participants approached Sepia and Smiley to ask us if we were also exhibited in the artwork. We both pointed at our images, celebrating each other by complementing our sexy poses. She told us that it was her first time ever taking photos in lingerie, and that playing with the shoot was empowering. We both agreed, because as burlesque dancers and students, stripping to nakedness has had multiple effects on the way we viewed our bodies, and their sensuality. Can you listen to how we use boudoir, erotic art and burlesque to create a visual archive of fat-sex-positivity?
Although Raven was not able to attend the opening of the show, she saw it through Buttah’s Instagram story. When I texted Raven, she told me she almost cried from seeing her photos framed on the wall. Raven was art, a fat femme was art. But even though she was not there, her photos transmitted energy and a fat perversity: her fat eyes talked, her fat eyes teased, her fat eyes fucked us.

Prrruuuuuu-nnnnnnneeeeee
We moan.
—
All images courtesy of the author.
—
Yessica Garcia Hernandez is a doctoral candidate and filmmaker in the Department of Ethnic Studies at the University of California San Diego. Her scholarship bridges fan studies, sound studies, women of color feminisms, fat studies, girl studies, and sexuality/porn studies to think about intergenerational fans of Mexican regional music. Yessica earned her B.A. in Chicanx Studies from University of California, Riverside and an M.A. in Chicanx and Latinx Studies at California State University Los Angeles. She has published in the Journal of Popular Music, New American Notes Online, Imagining America, Journal of Ethnomusicology, and the Chicana/Latina Studies Journal. Her dissertation entitled, “Boobs and Booze: Jenni Rivera, the Erotics of Transnational Fandom, and Sonic Pedagogies” examines the ways in which Jenni Rivera fans reimagine age, gender, sexuality, motherhood, and class by listening to her music, engaging in fandom, and participating in web communities. She explores the social element of their gatherings, both inside and outside the concert space, and probe how these moments foreground transmissions of Latina power. Yessica’s broader research interests includes paisa party crews, Banda Sinaloense, Contestaciones, and Gordibuena/BBW erotics. She is a co-founder and member of the Rebel Quinceañera Collective, a project that utilizes art, music, photography, creative writing, filmmaking, and charlas to activate spaces for self-expression and radical education by and for youth of color in San Diego.
—
 REWIND!…If you liked this post, check out:
REWIND!…If you liked this post, check out:
Unapologetic Paisa Chingona-ness: Listening to Fans’ Sonic Identities–Yessica Garcia Hernandez
Freedom Back: Sounding Black Feminist History, Courtesy the Artists– Tavia Nyong’o
Mediated Sexuality in ASMR Videos–Emma Leigh Waldron



















Recent Comments