SO! Reads: Danielle Shlomit Sofer’s Sex Sounds: Vectors of Difference in Electronic Music

Distance, therefore, preserves a European austerity in recorded musical practices, and electroacoustic practice is no exception; it is perhaps even responsible for reinvigorating a colonial posterity in contemporary music as so many examples in this book follow this pattern–Danielle Shlomit Sofer, Sex Sounds, 14.

Sex Sounds: Vectors of Difference in Electronic Music (MIT Press, 2022) by Danielle Shlomit Sofer brings a complex analysis for contemporary de-colonial, queer and feminist readers. This book did its best to sustain an argument diving into eleven case studies and strongly problematising the Western white cis gaze. Sofer offers readers a new perspective in both the history of music and the decolonisation of that history.
In a moment when discussions of consent, censorship, pleasure, and surveillance are reshaping how we think about media, Sofer asks: What does sex sound like, and why does it matter? Their analysis cuts across high art and popular culture, from avant-garde compositions to pop music to porn, revealing how sonic expressions of sex are never neutral—they’re deeply entangled in gendered, racialized, and heteronormative structures. In doing so, Sex Sounds resonates with broader critical work on listening as a political act, aligning with ongoing conversations in sound studies about the ethics of hearing and the politics of voice, noise, and silence

The main focus of Sex Sounds is the historical loop of sexual themes in electronic music since the 1950s. Sofer writes from the perspective of a mixed-race, nonbinary Jewish scholar specializing in music theory and musicology. They argue that the way the Western world teaches music history involves hegemonic narratives. In other words, the author’s impetus is to highlight the construction of mythological figures such as Pierre Schaeffer in France and Karlheinz Stockhausen in Germany who represent the canon of the Eurocentric music phenomena.
Sex Sounds specifically follows the concept of “Electrosexual Music,” defined by Sofer as electroacoustic Sound and Music interacting with sex and eroticism as socialized aesthetics. The issue of representation in music is a key research focus navigating questions such as: “How does music present sex acts and who enacts them? ” as well as: “how does a composer represent sexuality? How does a performer convey sexuality? And how does a listener interpret sexuality?” (xxiv & xxix). Moreover, Sofer traces: “the threats of representation, namely exploitation and objectification” (xxxvii) as the result of white male privilege and the historical harm and violence this means (xiix & 271).
By exploring answers to these questions, Sofer successfully exposes how electroacoustic sexuality has historically operated as a constant presence in many music genres, as well as proving that music and sound did not begin in Europe nor belongs only to the Anglo-European provincial cosmos. Sex Sounds gives visibility to peripheral voices ignored by the Eurocentric canon, arguing for a new history of music where countries such as Egypt, Ghana, South Africa, Chile, Japan or Korea are central.
Sofer further vivisects the meaning of sexual sounds as not only Eurocentric and colonial but patriarchal and sexist. What is the history behind sex sounds in the electroacoustic music field? Can we find liberation in sex sounds or have they only reproduced dominance? Which role do sex sounds play in the territories of otherness and racial representation? Are there examples where minoritized people have reclaimed their voice? Sex is part of our humanity. But how do sex sounds dehumanize female subjects? These are more of the fundamental questions Sofer responds to in this study.

I aim, first and foremost, to show that electrosexual music is far representative a collection than the typically presented electroacoustic figures -supposedly disinterested, disembodied, and largely white cis men from Europe and North America –Sofer, Sex Sounds,(xvi).
The time frame of the study ranges from 1950 until 2012, analysing four case studies. Sofer divides the book in two parts: Part I: “Electroacoustics of the Feminized Voice” and Part II: “Electrosexual Disturbance.” The first part contextualizes “electrosexual” music within the dominant cis white racial frame. The main argument is to demonstrate how many canonic electroacoustic works in the history of Western sound have sustained an ongoing dominance as a historical habit locating the male gaze at the center as well as instrumentalizing the ‘feminized voice’ as mere object of desire without personification and recognition as fundamental actor in the compositions. Under such a premise, Sofer vivisects sound works such as “Erotica” by the father of Musique Concretè Pierre Schaffer and Pierre Henry (1950-1951), Luc Ferrari’s “les danses organiques” (1973) and Robert Normandeu’s “Jeu de Langues” (2009), among other pieces.
Luc Ferrrari’s work from 1973 is one of many examples in which Sofer makes evident the question of consent, since the women’s voices he includes were used in his work without their knowledge, a pattern of objectivation that mirrors structures of patriarchal domination. Sofer “defines and interrogates the assumed norms of electroacoustic sexual expression in works that represent women’s presumed sexual experience via masculinist heterosexual tropes, even when composed by women” (xivii-xiviii). Sofer emphasises the existence of “distance” as a gendered trope in which women’s audible sexual pleasure is presented as “evidence” in the form of sexualized and racialized intramusical tropes. Philosophically speaking, this phenomena, Sofer argues, goes back to Friedrich Nietzsche and his understanding of the “women’s curious silence” (xxvii). In other words, a woman can be curious but must remain silent and in the shadows.
This is the case in Schaeffer and Henry’s “Erotica” (1950-1951), one of the earliest colonial impetus to electrosexual music in which female voices are both present and erased, present in the recording but erased as subjects of sonic agency, since the composers did not credit the woman behind the voice recordings. She has no name nor authorship, but her sexualized voice is the main element in the composition. This paradox shows the issue of prioritising the ‘Western’ white European cis male gaze. This gaze uses women’s sexuality as a commerce where only the composer benefits from this use. This exposes the problem of labor and exploitation within electroacoustic practice historically dominated by white men.
“Erotica” stands out for its sensual tension, abstract eroticism, and experimental use of the body as both subject and instrument. This work belongs to the hegemonic narrative of electroacoustic music with the use of sex sounds as aesthetic objects that insinuate erotic arousal as a construct of the male gaze.
Through examples like “Erotica” Sofer strongly questions the exclusion of women as active agents of aesthetic sonic creation since: “electroacoustic spaces have long excluded women’s contributions as equal creators to men, who are more typically touted as composers and therefore compensated with prestige in the form of academic positions or board dominations” (xxxix). This book considers: “the threats of representation, namely exploitation and objectification” (xxxvii). Here we navigate the questions of how something is presented, by whom, and with which profit or intention. In other words, how sounds: “are created, for what purposes, and in turn, how sounds are interpreted and understood” (xxxiii).These are problems rooted in both patriarchy and capitalism.
This book is a strong contribution to decolonize the history of music as we know it, although the citations here could be richer, including studies by Rachel McCarthy (“Marking the ‘Unmarked’ Space: Gendered Vocal Construction in Female Electronic Artists” 2014), Tara Rodgers (“Tinkering with Cultural Memory: Gender and the Politics of Synthesizer Historiography” 2015), and the work of Louise Marshall and Holly Ingleton, who used intersectional feminist frameworks to analyze the work of marginalized composers (including women of color) and the curatorial practices that shape electronic music history. Also, not to forget: Chandra Mohanty’s “Under Western Eyes: Feminist Scholarship and Colonial Discourses” (1988).
Musical artist Sylvester
I argue that, although many composers of color work in electronic music, the search term ‘electroacoustic’ remains exclusionary because of who declares themselves as an advocate of this music, and not necessarily in how their music is made–Sofer, Sex Sounds, (xiv).
After a deep dive into the genealogy of the patriarchal practices in electroacoustic music understood as electrosexual works (hence: “Sex is only re-presented in music p. xxix), Sofer moves to the territory of feminist contra-narratives. In the second part of their study, Sofer offers sonic practices and concrete examples that: “break the electroacoustic mold either by consciously objecting to its narrow constraints or by emerging from, building on, and, in a sense, competing with a completely different historical trajectory” (xlvi). Contra-narratives from the racialized periphery and underground landscapes appear in this book as case studies to hold the argument and expand the homocentric and patriarchal telos found even in the sonic archives as well as the Western theoretical corpus. These ‘Others’ reclaim their voices going a step further and gaining recognition.
After examining examples of racialisation and objectification, Sofer selects some case studies from 1975 to 2013 in the second chapter of this section titled: “Electrosexual Disturbance.” In this section, Sofer also points to new forms of exclusion and instrumentalisation via “racial othering,” specifically in the context of popular music such as Disco where we find an emphasis on the feminized voice. Disco, as a genre rooted in Black, queer, and marginalized communities, inherently grappled with racial and gendered dynamics. Donna Summer’s “Love to Love You Baby” (1975) exemplifies this tension.
The track’s erotic vocal performance (23 simulated orgasms over 16 minutes) became emblematic of the hypersexualization of Black women in popular music. Summer’s persona as the “first lady of love” reinforced stereotypes of Black female sexuality as inherently exotic or excessive, a trope traced to racist and sexist historical narratives. Simultaneously, disco provided a space for liberation: Black and LGBTQ+ artists like Summer, Sylvester, and Gloria Gaynor used the genre to assert agency over their identities and bodies, challenging mainstream exclusion. The tropes of sex and race are a paradoxical combination bringing both oppression as well as liberation.
Sofer argues that Summers was commercially recognized but her figure as a composer was destroyed, creating consequently a hierarchy of labor. She was acknowledged for her amazing sexualized voice and performance on stage, but not recognized as a musician or equal to music producers. Here we see the practice of epistemological discrimination and extreme racial sexualisation. On the positive side, Summer became the Black Queen idol for gay liberation. Nevertheless, she remained as the sexualized and racial voice of the seventies.
Sofer also presents the case of ex-sex worker, sex-educator and radical ecosex-activist Annie Sprinkle collaborating in a post-porn art video with the legendary Texan and lesbian composer Pauline Oliveros. For Sprinkle and Oliveros, Sofer offers a different phenomena at work, since both queer-women/Lesbian-women collaborated from the point of feminist independence and sexual liberation coming together for educational purposes.

Sluts & Goddesses (1992) is a porn film with an Oliveros soundtrack, produced by radical women– with only women–in a self-determined frame. The movie offers an example of collaboration moving from avantgarde sound composition expertise to trashy whoring and interracial lesbian power. This example was rare, but inspiring for the coming generations. Two lesbian Titans united for electrosexual disturbance from the feminist gaze, Sprinkle and Oliveros were a duo that broke silence.
This book revisits the acousmatic in its electronic manifestations to examine and interrogate sexual and sexualized assumptions underwriting electroacoustic musical philosophies.–Sofer, Sex Sounds, (xxi)
Sofer’s Sex Sounds enters into a vital and still-emerging conversation about how sound—particularly sonic expressions of sex and eroticism—shapes, disrupts, and reinscribes power. At a time when sonic studies increasingly reckon with embodiment, affect, and intimacy, Sofer brings a feminist and queer critique to the center of how we listen to, interpret, and culturally regulate the sounds of sex. Their book invites us to reconsider not only what we hear in erotic audio, but how we’ve been taught—socially, politically, morally—to hear it.
This book doesn’t just fill a gap—it pushes the field toward a more nuanced, bodily-aware mode of scholarship. For SO! readers, Sex Sounds offers both a provocation and a methodology: it challenges us to hear differently, to ask how power works not only through what is seen or said, but through what is moaned, whispered, muffled, or made to be heard too loudly.
—
Featured Image: “Stamen,” by Flickr User Sharonolk, CC BY 2.0
—
Verónica Mota Galindo is an interdisciplinary researcher based in Berlin, where they study philosophy at the Freie Universität. Their work goes beyond the academic sphere, blending sound art, critical epistemology, and community engagement to make complex philosophical ideas accessible to broader audiences. As a dedicated educator and sound artist, Mota Galindo bridges the gap between academic research and lived material experience, inviting others to explore the transformative power of critical thought and creative expression. Committed to bringing philosophy to life outside traditional boundaries, they inspire new ways of thinking aimed at emancipation of the human and non-human for collective survival.
—

REWIND!…If you liked this post, check out:
Into the Woods: A Brief History of Wood Paneling on Synthesizers*–Tara Rodgers
Ritual, Noise, and the Cut-up: The Art of Tara Transitory—Justyna Stasiowska
SO! Reads: Zeynep Bulut’s Building a Voice: Sound, Surface, Skin –Enikő Deptuch Vághy
On the Poetics of Balloon Music: Sounding Air, Body, and Latex (Part One)

I see them in the streets and in the subway, at dollar stores, hospital rooms, and parties. I see them silently dangling from electrical cables and tethered to branches of trees. Balloons are ghost-like entities floating through the cracks of places and memories. They are part of our rituals of loss, celebration and apology. Yet, they are also part of larger systems, weather sciences, warfare and surveillance technologies, colonialist forces and the casual UFO conspiracy theory. For a child, the ephemeral life of the balloon contrasts with the joy of its bright colors and squeaky sounds. Psychologists encourage the use of the balloon as an analogy for death, while astronomers use it as a representation for the cosmological inflation of the universe. In between metaphors of beginning and end, the balloon enables dialogues about air, breath, levity, and vibration.
The philosopher Luce Irigaray argues that Western thought has forgotten air despite being founded on it. “Air does not show itself. As such, it escapes appearing as (a) being. It allows itself to be forgotten,” writes Irigaray. Air is confused with absence because it “never takes place in the mode of an ‘entry into presence.'” Gaston Bachelard, in Air and Dreams, calls for a philosophy of poetic imagination that grows out of air’s movement and fluidity. For Bachelard, an aerial imagination brings forth a sense of the sonorous, of transparency and mobility. In this article, I propose exploring the balloon as a sonic device that turns our attention to the element of air and opens space for musical practices outside classical traditions. Here, the balloon is defined broadly as an envelope for air, breath, and lighter-than-air gases, including toy balloons, weather balloons, hydrogen and hot-air balloons.
PLACE /
Vertical Dimension: Early Experiments in Ballooning, Sounding, and Silence
On September 1939, Jean-Paul Sartre was assigned to serve the French military in a meteorological station in Alsace behind the frontline. His duties consisted of launching weather balloons, monitoring them every two hours and radioing the meteorological observations to another station. Faced with the dread of war and an immediate geography that he compared to a “madmen’s delusion,” Sartre took his gaze upwards to the weather balloon and its surrounding atmosphere to find refuge. In Notebooks from a Phony War, Sartre describes the sky as “my vertical dimension, a vertical prolongation of myself, and also abode beyond my reach.” The balloon becomes a vessel for an affective relationship with the atmosphere that is mediated by the sounding of meteorological data. While gazing into the upper air, Sartre experiences a tension between the withdrawn”frozen blackness” of the atmosphere and the pull for feelings of oneness with it.

Falling Stars as Observed From the Balloon, Travels in Air by James Glaisher, 1871
The first balloonists to explore the atmosphere felt similar sensations of belonging by moving along masses of air, and at the same time, experiencing a deep sense of otherworldliness. Despite the dangerous enterprise, early balloon travelers repeatedly recounted expressions of the sublime associated with the acoustic qualities of the upper air. Late 18th and 19th-century balloon literature features countless textual soundscapes of balloon ascents that reveal how the experience of sound and silence helped frame early narratives of “being in air/being one with air.”
Ballooning developed in France and England among the emergent noise of industrialized urban life. The balloon prospect, as the author Jesse Taylor put it, spoke to “the Victorian fantasy of rising above the obscurity of urban experience.” Floating over the city, the English aeronaut Henry Coxwell describes hearing “the roar of London as one unceasing rich and deep sound.” In the same spirit, the balloonist James Glaisher compares the “deep sound of London” to the “roar of the sea,” whose “murmuring noise” is heard at great elevations. Ascending to higher altitudes, Coxwell hears the sounds from the earth become “fainter and fainter, until we were lost in the clouds when a solemn silence reigned.”
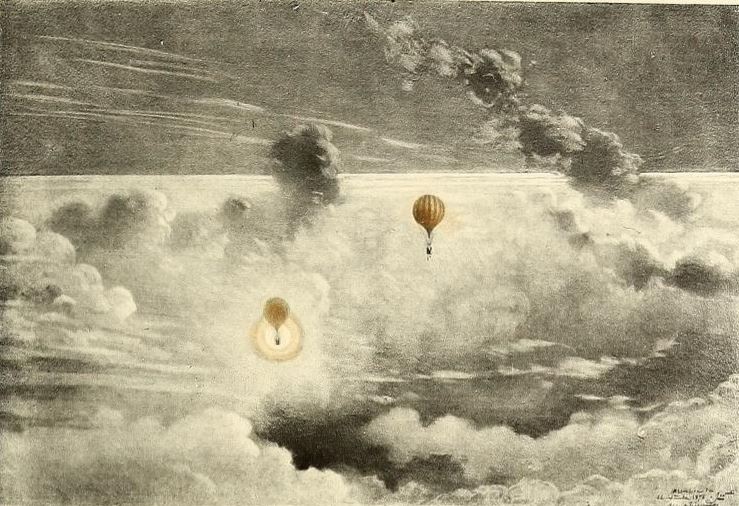

L’exploration de l’air, In Histoire des ballons et des aÇronauts cÇläbres, 1887
The balloon not only allowed access to a panoramic and surveilling gaze in the midst of boundless space but also a privileged access to a place of quietude and silence. In the memoir Aeronautica (1838), Thomas Monck Mason speaks to this point when he writes, “no human sound vibrated (…) a universal Silence reigned! An empyrean Calm! Unknown to Mortals upon ‘Earth.” According to Mason, when the balloonist goes “undisturbed by interferences of ordinary impressions,” like the sounds from terrestrial life, “his mind more readily admits the influence of those sublime ideas of extension and space.”
The experience of silence in the upper air brought forward in the Victorian white elite the longing for freedom, individuality, and assertion of social identity. Balloon flights provided a form of escapism from the confines of city walls reverberating with the aural manifestations of the Other. In Victorian Soundscapes, John Picker examines the struggles of London’s upper class of creatives (academics, doctors, artists and clergy) in finding spaces of silence away from the bustling noise of the urban environment. During the mid-19th century, the influx of immigration and the rise of commercial trade and street musicians altered the soundscape of the city. As Picker documents, the English elites rallied against this emergent aurality through racialized listening made evident by the use of sonic descriptors like invasion and containment that underlined anxieties related to the dilution of national identity, culture, class division and territory. For the elite, to physically ascend above the noise of the Other into the silent regions of the atmosphere via balloon, an instrument that dramatizes scientific prowess, validated an auditory construction of whiteness organized around ideals of order, rationality and harmony.
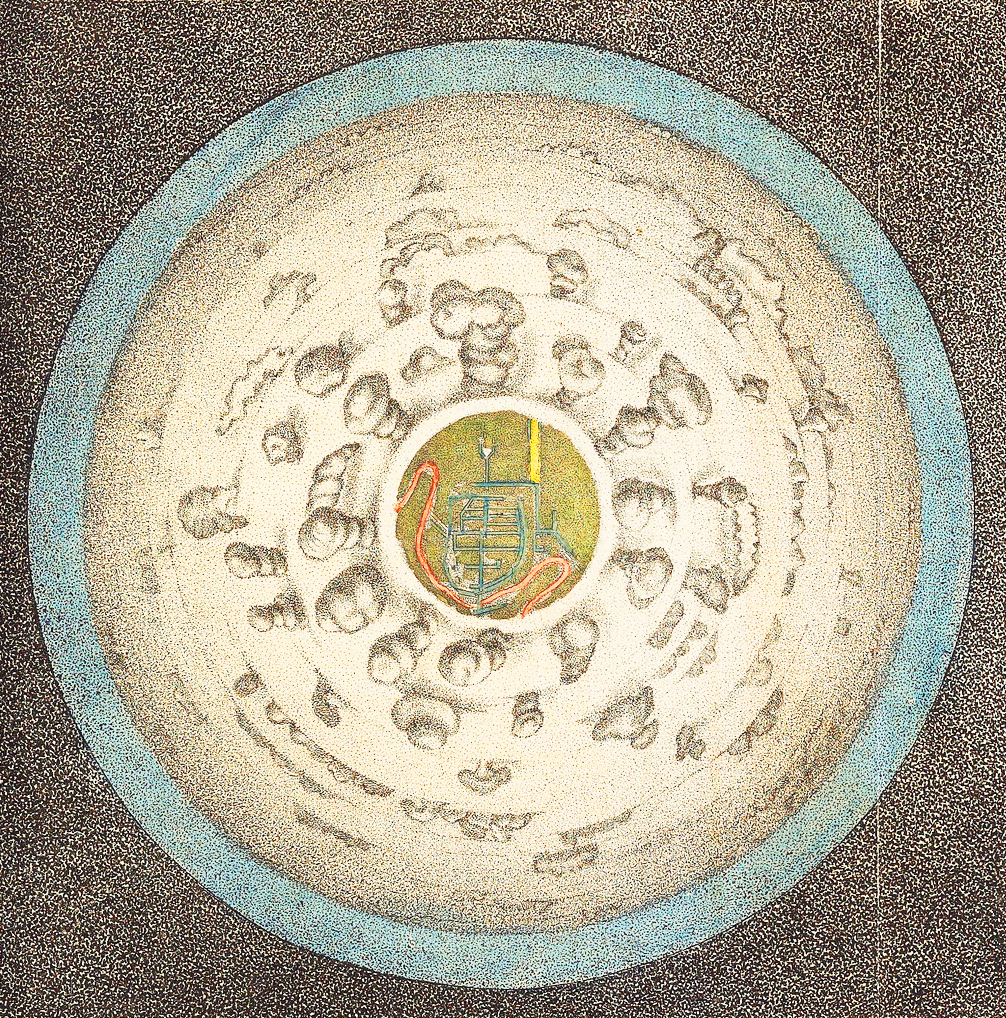

Circular View From the Balloon in Airopaidia by Thomas Baldwin, 1786
The descriptions of balloon ascents featured in James Glaisher’s book Travels in the Air (1871) are a vivid manifestation of these ideals. Experiences of floating at high altitudes were often met with poetic reports on the “sublime harmony of colors, light and silence,” the “perfect stillness,” and the “absolute silence” reigning “supreme in all its sad majesty.” The nineteenth century’s constructs of “harmony” and “quietude,” argues Jennifer Stoever, were markers of whiteness used to segregate and de-humanize those who embodied an alternative way of sounding. The Victorian balloon memoir echoes the construction of this sonic identity rooted in the white privilege of being lighter-than-air and claiming atmospheric silence. The balloonist Camille Flammarion, upon hearing “various noises” from the “dark earth” below, questions what prompts “the listening ear” to be sensitive to difference. “Is it the universal silence which causes our ears to be more attentive?” asks the aeronaut.

Balloon Prospect, In Airopaidia, Thomas Baldwin, 1786
Balloonist’s encounters with silence in the upper air and the sigh of “boundless planes” and “infinite expanse of sky” were accompanied by feelings of safeness and overwhelming serenity. Elaine Freedgood argues that the balloon with its silk folds and wicker baskets were a perfect container for states of regression and the suspension of the boundaries of the self into an oceanic feeling of at-oneness with the atmosphere. According to the author, the self and sublime become momentarily entangled originating a sense of heroic masculinity, power, and the rehearse of imperial and colonial ventures. This emotional state justified an unprecedented mobility and the sense of losing oneself to the whims of the wind with no preoccupations of where to land. However, in an image that contrasts the privileges of mobility, Frederick Douglass uses the metaphor of the balloon as the terrifying anxiety of uncertain landing – either in freedom or slavery. The novel Washington Black (2018) by Esi Edugyan, deals with similar issues by fictionalizing the balloon ascent and traveling of a young slave, whose hearing is tuned to the “ghostly sound“ of human suffering coming from beneath.
By late 1780s, thousands of people witnessed the European wave of balloon flights, but only a small fraction had access to them. Mi Gyung Kim, author of The Imagined Empire, draws attention to the silence imposed on the figure of the “balloon spectator” whose dissident voices were erased by the dominant colonial narrative of aerial empire. Mostly, the balloon spectator is featured in Victorian texts within a soundscape of affects characterized by “vociferations of joy, shrieks of fear” and “expressions of applause” that advanced the dominant colonial narrative.
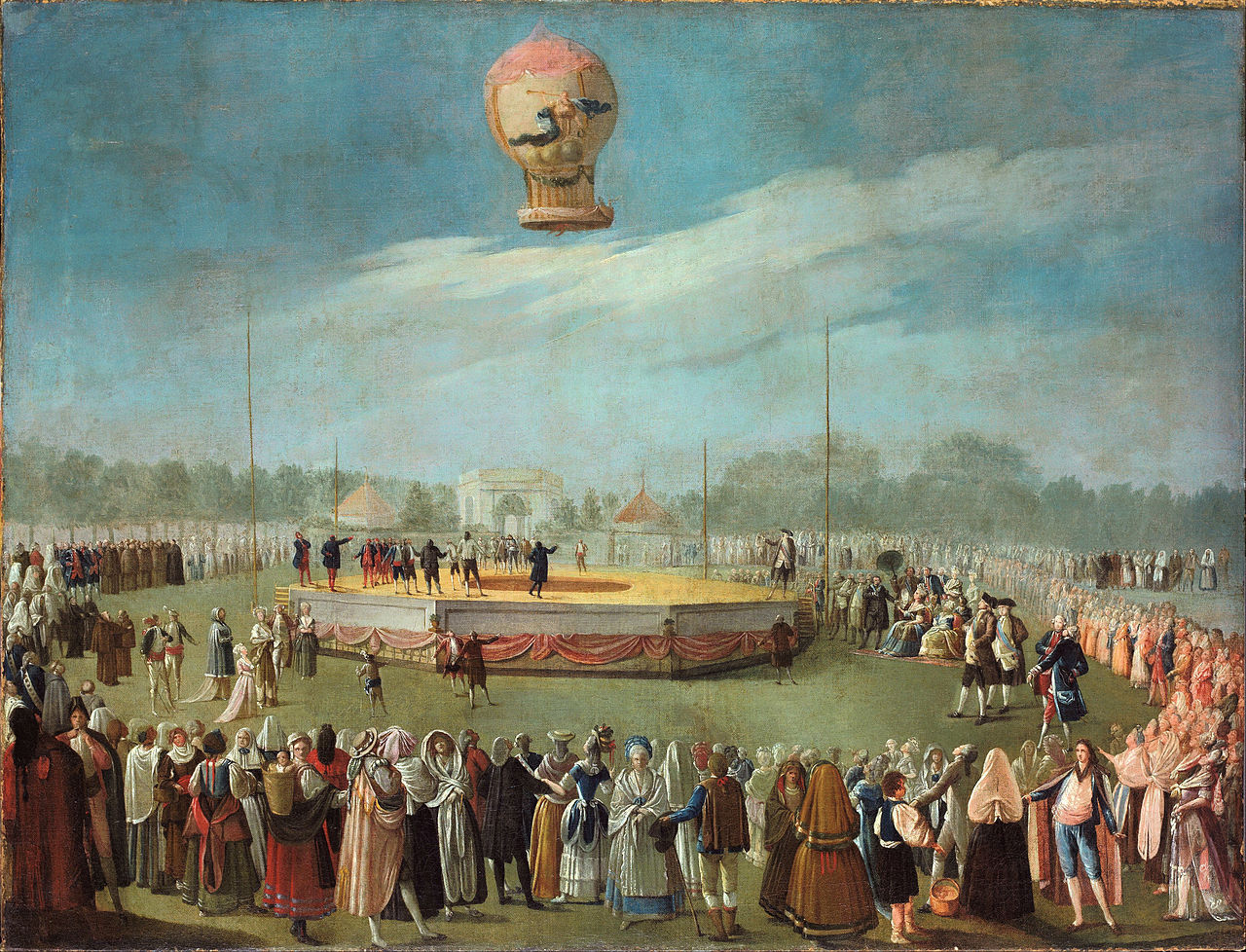
Ascent of a Balloon in the Presence of the Court of Charles IV by Antonio Carnicero, 1783
Although explorations in sound were one of the many goals to legitimize the balloon as an instrument in modern natural philosophy, the scientific utility of the balloon succumbed to spectacle and entertainment. Early aeronauts tried to use their voices and speaking trumpets to sound the atmosphere and experiment with echo as a measurement of distance. Derek McCornack in his book Atmospheric Things, says that these balloonists were most of all “generating a sonorous affective-aesthetic experience” with the atmosphere. Along with scientific tools, balloonists often ascended with musical instruments and, in other instances, the balloon itself became the stage for operatic performances. More than a century before modern composers had transformative encounters with silence in anechoic chambers, aeronauts had already described its subjective qualities and effects in detail. In 1886, the photographer John Doughty and reluctant balloon traveler, while floating in a silent ocean of air, recalls hearing only two bodily sounds: “the blood is plainly heard as it pulses through the brain; while in moments of extra excitement the beating of the heart sounds so loud as almost to constitute an interruption to our thoughts.”
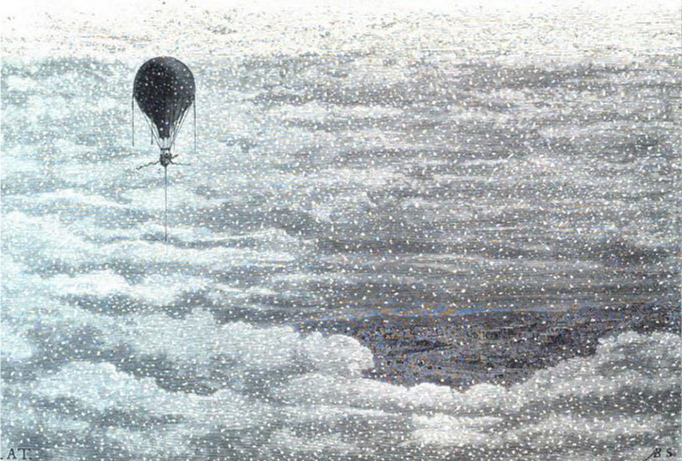

Travels in the Air, James Glaisher, 1871
PROBE /
I feel like a balloon going up into the atmosphere, looking, gathering information, and relaying it back. Rachel Rosenthal, 1985
The first untethered balloon ascents happened between 1783 and 1784. In current literature, this period is most cited for the patent of the steam engine, the beginning of the carbonification of the atmosphere by the burning of coal, and the start of the Anthropocene. In the industrialized society, the balloon floats through irreversibly modified atmospheres. “We are still rooted in air,” writes Philippopoulos-Mihalopoulos. However, this air is partitioned and engineered to facilitate consumerism, war, terror and pollution.
Contemporary art practices using the balloon address some of these concerns. The balloon functions as an atmospheric probe that reveals “invisible topographies” and “politics of air” such as human interference, air quality, air ownership, borders, surveillance and the privileges of buoyancy. As a playful, non-threatening object, the balloon can elicit practices of inclusivity (e.g. balloon mapping) and affect. The transmission and reception of sound and music through the balloon help manifest air’s qualities and warrants artistic and social encounters with weather systems.

“Travels in the Air” by James Glaisher, 1871
During the 6th Annual Avant-Garde Festival parade going up Central Park West in 1968, the body of the cellist Charlotte Moorman rose a few feet above the floor attached to a bouquet of helium-filled balloons. This led the police to chase her and demand an FCC license for flying, to which Moorman replied: “I’m not flying – I’m floating.” Moorman was performing a piece called Sky Kiss, conceived by the visual artist Jim McWilliams that involved cello playing suspended by balloons.
In an interview for the book Topless Cellist by Joan Rothfuss, McWilliams explains that the original concept of Sky Kiss was to sever the connection between the cello’s endpin and the floor and expand the idea of kiss to an aerial experience. According to Rothfuss, McWilliams intended this piece to be an expression of the ethereal. But Moorman preferred the playfulness and the communal experience of the airspace. Instead of avant-garde music, she played popular tunes like “Up up and away” and “The Daring Young Man on the Flying Trapeze.” Dressed with a super-heroin satin cape, Moorman infused Sky Kiss with humor and visual spectacle, posing a challenge to the restrictive access to buoyancy.

Charlotte Moorman and Nam June Paik, Sky Kiss by Jim McWilliams, above the Sydney Opera House Forecourt, 1976, Kaldor Public Art Project 5, Photo by Karry Dundas
Furthermore, Charlotte Moorman collaborated with sky artist Otto Piene to establish the right quantities of lighter-than-air gas to reach higher altitudes. Otto Piene, was a figure of the postwar movement Zero and coined the term Sky Art to describe his flying sculptures, multimedia balloon operas, and kinetic installations. For Piene, a child growing up during World War II, “the blue sky had been a symbol of terror in the aerial war.” The balloon collaboration between Charlotte Moorman and Otto Piene was a form of acknowledging aerial space in a musical and peaceful way. In his manifesto Paths to Paradise (1961), Piene questions: why do we have no exhibitions in the sky?(…) up to now we have left it to war to dream up a naive light ballet for the night skies, we have left it up to war to light up the sky.
Phil Dadson’s work Breath of Wind (2008) lifts an entire brass band of 24 musicians into the sky with 17 hot-air balloons. Brass instruments, usually associated with moments of revelation in religious texts, serve here as a calling for an aesthetic experience of wind and air currents. Since 1970s, Dadson’s environmental activism has brought forward sonic tensions between the human subject and Aeolian forces, as in Hoop flags (1970), Flutter (2003) or Aerial Farm (2004).
Similarly, the artist Luke Jerram displaces the experience of a concert hall to the sky. His project Sky Orchestra comprises of seven hot-air balloons floating across a city with speakers playing a soundscapes design to induce peaceful dreams. The hot-air balloon orchestra ascends at dawn or dusk so the airborne music can reach people’s homes during sleep or while in states of semi-consciousness. The sound-targeting of residential areas during periods of dimmed awareness exposes the entangling capacities of airspace, and the vulnerability of the private space.
Artist and architect Usman Haquem utilizes a cloud of helium balloons as a platform to identify and sonify changes in the electromagnetic spectrum. This project, Sky Ear (2004), reveals our meddling with the urban Hertzian culture via mobile phones and other electronic devices. Andrea Polli’s environmental work features sonifications of data sets captured by weather balloons. These sonifications provide audiences an emotional window to frame complex climate data. In Sound Ship (descender 1) by Joyce Hinterding and David Haines, an Aelion harp is attached to a weather balloon that ascends into the edges of space. The result is a musical trace of the vertical volume of our atmosphere and the sonification of masses of air as the balloon journeys upwards.
Haines and Hinterding, Sound Ship (decender1), 4-min extract, 2016
Yoko Ono and John Lennon created similar exercise in sounding in the film Apotheosis (1970). A boom microphone and camera attached to a hydrogen balloon ascends over a small English town documenting a sonic geography of the upper air. The artists stay in the ground as the balloon rises. In a period of great media spectacle, the couple choses to stay with trouble while balloon records Earth’s utterances slowly fading into atmospheric silence.
It is important to note that these musical and sound based works that expose the physicality of air movements and assemble affective meanings with atmosphere and weather systems are not particular to contemporary practices. The scholar Jane Randerson draws attention to indigenous modes of knowing and sensing air and the weather that incorporate sounding instruments. In Weather as Medium, Randerson writes: “in Indigenous cosmologies, the sense of interconnectedness “discovered” in late modern meteorological science merely described what many cultures already sensed and encoded in social and environmental lore.”
The balloon has a lighter than air object mediates our relationship with the airspace and offers opportunities to expand our aerial imagination. By sensing changes in the atmosphere, the balloon is a platform that generates knowledge and can help us experiment with new forms of being-in-air some inclusive and empowering, others much more invested in exclusivity sounded through the rare air of silence and the silencing power dynamics fostered via the view from above.
—
I would like to express my immense gratitude to Jennifer Stoever for editing this paper and for sharing her scholarship and input on this article. Thank you to Phil Dadson for sharing his video.
—
Featured Image: Scientific Balloon of James Glaisher, 1862, Georges Naudet Collection, Creative Commons
—
Carlo Patrão is a Portuguese radio producer and independent researcher based in New York city.
—
 REWIND! . . .If you liked this post, you may also dig:
REWIND! . . .If you liked this post, you may also dig:
Instrumental: Power, Voice, and Labor at the Airport – Asa Mendelsohn
Botanical Rhythms: A Field Guide to Plant Music -Carlo Patrão
Sounding Out! Podcast #58: The Meaning of Silence – Marcella Ernest


















Recent Comments