What Feels Good to Me: Extra-Verbal Vocal Sounds and Sonic Pleasure in Black Femme Pop Music
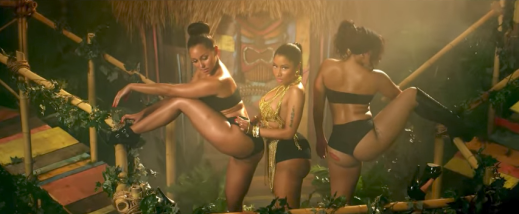
The lyrics to Beyoncé’s 2008 song “Radio” treats listening pleasure as a thinly-veiled metaphor for sexual pleasure. For example, they describe how turning up a car stereo transforms it into a sex toy: “And the bassline be rattlin’ through my see-eat, ee-eats/Then that crazy feeling starts happeni-ing- i-ing OH!” Earlier in the song, the lyrics suggest that this is a way for the narrator to get off without arousing any attempts to police her sexuality: “You’re the only one that Papa allowed to hang out in my room/…And mama never freaked out when she heard it go boom.” Because her parents wouldn’t let her be alone in her bedroom with anyone or anything that they recognized as sexual, “Radio”’s narrator finds sexual pleasure in a practice that isn’t usually legible as sex. In her iconic essay “On A Lesbian Relationship With Music,” musicologist Suzanne Cusick argues that if we “suppose that sexuality isn’t necessarily linked to genital pleasure” and instead “a way of expressing and/or enacting relationships of intimacy through physical pleasure shared, accepted, or given” (70), we can understand the physical pleasures of listening to music, music making, and music performance as kinds of sexual pleasure.
Though Cusick’s piece overlooks the fact that sexual deviance has been, since the invention of the idea of sexuality in the late 19th century, thoroughly racialized, her argument can be a good jumping-off point for thinking about black women’s negotiations of post-feminist ideas of sexual respectability; it focuses our attention on musical sound as a technique for producing queer pleasures that bend the circuits connecting whiteness, cispatriarchal gender, and hetero/homonormative sexuality. In an earlier SO! Piece on post-feminism and post-feminist pop, I defined post-feminism as the view that “the problems liberal feminism identified are things in…our past.” Such problems include silencing, passivity, poor body image, and sexual objectification. I also argued that post-feminist pop used sonic markers of black sexuality as representations of the “past” that (mostly) white post-feminists and their allies have overcome. It does this, for example, by “tak[ing] a “ratchet” sound and translat[ing] it into very respectable, traditional R&B rhythmic terms.” In this two-part post, I want to approach this issue from another angle. I argue that black femme musicians use sounds to negotiate post-feminist norms about sexual respectability, norms that consistently present black sexuality as regressive and pre-feminist.
 Black women musicians’ use of sound to negotiate gender norms and respectability politics is a centuries-old tradition. Angela Davis discusses the negotiations of Blues women in Blues Legacies & Black Feminism (1998), and Shana Redmond’s recent article “This Safer Space: Janelle Monae’s ‘Cold War’” reviews these traditions as they are relevant for black women pop musicians in the US. While there are many black femme musicians doing this work in queer subcultures and subgenres, I want to focus here on how this work appears within the Top 40, right alongside all these white post-feminist pop songs I talked about in my earlier post because such musical performances illustrate how black women negotiate hegemonic femininities in mainstream spaces.
Black women musicians’ use of sound to negotiate gender norms and respectability politics is a centuries-old tradition. Angela Davis discusses the negotiations of Blues women in Blues Legacies & Black Feminism (1998), and Shana Redmond’s recent article “This Safer Space: Janelle Monae’s ‘Cold War’” reviews these traditions as they are relevant for black women pop musicians in the US. While there are many black femme musicians doing this work in queer subcultures and subgenres, I want to focus here on how this work appears within the Top 40, right alongside all these white post-feminist pop songs I talked about in my earlier post because such musical performances illustrate how black women negotiate hegemonic femininities in mainstream spaces.
As America’s post-identity white supremacist patriarchy conditionally and instrumentally includes people of color in privileged spaces, it demands “normal” gender and sexuality performances for the most legibly feminine women of color as the price of admission. As long as black women don’t express or evoke any ratchetness–any potential for blackness to destabilize cisbinary gender and hetero/homonormativity, to make gender and sexuality transitional–their expressions of sexuality and sexual agency fit with multi-racial white supremacist patriarchy.
It is in this complicated context that I situate Nicki Minaj’s (and in my next post Beyoncé’s and Missy Elliott’s) recent uses of sound and their bodies as instruments to generate sounds. If, as I argued in my previous post, the verbal and visual content of post-feminist pop songs and videos is thought to “politically” (i.e., formally, before the law) emancipate women while the sounds perform the ongoing work of white supremacist patriarchy, the songs I will discuss use sounds to perform alternative practices of emancipation. I’m arguing that white bourgeois post-feminism presents black women musicians with new variations on well-worn ideas and practices designed to oppress black women by placing them in racialized, gendered double-binds.
 For example, post-feminism transforms the well-worn virgin/whore dichotomy, which traditionally frames sexual respectability as a matter of chastity and purity (which, as Richard Dyer and others have argued, connotes racial whiteness), into a subject/object dichotomy. This dichotomy frames sexual respectability as a matter of agency and self-ownership (“good” women have agency over their sexuality; “bad” women are mere objects for others). As Cheryl Harris argues, ownership both discursively connotes and legally denotes racial whiteness. Combine the whiteness of self-ownership with well-established stereotypes about black women’s hypersexuality, and the post-feminist demand for sexual self-ownership puts black women in a catch-22: meeting the new post-feminist gender norm for femininity also means embodying old derogatory stereotypes.
For example, post-feminism transforms the well-worn virgin/whore dichotomy, which traditionally frames sexual respectability as a matter of chastity and purity (which, as Richard Dyer and others have argued, connotes racial whiteness), into a subject/object dichotomy. This dichotomy frames sexual respectability as a matter of agency and self-ownership (“good” women have agency over their sexuality; “bad” women are mere objects for others). As Cheryl Harris argues, ownership both discursively connotes and legally denotes racial whiteness. Combine the whiteness of self-ownership with well-established stereotypes about black women’s hypersexuality, and the post-feminist demand for sexual self-ownership puts black women in a catch-22: meeting the new post-feminist gender norm for femininity also means embodying old derogatory stereotypes.
I think of the three songs (“Anaconda,” “WTF,” and “Drunk in Love”) as adapting performance traditions to contemporary contexts. First, they are part of what both Ashton Crawley and Shakira Holt identify as the shouting tradition, which, as Holt explains, is a worship practice that “can include clapping, dancing, pacing, running, rocking, fainting, as well as using the voice in speaking, singing, laughing, weeping, yelling, and moaning.” She continues, arguing that “shouting…is also a binary-breaking performance which confounds—if only fleetingly—the divisions which have so often oppressed, menaced, and harmed them.” These vocal performances apply the shouting tradition’s combination of the choreographic and the sonic and binary-confounding tactics to queer listening and vocal performance strategies.
Francesca Royster identifies such strategies in both Michael Jackson’s work and her audition of it. According to Royster, Jackson’s use of non-verbal sounds produces an erotics that exceeds the cisheteronormative bounds of his songs’ lyrics. They were what allowed her, as a queer teenager, to identify with a love song that otherwise excluded her:
in the moments when he didn’t use words, ‘ch ch huhs,’ the ‘oohs,’ and the ‘hee hee hee hee hees’…I ignored the romantic stories of the lyrics and focused on the sounds, the timbre of his voice and the pauses in between. listening to those nonverbal moments–the murmured opening of “Don’t Stop Till You Get Enough,” or his sobbed breakdown at the end of “She’s Out of My Life,’ I discovered the erotic (117).
Royster references a black sexual politics in line with Audre Lorde’s notion of the erotic in “The Uses of the Erotic,” which is bodily pleasure informed by the implicit and explicit knowledges learned through lived experience on the margins of the “European-American male tradition” (54), and best expressed in the phrase “it feels right to me” (54). Lorde’s erotic is a script for knowing and feeling that doesn’t require us to adopt white supremacist gender and sexual identities to play along. Royster calls on this idea when she argues that Jackson’s non-verbal sounds–his use of timbre, rhythm, articulation, pitch–impart erotic experiences and gendered performances that can veer off the trite boy-meets-girl-boy-loses-girl stories in his lyrics. “Through his cries, whispers, groans, whines, and grunts, Jackson occupies a third space of gender, one that often undercuts his audience’s expectations of erotic identification” (119). Like shouting, “erotic” self-listening confounds several binaries designed specifically to oppress black women, including subject/object binaries and binary cisheterogender categories.
Nicki Minaj uses extra-verbal sounds as opportunities to feel her singing, rapping, vocalizing body as a source of what Holt calls “sonophilic” pleasure, pleasure that “provide[s] stimulation and identification in the listener” and invites the listener to sing (or shout) along. Minaj is praised for her self-possession when it comes to business or artistry, but such self-possession is condemned or erased entirely when discussing her performances of sexuality. As Treva B. Lindsey argues, “the frequency that Nicki works on is not the easiest frequency for us to wrestle with, because it’s about…whether we can actually tell the difference between self-objectification and self-gratification.’’ Though this frequency may be difficult to parse for ears tempered to rationalize post-feminist assumptions about subjectivity and gender, Minaj uses her signature wide sonic pallette to shift the conversation about subjectivity and gender to frequencies that rationalize alternative assumptions.
In her 2014 hit “Anaconda,” she makes a lot of noises: she laughs, snorts, trills her tongue, inhales with a low creaky sound in the back of her throat, percussively “chyeah”s from her diaphragm,among other sounds. The song’s coda finds her making most of the extraverbal sounds. This segment kicks off with her quasi-sarcastic cackle, which goes from her throat and chest up to resonate in her nasal and sinus cavities. She then ends her verse with a trademark “chyeah,” followed by another cackle. Then Minaj gives a gristly, creaky exhale and inhale, trilling her tongue and then finishing with a few more “chyeah”s. While these sounds do percussive and musical work within the song, we can’t discount the fact that they’re also, well…fun to make. They feel good, freeing even. And given the prominent role the enjoyment of one’s own and other women’s bodies plays in “Anaconda” and throughout Minaj’s ouevre, it makes sense that these sounds are, well, ways that she can go about feelin herself.
Listening to and feeling sonophilic pleasure in sounds she performs, Minaj both complicates post-feminism’s subject/object binaries and rescripts cishetero narratives about sexual pleasure. “Anaconda” flips the script on the misogyny of Sir Mix-a-Lot’s hit “Baby Got Back” by sampling the track and rearticulating cishertero male desire as Nicki’s own erotic. First, instead of accompanying a video about the male gaze, that bass hook now accompanies a video of Nicki’s pleasure in her femme body and the bodies of other black femmes, playing as she touches and admires other women working out with her. Second, Nicki re-scripts the bass line as a syllabification: “dun-da-da-dun-da-dun-da-dun-dun,” which keeps the pattern of accents on 1 and 4, while altering the melody’s pitch and rhythm.
Just as “Anaconda”’s lyrics re-script Mix-A-Lot’s male gaze, so do her sounds. If the original hook sonically orients listeners as cishetero “men” and “women,” Nicki’s vocal performance reorients listeners to create and experience bodily pleasure beyond the “legible” and the scripted. Though the lyrics are clearly about sexual pleasure, the sonic expression or representation of that pleasure–i.e., the performer’s pleasure in hearing/feeling herself make all these extraverbal sounds–makes it physically manifest in ways that aren’t conventionally understood as sexual or gendered. Because it veers off white ciseterogendered scripts about both gender and agency, Minaj’s performance of sonophilia is an instance of what L.H. Stallings calls hip hop’s “ratchet imagination.” This imagination is ignited by black women’s dance aesthetics, wherein “black women with various gender performances and sexual identities within the club, on stage and off, whose bodies and actions elicit new performances of black masculinity” renders both gender and subject/object binaries “transitional” (138).
Nicki isn’t the only black woman rapper to use extra-verbal vocal sounds to re-script gendered bodily pleasure. In my next post, I’ll look at Beyoncé and Missy Elliot’s use of extra-vocal sounds to stretch beyond post-feminism pop’s boundaries.
—
Featured image: screenshot from “Anaconda” music video
—
Robin James is Associate Professor of Philosophy at UNC Charlotte. She is author of two books: Resilience & Melancholy: pop music, feminism, and neoliberalism, published by Zer0 books last year, and The Conjectural Body: gender, race and the philosophy of music was published by Lexington Books in 2010. Her work on feminism, race, contemporary continental philosophy, pop music, and sound studies has appeared in The New Inquiry, Hypatia, differences, Contemporary Aesthetics, and the Journal of Popular Music Studies. She is also a digital sound artist and musician. She blogs at its-her-factory.com and is a regular contributor to Cyborgology.
—
 REWIND! . . .If you liked this post, you may also dig:
REWIND! . . .If you liked this post, you may also dig:
“I Love to Praise His Name”: Shouting as Feminine Disruption, Public Ecstasy, and Audio-Visual Pleasure–Shakira Holt
Music Meant to Make You Move: Considering the Aural Kinesthetic–Imani Kai Johnson
Something’s Got a Hold on Me: ‘Lingering Whispers’ of the Atlantic Slave Trade in Ghana–Sionne Neely
























Recent Comments