- by jaquial
- in Aesthetics, American Studies, Article, Black Studies, Cultural Studies, Diasporic Sound, Hip Hop, History, Identity, jazz, Latin American Studies, Listening, Memory, Music, Music Production, Popular Music Studies, Recording, Rhetoric, Sampling and Remix Culture, Sound, Sound and Pleasure, Sound Studies, Soundscapes, Technology
- 1 Comment
The Sonic Rhetoric of Quincy Jones (feat. Nasir Jones)

.
The passing of Quincy Jones has left a silence that feels almost impossible to fill. Every time I play Thriller at home now, it’s no longer just a celebration of his unparalleled artistry. It’s a ritual to sit with his legacy, listen more closely, and honor how his music shaped the sound of memory itself. With each spin of the record, my family and I find ourselves inside his arrangements, held by their richness, precision, and sense of story as though the music is breathing with us, speaking back across time. Jones’s work was never just production; it was communication. A language of sound connected us to melody and beat and the fuller spectrum of emotion, culture, and memory that lives in Black music.
This piece joins a tradition of Black sonic remembrance that Sounding Out! has previously offered in moments of profound cultural loss, from Regina Bradley’s remembrances of listening to Whitney Houston on the radio with her mother to Ben Tausig’s reflection on Prince’s passing to Kristin Moriah’s meditation on Savion Glover’s tap dance tribute to Amiri Baraka. Such pieces remind us that mourning Black artists is not only about personal grief; it’s about listening to the soundscapes they left behind, tracing how their artistry shaped how we collectively move, mourn, and remember. Houston’s voice, much like Jones’s production, was a vessel of Black sonic innovation, shaping how we collectively move, mourn, and remember. Like Prince, Jones’s catalog is a vast archive of Black sonic innovation, where every horn line, bass groove, and percussive hit tells part of a larger story about Black life, joy, survival, and creativity. Jones, like Baraka, understood the radical potential of sound to entertain and agitate, educate, and summon history into the present. Writing about Jones now in the quiet left by his absence is a mourning and a celebration, an offering of flowers in the form of careful attention, deep gratitude, and collective remembrance. This is a way of honoring him as a producer or composer and as a practitioner of sonic rhetoric, a storyteller who spoke through sound and whose language of rhythm and harmony shaped how we feel, remember, and belong.
Two new books published in 2024, Matthew D. Morrison’s Black Sound and Earl H. Brooks’s On Rhetoric and Black Music, arrived at a particularly poignant moment, offering critical frameworks for understanding sonic rhetoric as a vital Black cultural practice. Morrison positions Black music as a vessel for cultural identity and history, emphasizing how it carries narratives that transcend mere auditory pleasure. Brooks extends this argument, demonstrating how Black music functions as a living, breathing rhetorical form, shaping and reshaping cultural identity and narrative with each performance, each recording, and each arrangement. That these books emerged in the same year the world lost Quincy Jones feels deeply significant, a reminder that his life’s work embodies precisely what they describe. Jones mastered using rhythm, melody, and arrangement to shape cultural memory and invite reflection. His genius does not reside solely in his ability to create captivating music but rather in his ability to layer each note with history, emotion, and meaning, sound as storytelling, sound as cultural conversation.
As I reflect on Quincy Jones’s legacy, I realize that his production and compositional skills have profoundly changed my understanding of sound. My admiration for Jones’s mastery of sound and his unique way of using music to communicate drove me to explore sound rhetoric more profoundly, especially how his work became the foundation of new sonic storytelling. His work allows me to imagine myself as a young Black boy, playing with sound and allowing it to communicate in ways that speak to the world. I am grateful for his inspiration, enabling us to envision the possibilities of sound and its power to connect us all. To honor Quincy Jones in rhetoric and sound, we must recognize his pioneering contributions to music as a form of communication. By studying his innovative approaches and the sonic landscapes he crafted, we can deepen our understanding of how sound shapes cultural narratives and personal identities. Engaging with his work encourages us to appreciate music’s profound impact on our lives and the stories it tells, ensuring that his legacy continues to inspire future generations of artists and listeners alike.

For readers who may not be as familiar with his legacy, Quincy Jones is one of the most influential and celebrated figures in music history. His career spans more than seven decades, marked by numerous Grammy Awards, groundbreaking collaborations, and an ability to shape the sound of entire musical eras. Jones’s journey into music began with a chance discovery that would define the course of his life. As a young boy, he broke into an armory and found an upright piano, sparking his lifelong passion for music. This serendipitous moment led him to explore various instruments, from percussion to trombone, sousaphone, and eventually the trumpet, which would become his instrument of choice. These formative experiences gave Jones a diverse and rich understanding of sound that he would later weave into his compositions. His journey through different musical styles, be it jazz, R&B, or orchestral arrangements, allowed him to develop a unique ability to merge genres and cultures, creating works that resonated on a global scale. Jones’s work as a producer, composer, and arranger redefined what it meant to be a producer in the music industry, elevating the role to that of a creative force, an artist in their own right. Most famously known for his work with Michael Jackson, Jones’s sonic contributions to Thriller transformed pop music and how producers and artists interact to create timeless music. His groundbreaking approach to music production changed how the world listens to music, showing how sound can transcend entertainment and become a powerful form of cultural communication.

For example, celebrating the Thriller album with my children has been an ongoing discovery. I am captivated by their responses to the music. They quickly catch specific sounds, anticipate instrumental flourishes, and react to subtle details, proving the immersive quality of Quincy Jones’s work. His production goes beyond entertainment; it engages listeners, inviting even young ears to feel part of the experience. The power of sonic storytelling is the ability to craft a narrative or evoke emotion purely through sound without relying on visuals or lyrics alone. Quincy Jones’s genius lies in how he layers instruments, sound effects, and vocal textures to create mood and atmosphere, building stories that listeners can feel unfolding around them. Sonic storytelling turns production into a cinematic experience, where a sudden bassline shift, a carefully placed synth, or an eerie silence all contribute to the larger emotional arc of a song. Jones doesn’t just produce songs. He builds immersive worlds through sound, showing how music, at its best, can tell stories as vividly as any film or novel. Songs such as “Thriller,” “Beat It,” and “Billie Jean” epitomize Jones’s mastery of this craft. Thriller is a prime example of his brilliance, each track meticulously balancing complex soundscapes with universal appeal.
With eerie beats, haunting synths, and Vincent Price’s chilling monologue, “Thriller” has become synonymous with Halloween, transforming it into an auditory icon that reshapes how we experience the holiday. It has a layered, cinematic arrangement, where Jones fuses a creeping synthesizer line with lush orchestral swells and Vincent Price’s velvety horror monologue. Each sonic element functions as a narrative device, placing the listener inside a haunted space where sound, the creak of a door, and the hiss of wind become part of the story. Brooks’s On Rhetoric and Black Music reminds us that sound arrangements can evoke emotion and memory, and Jones’s work exemplifies that power.
Then, consider the storytelling pulsing in the bassline of “Billie Jean,” a throbbing heartbeat grounding the song’s tale of obsession, fame, and denial in something bodily, felt in the chest and gut before the mind catches up. With every layered texture, from the crisp snap of the drum machine to the soaring, wordless vocal harmonies, Jones does not simply produce music; he scripts sonic stories where Black creativity and cultural history converge in every beat.
Jones’s approach to production embodies this idea, transforming how we listen and engage with music. Take “Wanna Be Startin’ Somethin’,” where layered percussion, call and response vocals, and a pulsing bassline create a sonic landscape that feels alive, constantly shifting and evolving. The song’s now iconic “Mama say mama sa mama coo sa” chant reaches back to the Cameroonian makossa tradition, embedding a diasporic history within a global pop hit (listen to the opening seconds of Manu Dijbango’s 1972 “Soul Makossa” to hear the resonance).
Then, in “Human Nature,” Jones works in the opposite direction, crafting an atmospheric, dreamlike arrangement where gentle synth pads and delicate electric guitar melodies wrap around Michael Jackson’s voice like mist, evoking a sense of vulnerability and wonder. These tracks, like so many in Jones’s catalog, do not merely present melodies and rhythms. They create spaces where memory, emotion, and history converge.
Jones’s ability to craft soundscapes has long extended beyond Thriller, both backward and forward in time. His track “Soul Bossa Nova” (1962), famously featured in the Austin Powers films, evokes nostalgia and joy, transporting listeners to memories of sunny beach days and family vacations. But there’s a deeper story behind this piece that’s often overlooked that spoke volumes in its original context. Originally released on Jones’s album Big Band Bossa Nova, the track arrived when the genre and the term “bossa nova” were being culturally sanitized and marketed to white audiences, particularly in the U.S. As scholars have noted, Black Brazilian musicians whose innovative work laid the foundation for bossa nova, were often erased from the story as the genre’s global fame became linked to lighter-skinned artists palatable to international audiences.
Jones’s decision to title the track “Soul Bossa Nova” at the height of the Civil Rights Movement and during the global rise of Bossa Nova was not merely clever branding. It bridged the emerging coolness of Bossa Nova with the distinct sensibilities and innovations of African American music, at a time when both the U.S. and Brazil were grappling with deep racial segregation and the commodification of Black art. It was also a subtle reclamation, insisting on Black presence in a genre already experiencing the erasure of Black Brazilian pioneers such as Johnny Alf. In “Soul Bossa Nova,” Jones fused the light bounce of Brazilian rhythms with a brassy, big-band jazz sensibility, centering Black sonic playfulness and cultural hybridity at a time when both were under threat from the forces of segregation and global anti-Blackness. The track’s instantly recognizable piccolo flute riff, playful, mischievous, and a little sly, becomes, in this light, not only catchy but also defiant, a declaration that Black sound is limitless, able to traverse continents and contexts while carrying the weight of memory, history, and joy.
And the story did not end there. Decades later, Ludacris and various hip-hop artists paid homage to Jones’s legacy in Jones’s last album, the 2010 project Q: Soul Bossa Nostra. This playful yet reverent tribute sampled and reimagined Jones’s catalog for a new generation. Soul Bossa Nostra is a clever play on “Cosa Nostra,” merging the sonic underworld of Jones’s orchestrations with the familial pride and intergenerational respect that defines hip hop’s tribute culture.
This interweaving of “Soul Bossa Nova”‘s history, from its quiet defiance in 1962 to its unexpected resurgence through Austin Powers to its embrace by Ludacris, exemplifies the lasting power of Jones’s compositions to connect across eras and genres, all while telling a much larger story about race, ownership, and the endurance of Black sonic innovation.
In Thriller and “Soul Bossa Nova,” Jones’s compositions offer listeners an immersive experience that connects personal and cultural narratives, proving that his work is more than entertainment. It is a powerful form of artistic communication that resonates across generations. I have experienced this firsthand, listening to these songs with my children, not just once or twice, but as an ongoing, evolving family ritual. Their responses, the way they anticipate certain flourishes, react to subtle shifts, or sing along with total abandon, remind me that Jones’s work does not sit still in time. It moves through us, binding my children’s joy to my own memories of discovery, just as it ties us all to the larger, unfolding story of Black sonic creativity. Through Jones’s soundscapes, we are not only hearing songs. We are participating in cultural memory, shaping it anew with every listen.
***
Being known as an unparalleled intergenerational sonic storyteller is already a feat, but Quincy Jones’s influence is embedded in the DNA of contemporary music production in other important ways. From the way producers are now seen as creative equals to artists to the expectation that producers bring their signature sound to every project they touch, every time a contemporary music producer is celebrated as a vital voice in shaping a record, they stand on the foundation Quincy Jones laid. Long before the term “producer” carried the weight and cultural significance it does today, Jones redefined what it meant to hold that title.
In today’s music landscape, the constructive collaboration between an artist and producer can be a defining force, shaping careers and setting entire musical eras into motion. This reality exists in large part because of Jones, who was not just arranging instruments or overseeing technical sessions but building entire sonic worlds, shaping the emotional architecture of songs, and helping artists translate their most personal visions into soundscapes that could speak to the world. His work with Michael Jackson epitomizes the collaborative alchemy possible when a producer steps into the role of creative partner, cultural interpreter, and sonic architect all at once. With Thriller Jones did not merely produce an album, he co-authored a cultural phenomenon. Jones and Jackson’s collaboration not only redefined pop music but also set a lasting standard for artist-producer dynamics, showcasing the brilliance that can arise when two creative minds align. Jones’s legacy as a producer is one of vision, trust, and translation, helping artists hear possibilities in their work they could not fully imagine and giving the listening public music that defined moments and movements.
Hip Hop, in particular, has carved out a prominent role for music producers in the style of Quincy Jones, something that Nas pays homage to in his track “Michael and Quincy” from King’s Disease III (2022). In doing so, Nas directly parallels the collaborative genius between Quincy Jones and Michael Jackson with his recent creative collaboration with producer Hit-Boy, now running 6 albums strong.
This is not just a passing reference. It is part of Nas’s more prominent, ongoing project of honoring hip hop creators and the artistic lineages that shaped his career. Across the King’s Disease trilogy and in his The Bridge podcast (which he co-hosts with Miss Info), Nas has taken deliberate care to uplift the cultural architects of hip hop, weaving their stories into his narrative and preserving their legacies for future generations. On “Michael and Quincy,” Nas celebrates the power of collaboration, positioning the artist-producer relationship as a crucible for innovation and cultural impact. The track’s lyrics paint vivid images of creative combustion, with Nas rapping, “Smoke steaming off the microphone,” evoking the almost supernatural energy that fueled Michael and Quincy’s sessions. This imagery extends to Nas and Hit-Boy, capturing the intensity and urgency they bring to their creative process.
Sonically, “Michael and Quincy” also mirrors this spirit of collaborative innovation. Hit-Boy’s production constantly shifts, blending classic boom-bap drums with more atmospheric textures, creating a soundscape that feels both reverent and forward-thinking. The beat morphs beneath Nas’s verses, never settling into predictability, much like how Quincy Jones infused “Thriller” with unexpected sonic twists. Nas and Hit-Boy’s sonic interplay echoes the Jackson-Jones dynamic, where the producer’s vision expands and amplifies the artist’s voice. In its lyrics and production, “Michael and Quincy” serves as a sonic tribute, not just to a legendary duo, but to the transformative power of artist-producer partnerships, a lineage Quincy Jones helped define and one Nas is determined to carry forward. The era-defining success of Thriller still ripples through music today.



 “
“Nas’s tribute serves as a powerful reminder of these partnerships’ enduring impact, bridging genres and generations. The image of “smoke steaming off of the microphone” is one I carry with me, embodying the intense, creative spirit that Michael and Quincy brought to their collaborations, a legacy now celebrated and extended through Nas’s words and music. Nas draws from their example to remind us that great partnerships, whether in music or other creative endeavors, are often the spark that ignites monumental cultural shifts. Their combined energy was undeniable as they pushed each other to new artistic heights. The success of their work was not only about the music; it was also about the more profound connection to culture, identity, and collective memory. Like the tracks he produced, his music lives on, inspiring us to reflect on how we listen to and engage with the world around us. By revisiting the breadth and depth of his work and the many sonic creations it has inspired, we continue to discover new layers of meaning and artistry, ensuring that Jones’s influence will be felt for generations to come.
—
Featured Image: SO! Screencap from Nas’s performance at Rolling Loud, November 11, 2024
—
Jaquial Durham is a multi-hyphenate social justice champion. The South Carolina native has spent over a decade actively engaged in various outreach initiatives to uplift and empower marginalized communities. He is also a passionate cultural enthusiast dedicated to exploring the rich tapestry of African American history, which drives him to continue making a meaningful impact in the lives of those around him. His advocacy for social-political issues that encompass race, prison culture and gender have been at the forefront of his work.
As the CEO of Public Culture Entertainment Group, an entity focused on raising public awareness about the myriad of components that influence culture, Durham spearheads the company’s TV/film projects and cultivates unique apparel capsules that showcase prominent African American figures, organizations and landmarks often absent from historical dialogue. The ambitious, young go-getter prolifically uses creative activism to amplify the voices, stories and experiences of those often overlooked. His
visionary brilliance can be seen in the groundbreaking documentary Southern Prison Culture, a cinematic film highlighting the challenges individuals face within the system and fiercely advocating for much-needed reforms. As a result of the film’s success, Durham has received prestigious awards like the Milan Gold Award, the Austin Lift-Off Film Festival Award and the London International Film Festival Award.
Durham has been a driving force behind various social justice reforms, calling for equitable and inclusive policies and practices. His unwavering dedication to helping others earned him widespread recognition that included opportunities to lecture at colleges such as American University, Benedict College, Claflin University, Clemson University and Texas State University. Durham was honored by Grammy-Award Winning rapper Killer Mike, who has respect and credibility within the culture. His dedication to the development of higher education institutions in America has led him to refine his intellectual and creative genius relentlessly. While Durham received a bachelor’s in African and African American Studies with a minor in Women and Gender Studies from Winston-Salem State University, he is pursuing a Ph.D.from Clemson University in Rhetorics, Communication and Information Design.
—

REWIND! . . .If you liked this post, you may also dig:
On Donuts, Sandwiches and Beattapes: Listening for J Dilla Six Years On–DJ Primus Luta
Unlearning Black Sound in Black Artistry: Examining the Quiet in Solange’s A Seat At the Table–Kimberly Williams
Deep Listening as Philogynoir: Playlists, Black Girl Idiom, and Love–Shakira Holt
“Heavy Airplay, All Day with No Chorus”: Classroom Sonic Consciousness in the Playlist Project–Todd Craig
Mingus Ah Um (1959) and An Ethics of Care in Jazz–Brittany Proctor
Black Mourning, Black Movement(s): Savion Glover’s Dance for Amiri Baraka

I don’t worry about the look of it so much. Choreography comes later, when I’m putting together a piece. I’m into the sound; for me, when I’m hittin’, layin’ it down, it’s all about the sound. –Savion Glover, My Life in Tap
It has been a little over a year since Amiri Baraka passed, and still I hear the echoes of his presence. I am especially attentive to the ways his work has been carried on by those involved in recent black uprisings in Ferguson, New York City, and Baltimore. Powerful political poetics that have emerged from these events include work by Danez Smith, Claudia Rankine and the many contributors to blackpoetsspeakouttumblr.com.
And yet, part of what I’ve witnessed in the streets, actual physical spaces of public protest against police violence and systemic racial oppression, is an example of what Thomas DeFrantz has termed “corporeal orature,” or the ability of bodies to resonate throughout public space and shift political discourse. In these moments, the body talk of protesters is not simply the sound of clattering feet through city streets, but a commitment to the ways in which physical gestures can speak truth to power. I am especially interested in connecting Baraka’s legacy to the larger conversation about the aural kinesthetic that Imani Kai Johnson has proposed, and in teasing out the various dimensions and potentials embedded in that category.
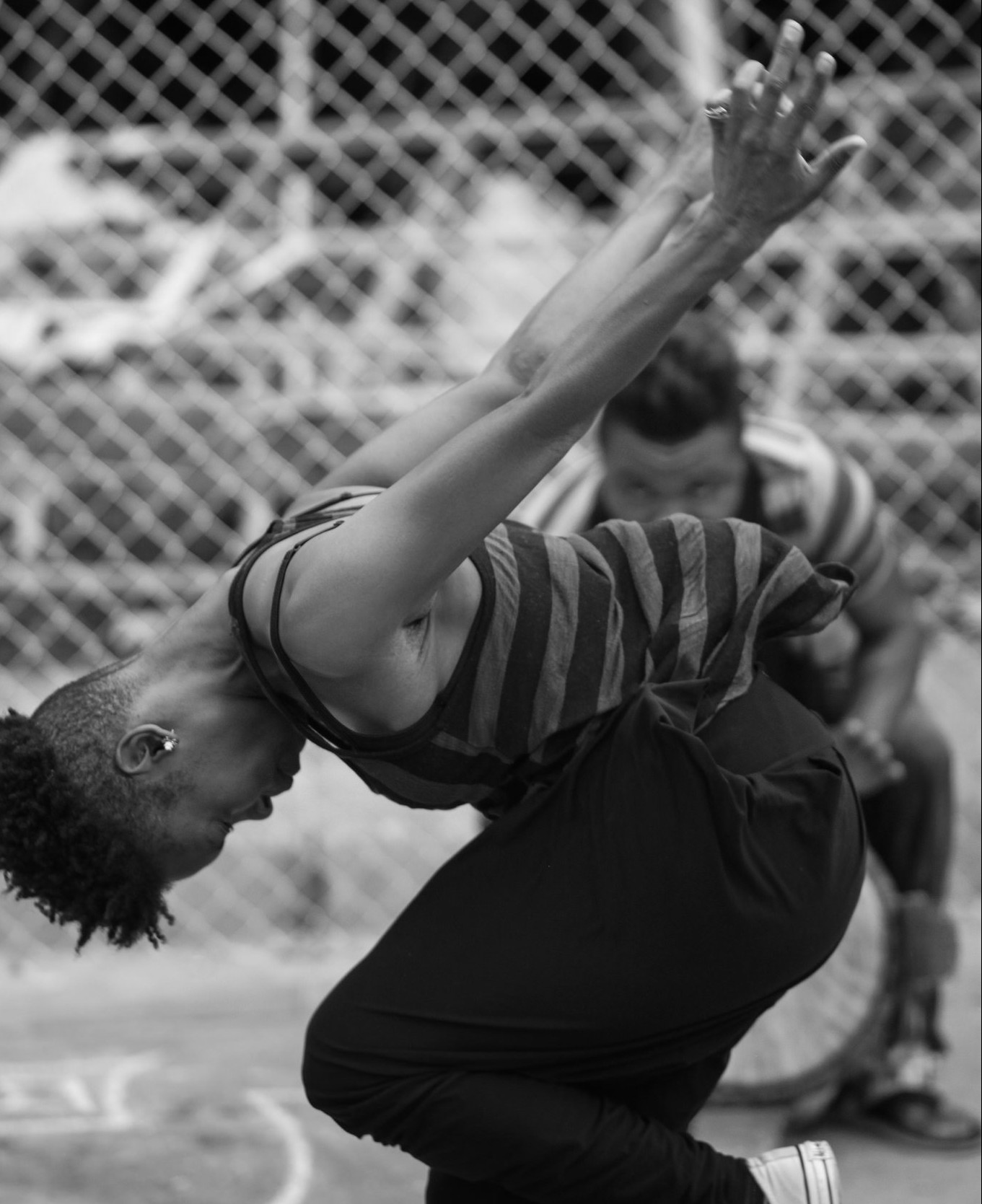
Dance at Ferguson Protests, 2014, Image by Shawn Semmler
For me, Savion Glover exemplified the lingering sound of Baraka’s spirit in his tap dance at his memorial service. Whenever I listen to the recording—which still brings tears to my eyes—I am reminded of the abundant sense of joy, sadness, and love that characterized Baraka’s service. Listening to Glover’s dance is an aural kinesthetic experience, like watching a comet pass across the night’s sky. I am reminded, too, of the way I clamored to record that moment, to keep a piece of the poet alive on my iPhone even after his public passing. And indeed, that performative sound of feet tapping, that measured excess of the body produced through movement, has kept Baraka alive for me; like his groundbreaking work, it is powerfully resistant to the proper rubrics of any one discipline except, perhaps for the study of sound itself.
So, this post then, is about tap dance and its ability to sound out Baraka’s name and life. But in a larger context, the intricate vibrations of Glover’s performance facilitate a deeper understanding of the relationship between sound and mourning, and a kind of mourning that is particularly African American, that is to say, American. It is a mourning that exists beyond the word, written text, or image and a sound practice that enables the bereaved to make a joyful noise and a mournful one at the very same time. So I ask, how do you write a eulogy with the body? How do you perform an embodied love? What does Black love and a reverence for Black life sound like? Sometimes, the answer is tap.
Audio Clip of Savion Glover’s Dance at Amiri Baraka’s Funeral, 18 Jan 2014
The dance explodes on stage like a burst of light. It begins with something approximating a drum roll – and then hard slow taps, hammering away like someone at a typewriter, I imagine, or a train gaining steam.
It is coming.
Slow, insistent and strong, with a little riff now and then, a little picking up of speed here and there. It is coming on louder now, that explosive thing, the tension you are noticing. He is doing the thing. And then there is that skillful, smooth, strong tap. Glover is at work, y’all.
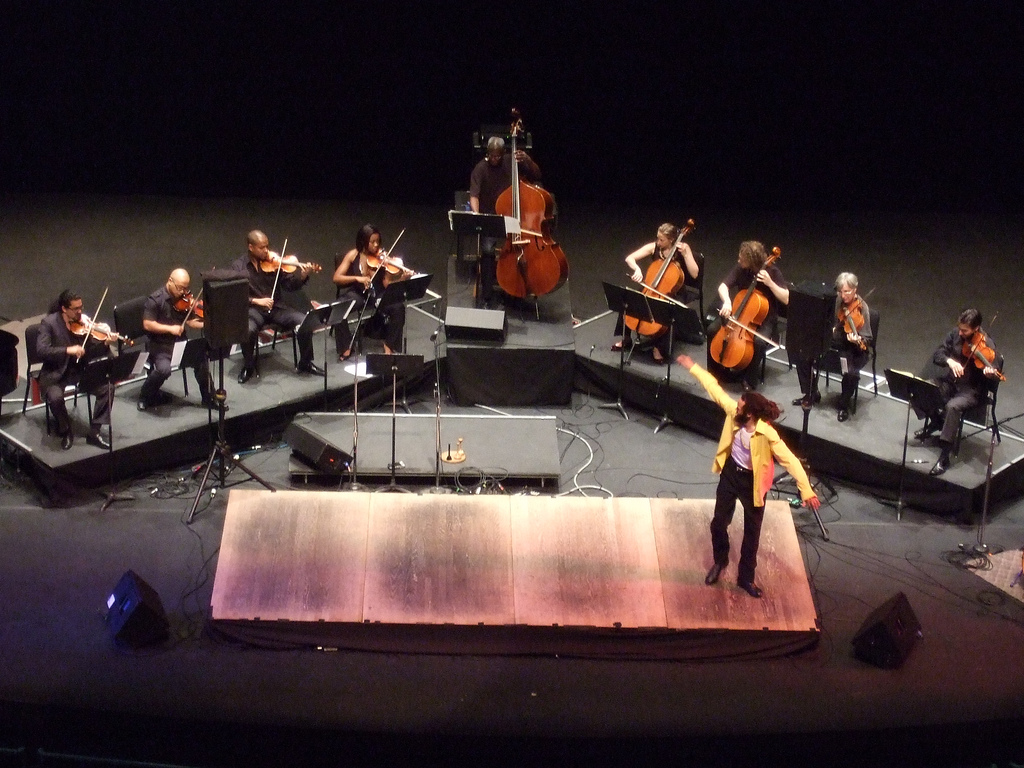

Savion Glover at Work, Image by Flickr Users Raquel and Soren
As a tribute to Baraka, Glover’s dance bears numerous stylistic implications. Among them, I understand the rhythm of Glover’s tap as the rhythm of writing, an aesthetic that complicates the way his dance can be understood as a manifestation of the black vernacular. Sketching out the early connections between her son’s artistry and the percussive taps of the keyboard, Yvette Glover says. “‘I was working for a judge, as an assistant, when I was pregnant with Savion…And when I would type, and the carriage would automatically return, he’d walk, he’d follow it, in my stomach. You could see him move” (39). He does it still. In the audio clip, Glover’s footwork evokes the dexterity of Baraka’s language, all the while telling a story of its own.

Savion Glover’s Shoes, Sadler’s Wells, 2007, Image by Tristram Kenton
But what about the intensity of the dance, its crescendo toward the end of the service, a flurry of percussive steps beside Baraka’s coffin? Baraka himself reminds us this particular musicality is so necessary here. In his discussion of “Afro-Christian Music and Religion” in Blues People, Baraka notes that in Black diasporic religious services, “the spirit will not descend without a song” (41). Glover’s dance takes place at a moment in the service when emotion exceeds the power of language, but not sound. He uses his body as an instrument of sound in its fullest sense. His performance is a choreography of embodied sound: full-on and at-once body poetry, mourning and tribute.
Elucidating the use of his body as an instrument of sound, Glover declares:
It’s like my feet are the drums and my shoes are the sticks[…]My left heel is stronger, for some reason, than my right; it’s my bass drum. My right heel is like the floor tom-tom. I can get a snare out of my right toe, a whip sound, not putting it down on the floor hard, but kind of whipping the floor with it. It get the sounds of a top tom-tom from the balls of my feet. The hi-hat is a sneaky one. I do it with a slight toe lift, either foot, so like a drummer, I can slip it in there anytime. And if I want cymbals, crash crash, that’s landing flat, both feet, full strength on the floor, full weight on both feet. That’s the cymbals. So I’ve got a whole drum set down there (19).
Combining his body’s drumbeat with the tic of Baraka’s keystrokes, Glover embeds the pattern of Baraka’s life in this tap dance, communicating it with the kind of deep and reverential love you are taught to have for your elders when you are young, appropriate and deep.
 But as powerful as his body-poetry is, Glover’s silences are also key. In those inaudible spaces, Glover spreads out his arms, offering up the dance in a gesture of expansive love; the immensity of the silent gestures mirroring the immensity of Baraka’s life. He holds it out as a gift towards the audience, bows his head, too.
But as powerful as his body-poetry is, Glover’s silences are also key. In those inaudible spaces, Glover spreads out his arms, offering up the dance in a gesture of expansive love; the immensity of the silent gestures mirroring the immensity of Baraka’s life. He holds it out as a gift towards the audience, bows his head, too.
In moments of sound and silence, the audience calls out to Glover the way they would a preacher. At these moments, the dance becomes a call and response akin to the way Baraka’s life’s work was a call and response. A call to respond. A call to take what was given to you and make it mean. Listeners to the dance are called up out of themselves. We are changed by the dance and by the listening.
Tap tap tap.
Glover’s performance shows us how his specific blend of African and European dance traditions exists in a spiritual and artistic dimension. There is a religious explanation for this, too. In African Dance, Kariamu Welsh-Asante explains the function of the African funeral dance in definite terms:
All African dances can be used for transcendence and transformational purposes. Transcendence is the term usually associated with possession and trance. Dance is the conduit for transcendent activities. Dance enables an initiate or practitioner to progress or travel through several altered states, thereby achieving communication with an ancestor to deity and receiving valuable information that he/she can relate back to the community. Repetition is key to this process as it guides the initiates, or dancers, through the process of the ceremony. The more a movement is repeated, the greater the level of intensity and the closer a dancer gets to the designated deity or ancestor. Transformation means to change from one state, or phase, to another (16).
Glover certainly brought us close to Baraka. And yet, I would go a step further to suggest that this is, above all, blues dance. As such, it reveals continuing relevance of social dance and movement to Baraka’s political legacy. Baraka and Glover work directs us towards the propulsive nature of black social/percussive dance forms. These sonic gestures clarify the ways black life matters, impacts the public sphere and policy. The politicized nature of Black Arts Movement performances and the performative elements of contemporary Black protest are still linked through sound. Politicized Black aesthetics continue to offer us multiple opportunities to witness the convergence of sound and movement. Ras Baraka, affirms this in his own eulogy for his father:
Have you seen black fire it burns deep it never goes out you can try and extinguish it but it never goes out it never goes out it never goes out only up or out as in broad as in multiply as in blues black base of the fire dancing flickering at times but never all the way gone dancing flickering at times but never all the way gone…
The power of the dance, of the Black Movement to move is still with us.
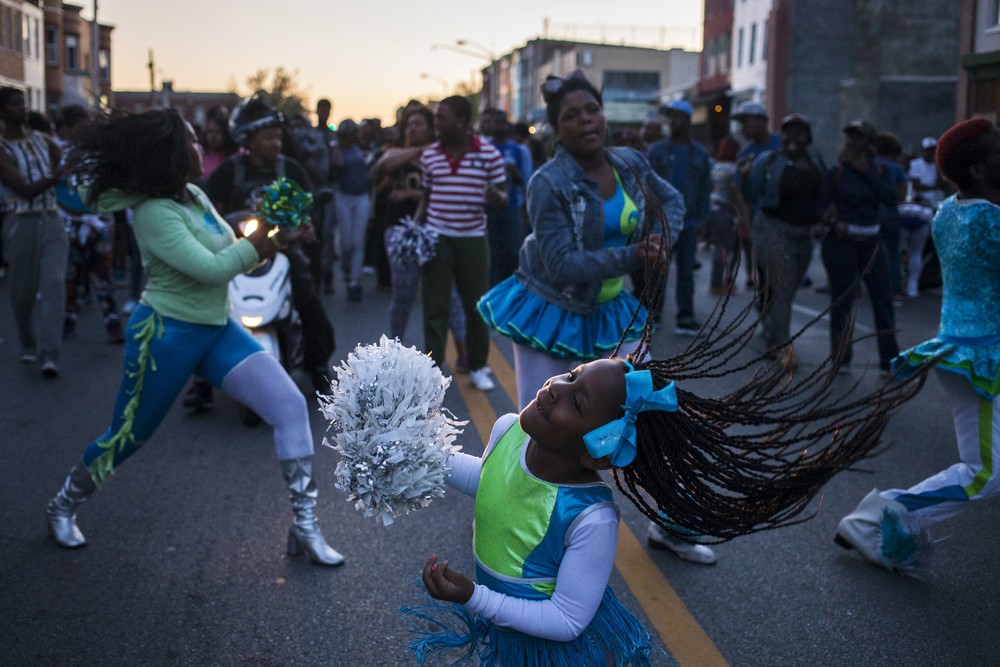
Protestors dance to a community band, Baltimore, MD, 28 April 2015, Photo by Adrees Latif/Reuters
—
Featured Image, Screen Capture of Savion Glover dancing by JS
—
Kristin Moriah is the editor of Black Writers and the Left (Cambridge Scholars Press, 2013) and the co-editor of Adrienne Rich: Teaching at CUNY, 1968-1974 (Lost & Found: The CUNY Poetics Document Initiative, 2014). Her critical work can be found in Callaloo, Theater Journal, TDR and Understanding Blackness Through Performance (Palgrave Macmillan, 2013). Moriah is completing a dissertation on African American literature and performance in transnational contexts at the CUNY Graduate Center. Her research has been funded through grants from the Social Science and Humanities Council of Canada, the Freie Universität Berlin and the Graduate Center’s Advanced Research Collaborative. She is a 2014-15 @IRADAC_GC Archival Dissertation Fellow and spring 2015 Scholar-in-Residence at the NYPL Schomburg Center for Research in Black Culture. Sometimes she tweets via @moriahgirl.
—
 REWIND! . . .If you liked this post, you may also dig:
REWIND! . . .If you liked this post, you may also dig:
“HOW YOU SOUND??”: The Poet’s Voice, Aura, and the Challenge of Listening to Poetry-John Hyland
Pretty, Fast, and Loud: The Audible Ali–Tara Betts
The Sounds of Anti-Anti-Essentialism: Listening to Black Consciousness in the Classroom-Carter Mathes
ISSN 2333-0309
Translate
Recent Posts
- SO! Reads: Alexis McGee’s From Blues To Beyoncé: A Century of Black Women’s Generational Sonic Rhetorics
- SO! Reads: Justin Eckstein’s Sound Tactics: Auditory Power in Political Protests
- Impaulsive: Bro-casting Trump, Part I
- Top Ten Sounding Out! Posts of 2025!
- SO! Reads: Marisol Negrón’s Made in NuYoRico: Fania Records, Latin Music, and Salsa’s Nuyorican Meanings
Archives
Categories
Search for topics. . .
Looking for a Specific Post or Author?
Click here for the SOUNDING OUT INDEX. . .all posts and podcasts since 2009, scrollable by author, date, and title. Updated every 5 minutes.


















Recent Comments